At which layer of the Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) model are the source and destination address for a datagram handled?
Transport Layer
Data-Link Layer
Network Layer
Application Layer
According to the CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests3, the layer of the Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) model that handles the source and destination address for a datagram is the Network Layer. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that defines the functions, services, and protocols of the communication system or network, as well as the interactions and interfaces among them. The OSI model consists of seven layers, each of which performs a specific function or service for the communication system or network, such as the Physical Layer, the Data-Link Layer, the Network Layer, the Transport Layer, the Session Layer, the Presentation Layer, or the Application Layer. The Network Layer is the third layer of the OSI model, which provides the functionality and service of routing and forwarding the data or information across the communication system or network, such as the Internet Protocol (IP) or the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). The Network Layer handles the source and destination address for a datagram, which is a unit or a packet of data or information that is transmitted or received over the communication system or network. The source and destination address for a datagram are the logical or numerical identifiers that specify the origin and the destination of the datagram, such as the IP address or the host name of the sender and the receiver of the datagram. The Network Layer uses the source and destination address for a datagram to determine the best path or route for the datagram to travel from the sender to the receiver, as well as to deliver the datagram to the correct destination. The Transport Layer is not the layer of the OSI model that handles the source and destination address for a datagram, although it may be the layer that handles the source and destination port for a segment. The Transport Layer is the fourth layer of the OSI model, which provides the functionality and service of ensuring the reliable and efficient transmission and reception of the data or information across the communication system or network, such as the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). The Transport Layer handles the source and destination port for a segment, which is a unit or a packet of data or information that is transmitted or received over the communication system or network. The source and destination port for a segment are the logical or numerical identifiers that specify the application or the service that is sending or receiving the segment, such as the port number or the socket number of the application or the service. The Transport Layer uses the source and destination port for a segment to establish, maintain, and terminate the connection or the session between the sender and the receiver, as well as to deliver the segment to the correct application or service. The Data-Link Layer is not the layer of the OSI model that handles the source and destination address for a datagram, although, it may be the layer that handles the source and destination address for a frame. The Data-Link Layer is the second layer of the OSI model, which provides the functionality and service of transferring and exchanging the data or information between the adjacent nodes or devices on the communication system or network, such as the Ethernet, the Wi-Fi, or the Bluetooth. The Data-Link Layer handles the source and destination address for a frame, which is a unit or a packet of data or information that is transmitted or received over the communication system or network. The source and destination address for a frame are the physical or hardware identifiers that specify the node or the device that is sending or receiving the frame, such as the Media Access Control (MAC) address or the Physical Address of the node or the device. The Data-Link Layer uses the source and destination address for a frame to identify, locate, and access the node or the device that is sending or receiving the frame, as well as to deliver the frame to the correct node or device. The Application Layer is not the layer of the OSI model that handles the source and destination address for a datagram, although it may be the layer that handles the source and destination address for a message.
In the network design below, where is the MOST secure Local Area Network (LAN) segment to deploy a Wireless Access Point (WAP) that provides contractors access to the Internet and authorized enterprise services?
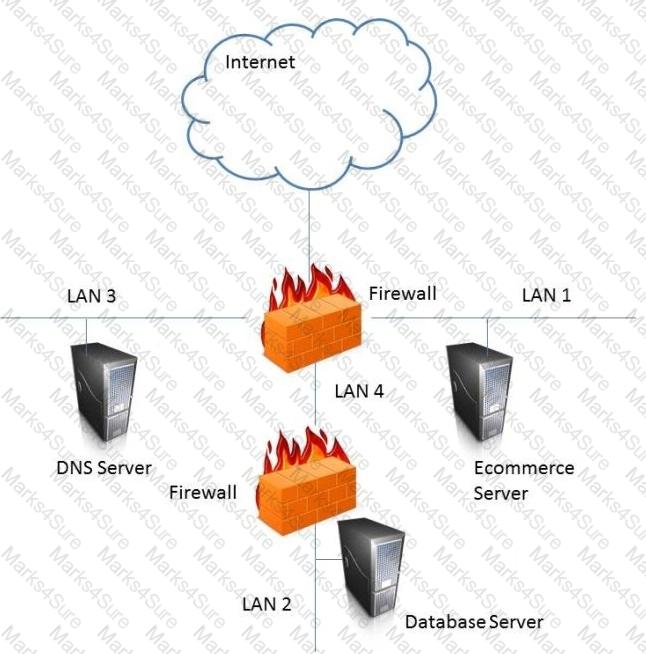
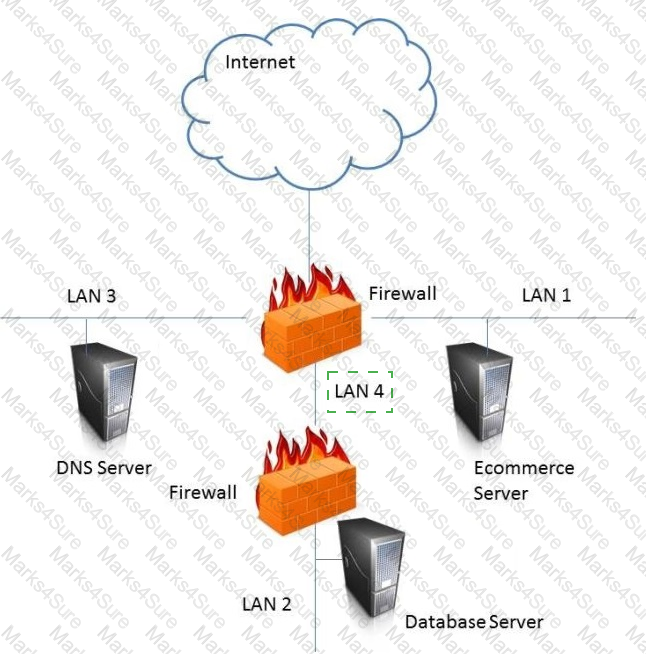
LAN 4
The most secure LAN segment to deploy a WAP that provides contractors access to the Internet and authorized enterprise services is LAN 4. A WAP is a device that enables wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or other wireless standards. A WAP can provide convenience and mobility for the users, but it can also introduce security risks, such as unauthorized access, eavesdropping, interference, or rogue access points. Therefore, a WAP should be deployed in a secure LAN segment that can isolate the wireless traffic from the rest of the network and apply appropriate security controls and policies. LAN 4 is connected to the firewall that separates it from the other LAN segments and the Internet. This firewall can provide network segmentation, filtering, and monitoring for the WAP and the wireless devices. The firewall can also enforce the access rules and policies for the contractors, such as allowing them to access the Internet and some authorized enterprise services, but not the other LAN segments that may contain sensitive or critical data or systems34 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6: Communication and Network Security, p. 317; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 4: Communication and Network Security, p. 437.
When designing a vulnerability test, which one of the following is likely to give the BEST indication of what components currently operate on the network?
Topology diagrams
Mapping tools
Asset register
Ping testing
According to the CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide2, when designing a vulnerability test, mapping tools are likely to give the best indication of what components currently operate on the network. Mapping tools are software applications that scan and discover the network topology, devices, services, and protocols. They can provide a graphical representation of the network structure and components, as well as detailed information about each node and connection. Mapping tools can help identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network configuration and architecture, as well as the exposure and attack surface of the network. Topology diagrams are not likely to give the best indication of what components currently operate on the network, as they may be outdated, inaccurate, or incomplete. Topology diagrams are static and abstract representations of the network layout and design, but they may not reflect the actual and dynamic state of the network. Asset register is not likely to give the best indication of what components currently operate on the network, as it may be outdated, inaccurate, or incomplete. Asset register is a document that lists and categorizes the assets owned by an organization, such as hardware, software, data, and personnel. However, it may not capture the current status, configuration, and interconnection of the assets, as well as the changes and updates that occur over time. Ping testing is not likely to give the best indication of what components currently operate on the network, as it is a simple and limited technique that only checks the availability and response time of a host. Ping testing is a network utility that sends an echo request packet to a target host and waits for an echo reply packet. It can measure the connectivity and latency of the host, but it cannot provide detailed information about the host’s characteristics, services, and vulnerabilities. References: 2
Which one of the following activities would present a significant security risk to organizations when employing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) solution?
VPN bandwidth
Simultaneous connection to other networks
Users with Internet Protocol (IP) addressing conflicts
Remote users with administrative rights
According to the CISSP For Dummies4, the activity that would present a significant security risk to organizations when employing a VPN solution is simultaneous connection to other networks. A VPN is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted tunnel over a public or untrusted network, such as the internet, to connect remote users or sites to the organization’s private network, such as the intranet. A VPN provides security and privacy for the data and communication that are transmitted over the tunnel, as well as access to the network resources and services that are available on the private network. However, a VPN also introduces some security risks and challenges, such as configuration errors, authentication issues, malware infections, or data leakage. One of the security risks of a VPN is simultaneous connection to other networks, which occurs when a VPN user connects to the organization’s private network and another network at the same time, such as a home network, a public Wi-Fi network, or a malicious network. This creates a potential vulnerability or backdoor for the attackers to access or compromise the organization’s private network, by exploiting the weaker security or lower trust of the other network. Therefore, the organization should implement and enforce policies and controls to prevent or restrict the simultaneous connection to other networks when using a VPN solution. VPN bandwidth is not an activity that would present a significant security risk to organizations when employing a VPN solution, although it may be a factor that affects the performance and availability of the VPN solution. VPN bandwidth is the amount of data that can be transmitted or received over the VPN tunnel per unit of time, which depends on the speed and capacity of the network connection, the encryption and compression methods, the traffic load, and the network congestion. VPN bandwidth may limit the quality and efficiency of the data and communication that are transmitted over the VPN tunnel, but it does not directly pose a significant security risk to the organization’s private network. Users with IP addressing conflicts is not an activity that would present a significant security risk to organizations when employing a VPN solution, although it may be a factor that causes errors and disruptions in the VPN solution. IP addressing conflicts occur when two or more devices or hosts on the same network have the same IP address, which is a unique identifier that is assigned to each device or host to communicate over the network.
During a fingerprint verification process, which of the following is used to verify identity and authentication?
A pressure value is compared with a stored template
Sets of digits are matched with stored values
A hash table is matched to a database of stored value
A template of minutiae is compared with a stored template
The method that is used to verify identity and authentication during a fingerprint verification process is that a template of minutiae is compared with a stored template. A fingerprint verification process is a type of biometric verification process that uses or applies the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device, to verify or to authenticate the identity or the authenticity of the user or the device, and to grant or to deny the access or the login to the system or the service. A fingerprint verification process can provide a high level of security or protection for the system or the service, as it can prevent or reduce the risk of impersonation, duplication, or sharing of the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device. The method that is used to verify identity and authentication during a fingerprint verification process is that a template of minutiae is compared with a stored template, which means that the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device that is captured or scanned by the fingerprint scanner or the sensor, is converted or transformed into a template or a model of minutiae, which are the points or the features of the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device, such as the ridge ending, the bifurcation, or the delta, and that are used or applied for the fingerprint verification process, and that the template or the model of minutiae of the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device is compared or matched with the template or the model of minutiae of the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device that is stored or registered in the system or the service, and that is used or compared for the verification or the authentication. If the template or the model of minutiae of the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device that is captured or scanned by the fingerprint scanner or the sensor, and the template or the model of minutiae of the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device that is stored or registered in the system or the service, are similar or identical, or within a certain threshold or tolerance, then the identity or the authenticity of the user or the device is verified or authenticated, and the access or the login to the system or the service is granted or allowed. If the template or the model of minutiae of the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device that is captured or scanned by the fingerprint scanner or the sensor, and the template or the model of minutiae of the fingerprint or the impression of the finger of the user or the device that is stored or registered in the system or the service, are different or dissimilar, or beyond a certain threshold or tolerance, then the identity or the authenticity of the user or the device is not verified or authenticated, and the access or the login to the system or the service is denied or rejected.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 149; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, page 214
Data remanence refers to which of the following?
The remaining photons left in a fiber optic cable after a secure transmission.
The retention period required by law or regulation.
The magnetic flux created when removing the network connection from a server or personal computer.
The residual information left on magnetic storage media after a deletion or erasure.
Data remanence refers to the residual information left on magnetic storage media after a deletion or erasure. Data remanence is a security risk, as it may allow unauthorized or malicious parties to recover the deleted or erased data, which may contain sensitive or confidential information. Data remanence can be caused by the physical properties of the magnetic storage media, such as hard disks, floppy disks, or tapes, which may retain some traces of the data even after it is overwritten or formatted. Data remanence can also be caused by the logical properties of the file systems or operating systems, which may not delete or erase the data completely, but only mark the space as available or remove the pointers to the data. Data remanence can be prevented or reduced by using secure deletion or erasure methods, such as cryptographic wiping, degaussing, or physical destruction56 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, p. 443; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 7: Security Operations, p. 855.
Which of the following is TRUE about Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) testing?
Operational networks are usually shut down during testing.
Testing should continue even if components of the test fail.
The company is fully prepared for a disaster if all tests pass.
Testing should not be done until the entire disaster plan can be tested.
Testing is a vital part of the Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) process, as it validates the effectiveness and feasibility of the plan, identifies gaps and weaknesses, and provides opportunities for improvement and training. Testing should continue even if components of the test fail, as this will help to evaluate the impact of the failure, the root cause of the problem, and the possible solutions or alternatives34. References: 3: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 10, page 10354: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 10, page 351.
Which of the following roles has the obligation to ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization?
Data Custodian
Data Owner
Data Creator
Data User
The role that has the obligation to ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization is the data owner. A data owner is a person or an entity that has the authority or the responsibility for the data or the information within an organization, and that determines or defines the classification, the usage, the protection, or the retention of the data or the information. A data owner has the obligation to ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization, as the data owner is ultimately accountable or liable for the security or the quality of the data or the information, regardless of who processes or handles the data or the information. A data owner can ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization, by performing the tasks or the functions such as conducting due diligence, establishing service level agreements, defining security requirements, monitoring performance, or auditing compliance. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 2, page 61; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 2, page 67
Which of the following activities BEST identifies operational problems, security misconfigurations, and malicious attacks?
Policy documentation review
Authentication validation
Periodic log reviews
Interface testing
The activity that best identifies operational problems, security misconfigurations, and malicious attacks is periodic log reviews. Log reviews are the process of examining and analyzing the records of events or activities that occur on a system or network, such as user actions, system errors, security alerts, or network traffic. Periodic log reviews can help to identify operational problems, such as system failures, performance issues, or configuration errors, by detecting anomalies, trends, or patterns in the log data. Periodic log reviews can also help to identify security misconfigurations, such as weak passwords, open ports, or missing patches, by comparing the log data with the security policies, standards, or baselines. Periodic log reviews can also help to identify malicious attacks, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, or denial of service, by recognizing signs of intrusion, compromise, or exploitation in the log data. The other options are not the best activities to identify operational problems, security misconfigurations, and malicious attacks, but rather different types of activities. Policy documentation review is the process of examining and evaluating the documents that define the rules and guidelines for the system or network security, such as policies, procedures, or standards. Policy documentation review can help to ensure the completeness, consistency, and compliance of the security documents, but not to identify the actual problems or attacks. Authentication validation is the process of verifying and confirming the identity and credentials of a user or device that requests access to a system or network, such as passwords, tokens, or certificates. Authentication validation can help to prevent unauthorized access, but not to identify the existing problems or attacks. Interface testing is the process of checking and evaluating the functionality, usability, and reliability of the interfaces between different components or systems, such as modules, applications, or networks. Interface testing can help to ensure the compatibility, interoperability, and integration of the interfaces, but not to identify the problems or attacks. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, p. 377; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, p. 405.
The application of which of the following standards would BEST reduce the potential for data breaches?
ISO 9000
ISO 20121
ISO 26000
ISO 27001
The standard that would best reduce the potential for data breaches is ISO 27001. ISO 27001 is an international standard that specifies the requirements and the guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an information security management system (ISMS) within an organization. An ISMS is a systematic approach to managing the information security of the organization, by applying the principles of plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle, and by following the best practices of risk assessment, risk treatment, security controls, monitoring, review, and improvement. ISO 27001 can help reduce the potential for data breaches, as it can provide a framework and a methodology for the organization to identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover from the information security incidents or events that could compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the data or the information. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, page 25; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, page 33
Which of the following is BEST suited for exchanging authentication and authorization messages in a multi-party decentralized environment?
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
Internet Mail Access Protocol
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is best suited for exchanging authentication and authorization messages in a multi-party decentralized environment. SAML is an XML-based standard that enables single sign-on (SSO) and federated identity management (FIM) between different domains and organizations. SAML allows a user to authenticate once at an identity provider (IdP) and access multiple service providers (SPs) without re-authenticating, by using assertions that contain information about the user’s identity, attributes, and privileges. SAML also allows SPs to request and receive authorization decisions from the IdP, based on the user’s access rights and policies. SAML is designed to support a decentralized and distributed environment, where multiple parties can exchange and verify the user’s identity and authorization information in a secure and interoperable manner. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is not best suited for exchanging authentication and authorization messages in a multi-party decentralized environment, as it is a protocol that enables access and management of directory services, such as Active Directory or OpenLDAP. LDAP is used to store and retrieve information about users, groups, devices, and other objects in a hierarchical and structured manner, but it does not provide a mechanism for SSO or FIM across different domains and organizations. Internet Mail Access Protocol is not best suited for exchanging authentication and authorization messages in a multi-party decentralized environment, as it is a protocol that enables access and management of email messages stored on a remote server. IMAP is used to retrieve and manipulate email messages from multiple devices and clients, but it does not provide a mechanism for SSO or FIM across different domains and organizations. Transport Layer Security (TLS) is not best suited for exchanging authentication and authorization messages in a multi-party decentralized environment, as it is a protocol that provides security and encryption for data transmission over a network, such as the internet. TLS is used to establish a secure and authenticated channel between two parties, such as a web browser and a web server, but it does not provide a mechanism for SSO or FIM across different domains and organizations.
When is a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) considered to be valid?
When it has been validated by the Business Continuity (BC) manager
When it has been validated by the board of directors
When it has been validated by all threat scenarios
When it has been validated by realistic exercises
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is considered to be valid when it has been validated by realistic exercises. A BCP is a part of a BCP/DRP that focuses on ensuring the continuous operation of the organization’s critical business functions and processes during and after a disruption or disaster. A BCP should include various components, such as:
A BCP is considered to be valid when it has been validated by realistic exercises, because it can ensure that the BCP is practical and applicable, and that it can achieve the desired outcomes and objectives in a real-life scenario. Realistic exercises are a type of testing, training, and exercises that involve performing and practicing the BCP with the relevant stakeholders, using simulated or hypothetical scenarios, such as a fire drill, a power outage, or a cyberattack. Realistic exercises can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the criteria for considering a BCP to be valid, but rather the steps or parties that are involved in developing or approving a BCP. When it has been validated by the Business Continuity (BC) manager is not a criterion for considering a BCP to be valid, but rather a step that is involved in developing a BCP. The BC manager is the person who is responsible for overseeing and coordinating the BCP activities and processes, such as the business impact analysis, the recovery strategies, the BCP document, the testing, training, and exercises, and the maintenance and review. The BC manager can validate the BCP by reviewing and verifying the BCP components and outcomes, and ensuring that they meet the BCP standards and objectives. However, the validation by the BC manager is not enough to consider the BCP to be valid, as it does not test or demonstrate the BCP in a realistic scenario. When it has been validated by the board of directors is not a criterion for considering a BCP to be valid, but rather a party that is involved in approving a BCP. The board of directors is the group of people who are elected by the shareholders to represent their interests and to oversee the strategic direction and governance of the organization. The board of directors can approve the BCP by endorsing and supporting the BCP components and outcomes, and allocating the necessary resources and funds for the BCP. However, the approval by the board of directors is not enough to consider the BCP to be valid, as it does not test or demonstrate the BCP in a realistic scenario. When it has been validated by all threat scenarios is not a criterion for considering a BCP to be valid, but rather an unrealistic or impossible expectation for validating a BCP. A threat scenario is a description or a simulation of a possible or potential disruption or disaster that might affect the organization’s critical business functions and processes, such as a natural hazard, a human error, or a technical failure. A threat scenario can be used to test and validate the BCP by measuring and evaluating the BCP’s performance and effectiveness in responding and recovering from the disruption or disaster. However, it is not possible or feasible to validate the BCP by all threat scenarios, as there are too many or unknown threat scenarios that might occur, and some threat scenarios might be too severe or complex to simulate or test. Therefore, the BCP should be validated by the most likely or relevant threat scenarios, and not by all threat scenarios.
Which security service is served by the process of encryption plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting cipher text with the sender’s public key?
Confidentiality
Integrity
Identification
Availability
The security service that is served by the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key is identification. Identification is the process of verifying the identity of a person or entity that claims to be who or what it is. Identification can be achieved by using public key cryptography and digital signatures, which are based on the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key. This process works as follows:
The process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key serves identification because it ensures that only the sender can produce a valid ciphertext that can be decrypted by the receiver, and that the receiver can verify the sender’s identity by using the sender’s public key. This process also provides non-repudiation, which means that the sender cannot deny sending the message or the receiver cannot deny receiving the message, as the ciphertext serves as a proof of origin and delivery.
The other options are not the security services that are served by the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key. Confidentiality is the process of ensuring that the message is only readable by the intended parties, and it is achieved by encrypting plaintext with the receiver’s public key and decrypting ciphertext with the receiver’s private key. Integrity is the process of ensuring that the message is not modified or corrupted during transmission, and it is achieved by using hash functions and message authentication codes. Availability is the process of ensuring that the message is accessible and usable by the authorized parties, and it is achieved by using redundancy, backup, and recovery mechanisms.
Who in the organization is accountable for classification of data information assets?
Data owner
Data architect
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
Chief Information Officer (CIO)
The person in the organization who is accountable for the classification of data information assets is the data owner. The data owner is the person or entity that has the authority and responsibility for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of a set of data. The data owner is also responsible for defining the purpose, value, and classification of the data, as well as the security requirements and controls for the data. The data owner should be able to determine the impact of the data on the mission of the organization, which means assessing the potential consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing the data. The impact of the data on the mission of the organization is one of the main criteria for data classification, which helps to establish the appropriate level of protection and handling for the data. The data owner should also ensure that the data is properly labeled, stored, accessed, shared, and destroyed according to the data classification policy and procedures.
The other options are not the persons in the organization who are accountable for the classification of data information assets, but rather persons who have other roles or functions related to data management. The data architect is the person or entity that designs and models the structure, format, and relationships of the data, as well as the data standards, specifications, and lifecycle. The data architect supports the data owner by providing technical guidance and expertise on the data architecture and quality. The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is the person or entity that oversees the security strategy, policies, and programs of the organization, as well as the security performance and incidents. The CISO supports the data owner by providing security leadership and governance, as well as ensuring the compliance and alignment of the data security with the organizational objectives and regulations. The Chief Information Officer (CIO) is the person or entity that manages the information technology (IT) resources and services of the organization, as well as the IT strategy and innovation. The CIO supports the data owner by providing IT management and direction, as well as ensuring the availability, reliability, and scalability of the IT infrastructure and applications.
Which of the following mobile code security models relies only on trust?
Code signing
Class authentication
Sandboxing
Type safety
Code signing is the mobile code security model that relies only on trust. Mobile code is a type of software that can be transferred from one system to another and executed without installation or compilation. Mobile code can be used for various purposes, such as web applications, applets, scripts, macros, etc. Mobile code can also pose various security risks, such as malicious code, unauthorized access, data leakage, etc. Mobile code security models are the techniques that are used to protect the systems and users from the threats of mobile code. Code signing is a mobile code security model that relies only on trust, which means that the security of the mobile code depends on the reputation and credibility of the code provider. Code signing works as follows:
Code signing relies only on trust because it does not enforce any security restrictions or controls on the mobile code, but rather leaves the decision to the code consumer. Code signing also does not guarantee the quality or functionality of the mobile code, but rather the authenticity and integrity of the code provider. Code signing can be effective if the code consumer knows and trusts the code provider, and if the code provider follows the security standards and best practices. However, code signing can also be ineffective if the code consumer is unaware or careless of the code provider, or if the code provider is compromised or malicious.
The other options are not mobile code security models that rely only on trust, but rather on other techniques that limit or isolate the mobile code. Class authentication is a mobile code security model that verifies the permissions and capabilities of the mobile code based on its class or type, and allows or denies the execution of the mobile code accordingly. Sandboxing is a mobile code security model that executes the mobile code in a separate and restricted environment, and prevents the mobile code from accessing or affecting the system resources or data. Type safety is a mobile code security model that checks the validity and consistency of the mobile code, and prevents the mobile code from performing illegal or unsafe operations.
The use of private and public encryption keys is fundamental in the implementation of which of the following?
Diffie-Hellman algorithm
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Message Digest 5 (MD5)
The use of private and public encryption keys is fundamental in the implementation of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). SSL is a protocol that provides secure communication over the Internet by using public key cryptography and digital certificates. SSL works as follows:
The use of private and public encryption keys is fundamental in the implementation of SSL because it enables the authentication of the parties, the establishment of the shared secret key, and the protection of the data from eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks.
The other options are not protocols or algorithms that use private and public encryption keys in their implementation. Diffie-Hellman algorithm is a method for generating a shared secret key between two parties, but it does not use private and public encryption keys, but rather public and private parameters. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a symmetric encryption algorithm that uses the same key for encryption and decryption, but it does not use private and public encryption keys, but rather a single secret key. Message Digest 5 (MD5) is a hash function that produces a fixed-length output from a variable-length input, but it does not use private and public encryption keys, but rather a one-way mathematical function.
Which of the following is a PRIMARY advantage of using a third-party identity service?
Consolidation of multiple providers
Directory synchronization
Web based logon
Automated account management
Consolidation of multiple providers is the primary advantage of using a third-party identity service. A third-party identity service is a service that provides identity and access management (IAM) functions, such as authentication, authorization, and federation, for multiple applications or systems, using a single identity provider (IdP). A third-party identity service can offer various benefits, such as:
Consolidation of multiple providers is the primary advantage of using a third-party identity service, because it can simplify and streamline the IAM architecture and processes, by reducing the number of IdPs and IAM systems that are involved in managing the identities and access for multiple applications or systems. Consolidation of multiple providers can also help to avoid the issues or risks that might arise from having multiple IdPs and IAM systems, such as the inconsistency, redundancy, or conflict of the IAM policies and controls, or the inefficiency, vulnerability, or disruption of the IAM functions.
The other options are not the primary advantages of using a third-party identity service, but rather secondary or specific advantages for different aspects or scenarios of using a third-party identity service. Directory synchronization is an advantage of using a third-party identity service, but it is more relevant for the scenario where the organization has an existing directory service, such as LDAP or Active Directory, that stores and manages the user accounts and attributes, and wants to synchronize them with the third-party identity service, to enable the SSO or federation for the users. Web based logon is an advantage of using a third-party identity service, but it is more relevant for the aspect where the third-party identity service uses a web-based protocol, such as SAML or OAuth, to facilitate the SSO or federation for the users, by redirecting them to a web-based logon page, where they can enter their credentials or consent. Automated account management is an advantage of using a third-party identity service, but it is more relevant for the aspect where the third-party identity service provides the IAM functions, such as provisioning, deprovisioning, or updating, for the user accounts and access rights, using an automated or self-service mechanism, such as SCIM or JIT.
Which of the following types of business continuity tests includes assessment of resilience to internal and external risks without endangering live operations?
Walkthrough
Simulation
Parallel
White box
Simulation is the type of business continuity test that includes assessment of resilience to internal and external risks without endangering live operations. Business continuity is the ability of an organization to maintain or resume its critical functions and operations in the event of a disruption or disaster. Business continuity testing is the process of evaluating and validating the effectiveness and readiness of the business continuity plan (BCP) and the disaster recovery plan (DRP) through various methods and scenarios. Business continuity testing can provide several benefits, such as:
There are different types of business continuity tests, depending on the scope, purpose, and complexity of the test. Some of the common types are:
Simulation is the type of business continuity test that includes assessment of resilience to internal and external risks without endangering live operations, because it can simulate various types of risks, such as natural, human, or technical, and assess how the organization and its systems can cope and recover from them, without actually causing any harm or disruption to the live operations. Simulation can also help to identify and mitigate any potential risks that might affect the live operations, and to improve the resilience and preparedness of the organization and its systems.
The other options are not the types of business continuity tests that include assessment of resilience to internal and external risks without endangering live operations, but rather types that have other objectives or effects. Walkthrough is a type of business continuity test that does not include assessment of resilience to internal and external risks, but rather a review and discussion of the BCP and DRP, without any actual testing or practice. Parallel is a type of business continuity test that does not endanger live operations, but rather maintains them, while activating and operating the alternate site or system. Full interruption is a type of business continuity test that does endanger live operations, by shutting them down and transferring them to the alternate site or system.
A continuous information security-monitoring program can BEST reduce risk through which of the following?
Collecting security events and correlating them to identify anomalies
Facilitating system-wide visibility into the activities of critical user accounts
Encompassing people, process, and technology
Logging both scheduled and unscheduled system changes
A continuous information security monitoring program can best reduce risk through encompassing people, process, and technology. A continuous information security monitoring program is a process that involves maintaining the ongoing awareness of the security status, events, and activities of a system or network, by collecting, analyzing, and reporting the security data and information, using various methods and tools. A continuous information security monitoring program can provide several benefits, such as:
A continuous information security monitoring program can best reduce risk through encompassing people, process, and technology, because it can ensure that the continuous information security monitoring program is holistic and comprehensive, and that it covers all the aspects and elements of the system or network security. People, process, and technology are the three pillars of a continuous information security monitoring program, and they represent the following:
The other options are not the best ways to reduce risk through a continuous information security monitoring program, but rather specific or partial ways that can contribute to the risk reduction. Collecting security events and correlating them to identify anomalies is a specific way to reduce risk through a continuous information security monitoring program, but it is not the best way, because it only focuses on one aspect of the security data and information, and it does not address the other aspects, such as the security objectives and requirements, the security controls and measures, and the security feedback and improvement. Facilitating system-wide visibility into the activities of critical user accounts is a partial way to reduce risk through a continuous information security monitoring program, but it is not the best way, because it only covers one element of the system or network security, and it does not cover the other elements, such as the security threats and vulnerabilities, the security incidents and impacts, and the security response and remediation. Logging both scheduled and unscheduled system changes is a specific way to reduce risk through a continuous information security monitoring program, but it is not the best way, because it only focuses on one type of the security events and activities, and it does not focus on the other types, such as the security alerts and notifications, the security analysis and correlation, and the security reporting and documentation.
What would be the MOST cost effective solution for a Disaster Recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours?
Warm site
Hot site
Mirror site
Cold site
A warm site is the most cost effective solution for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours. A DR site is a backup facility that can be used to restore the normal operation of the organization’s IT systems and infrastructure after a disruption or disaster. A DR site can have different levels of readiness and functionality, depending on the organization’s recovery objectives and budget. The main types of DR sites are:
A warm site is the most cost effective solution for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, because it can provide a balance between the recovery time and the recovery cost. A warm site can enable the organization to resume its critical functions and operations within a reasonable time frame, without spending too much on the DR site maintenance and operation. A warm site can also provide some flexibility and scalability for the organization to adjust its recovery strategies and resources according to its needs and priorities.
The other options are not the most cost effective solutions for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, but rather solutions that are either too costly or too slow for the organization’s recovery objectives and budget. A hot site is a solution that is too costly for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, because it requires the organization to invest a lot of money on the DR site equipment, software, and services, and to pay for the ongoing operational and maintenance costs. A hot site may be more suitable for the organization’s systems that cannot be unavailable for more than a few hours or minutes, or that have very high availability and performance requirements. A mirror site is a solution that is too costly for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, because it requires the organization to duplicate its entire primary site, with the same hardware, software, data, and applications, and to keep them online and synchronized at all times. A mirror site may be more suitable for the organization’s systems that cannot afford any downtime or data loss, or that have very strict compliance and regulatory requirements. A cold site is a solution that is too slow for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, because it requires the organization to spend a lot of time and effort on the DR site installation, configuration, and restoration, and to rely on other sources of backup data and applications. A cold site may be more suitable for the organization’s systems that can be unavailable for more than a few days or weeks, or that have very low criticality and priority.
What is the PRIMARY reason for implementing change management?
Certify and approve releases to the environment
Provide version rollbacks for system changes
Ensure that all applications are approved
Ensure accountability for changes to the environment
Ensuring accountability for changes to the environment is the primary reason for implementing change management. Change management is a process that ensures that any changes to the system or network environment, such as the hardware, software, configuration, or documentation, are planned, approved, implemented, and documented in a controlled and consistent manner. Change management can provide several benefits, such as:
Ensuring accountability for changes to the environment is the primary reason for implementing change management, because it can ensure that the changes are authorized, justified, and traceable, and that the parties involved in the changes are responsible and accountable for their actions and results. Accountability can also help to deter or detect any unauthorized or malicious changes that might compromise the system or network environment.
The other options are not the primary reasons for implementing change management, but rather secondary or specific reasons for different aspects or phases of change management. Certifying and approving releases to the environment is a reason for implementing change management, but it is more relevant for the approval phase of change management, which is the phase that involves reviewing and validating the changes and their impacts, and granting or denying the permission to proceed with the changes. Providing version rollbacks for system changes is a reason for implementing change management, but it is more relevant for the implementation phase of change management, which is the phase that involves executing and monitoring the changes and their effects, and providing the backup and recovery options for the changes. Ensuring that all applications are approved is a reason for implementing change management, but it is more relevant for the application changes, which are the changes that affect the software components or services that provide the functionality or logic of the system or network environment.
What should be the FIRST action to protect the chain of evidence when a desktop computer is involved?
Take the computer to a forensic lab
Make a copy of the hard drive
Start documenting
Turn off the computer
Making a copy of the hard drive should be the first action to protect the chain of evidence when a desktop computer is involved. A chain of evidence, also known as a chain of custody, is a process that documents and preserves the integrity and authenticity of the evidence collected from a crime scene, such as a desktop computer. A chain of evidence should include information such as:
Making a copy of the hard drive should be the first action to protect the chain of evidence when a desktop computer is involved, because it can ensure that the original hard drive is not altered, damaged, or destroyed during the forensic analysis, and that the copy can be used as a reliable and admissible source of evidence. Making a copy of the hard drive should also involve using a write blocker, which is a device or a software that prevents any modification or deletion of the data on the hard drive, and generating a hash value, which is a unique and fixed identifier that can verify the integrity and consistency of the data on the hard drive.
The other options are not the first actions to protect the chain of evidence when a desktop computer is involved, but rather actions that should be done after or along with making a copy of the hard drive. Taking the computer to a forensic lab is an action that should be done after making a copy of the hard drive, because it can ensure that the computer is transported and stored in a secure and controlled environment, and that the forensic analysis is conducted by qualified and authorized personnel. Starting documenting is an action that should be done along with making a copy of the hard drive, because it can ensure that the chain of evidence is maintained and recorded throughout the forensic process, and that the evidence can be traced and verified. Turning off the computer is an action that should be done after making a copy of the hard drive, because it can ensure that the computer is powered down and disconnected from any network or device, and that the computer is protected from any further damage or tampering.
A Business Continuity Plan/Disaster Recovery Plan (BCP/DRP) will provide which of the following?
Guaranteed recovery of all business functions
Minimization of the need decision making during a crisis
Insurance against litigation following a disaster
Protection from loss of organization resources
Minimization of the need for decision making during a crisis is the main benefit that a Business Continuity Plan/Disaster Recovery Plan (BCP/DRP) will provide. A BCP/DRP is a set of policies, procedures, and resources that enable an organization to continue or resume its critical functions and operations in the event of a disruption or disaster. A BCP/DRP can provide several benefits, such as:
Minimization of the need for decision making during a crisis is the main benefit that a BCP/DRP will provide, because it can ensure that the organization and its staff have a clear and consistent guidance and direction on how to respond and act during a disruption or disaster, and avoid any confusion, uncertainty, or inconsistency that might worsen the situation or impact. A BCP/DRP can also help to reduce the stress and pressure on the organization and its staff during a crisis, and increase their confidence and competence in executing the plans.
The other options are not the benefits that a BCP/DRP will provide, but rather unrealistic or incorrect expectations or outcomes of a BCP/DRP. Guaranteed recovery of all business functions is not a benefit that a BCP/DRP will provide, because it is not possible or feasible to recover all business functions after a disruption or disaster, especially if the disruption or disaster is severe or prolonged. A BCP/DRP can only prioritize and recover the most critical or essential business functions, and may have to suspend or terminate the less critical or non-essential business functions. Insurance against litigation following a disaster is not a benefit that a BCP/DRP will provide, because it is not a guarantee or protection that the organization will not face any legal or regulatory consequences or liabilities after a disruption or disaster, especially if the disruption or disaster is caused by the organization’s negligence or misconduct. A BCP/DRP can only help to mitigate or reduce the legal or regulatory risks, and may have to comply with or report to the relevant authorities or parties. Protection from loss of organization resources is not a benefit that a BCP/DRP will provide, because it is not a prevention or avoidance of any damage or destruction of the organization’s assets or resources during a disruption or disaster, especially if the disruption or disaster is physical or natural. A BCP/DRP can only help to restore or replace the lost or damaged assets or resources, and may have to incur some costs or losses.
An organization is found lacking the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit. What would be the MOST probable cause?
Absence of a Business Intelligence (BI) solution
Inadequate cost modeling
Improper deployment of the Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
Insufficient Service Level Agreement (SLA)
Insufficient Service Level Agreement (SLA) would be the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit. A Web hosting solution is a service that provides the infrastructure, resources, and tools for hosting and maintaining a website or a web application on the internet. A Web hosting solution can offer various benefits, such as:
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a contract or an agreement that defines the expectations, responsibilities, and obligations of the parties involved in a service, such as the service provider and the service consumer. An SLA can include various components, such as:
Insufficient SLA would be the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, because it could mean that the SLA does not include or specify the appropriate service level indicators or objectives for the Web hosting solution, or that the SLA does not provide or enforce the adequate service level reporting or penalties for the Web hosting solution. This could affect the ability of the organization to measure and assess the Web hosting solution quality, performance, and availability, and to identify and address any issues or risks in the Web hosting solution.
The other options are not the most probable causes for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, but rather the factors that could affect or improve the Web hosting solution in other ways. Absence of a Business Intelligence (BI) solution is a factor that could affect the ability of the organization to analyze and utilize the data and information from the Web hosting solution, such as the web traffic, behavior, or conversion. A BI solution is a system that involves the collection, integration, processing, and presentation of the data and information from various sources, such as the Web hosting solution, to support the decision making and planning of the organization. However, absence of a BI solution is not the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, because it does not affect the definition or specification of the performance indicators for the Web hosting solution, but rather the analysis or usage of the performance indicators for the Web hosting solution. Inadequate cost modeling is a factor that could affect the ability of the organization to estimate and optimize the cost and value of the Web hosting solution, such as the web hosting fees, maintenance costs, or return on investment. A cost model is a tool or a method that helps the organization to calculate and compare the cost and value of the Web hosting solution, and to identify and implement the best or most efficient Web hosting solution. However, inadequate cost modeling is not the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, because it does not affect the definition or specification of the performance indicators for the Web hosting solution, but rather the estimation or optimization of the cost and value of the Web hosting solution. Improper deployment of the Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a factor that could affect the ability of the organization to design and develop the Web hosting solution, such as the web services, components, or interfaces. A SOA is a software architecture that involves the modularization, standardization, and integration of the software components or services that provide the functionality or logic of the Web hosting solution. A SOA can offer various benefits, such as:
However, improper deployment of the SOA is not the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, because it does not affect the definition or specification of the performance indicators for the Web hosting solution, but rather the design or development of the Web hosting solution.
With what frequency should monitoring of a control occur when implementing Information Security Continuous Monitoring (ISCM) solutions?
Continuously without exception for all security controls
Before and after each change of the control
At a rate concurrent with the volatility of the security control
Only during system implementation and decommissioning
Monitoring of a control should occur at a rate concurrent with the volatility of the security control when implementing Information Security Continuous Monitoring (ISCM) solutions. ISCM is a process that involves maintaining the ongoing awareness of the security status, events, and activities of a system or network, by collecting, analyzing, and reporting the security data and information, using various methods and tools. ISCM can provide several benefits, such as:
A security control is a measure or mechanism that is implemented to protect the system or network from the security threats or risks, by preventing, detecting, or correcting the security incidents or impacts. A security control can have various types, such as administrative, technical, or physical, and various attributes, such as preventive, detective, or corrective. A security control can also have different levels of volatility, which is the degree or frequency of change or variation of the security control, due to various factors, such as the security requirements, the threat landscape, or the system or network environment.
Monitoring of a control should occur at a rate concurrent with the volatility of the security control when implementing ISCM solutions, because it can ensure that the ISCM solutions can capture and reflect the current and accurate state and performance of the security control, and can identify and report any issues or risks that might affect the security control. Monitoring of a control at a rate concurrent with the volatility of the security control can also help to optimize the ISCM resources and efforts, by allocating them according to the priority and urgency of the security control.
The other options are not the correct frequencies for monitoring of a control when implementing ISCM solutions, but rather incorrect or unrealistic frequencies that might cause problems or inefficiencies for the ISCM solutions. Continuously without exception for all security controls is an incorrect frequency for monitoring of a control when implementing ISCM solutions, because it is not feasible or necessary to monitor all security controls at the same and constant rate, regardless of their volatility or importance. Continuously monitoring all security controls without exception might cause the ISCM solutions to consume excessive or wasteful resources and efforts, and might overwhelm or overload the ISCM solutions with too much or irrelevant data and information. Before and after each change of the control is an incorrect frequency for monitoring of a control when implementing ISCM solutions, because it is not sufficient or timely to monitor the security control only when there is a change of the security control, and not during the normal operation of the security control. Monitoring the security control only before and after each change might cause the ISCM solutions to miss or ignore the security status, events, and activities that occur between the changes of the security control, and might delay or hinder the ISCM solutions from detecting and responding to the security issues or incidents that affect the security control. Only during system implementation and decommissioning is an incorrect frequency for monitoring of a control when implementing ISCM solutions, because it is not appropriate or effective to monitor the security control only during the initial or final stages of the system or network lifecycle, and not during the operational or maintenance stages of the system or network lifecycle. Monitoring the security control only during system implementation and decommissioning might cause the ISCM solutions to neglect or overlook the security status, events, and activities that occur during the regular or ongoing operation of the system or network, and might prevent or limit the ISCM solutions from improving and optimizing the security control.
Recovery strategies of a Disaster Recovery planning (DRIP) MUST be aligned with which of the following?
Hardware and software compatibility issues
Applications’ critically and downtime tolerance
Budget constraints and requirements
Cost/benefit analysis and business objectives
Recovery strategies of a Disaster Recovery planning (DRP) must be aligned with the cost/benefit analysis and business objectives. A DRP is a part of a BCP/DRP that focuses on restoring the normal operation of the organization’s IT systems and infrastructure after a disruption or disaster. A DRP should include various components, such as:
Recovery strategies of a DRP must be aligned with the cost/benefit analysis and business objectives, because it can ensure that the DRP is feasible and suitable, and that it can achieve the desired outcomes and objectives in a cost-effective and efficient manner. A cost/benefit analysis is a technique that compares the costs and benefits of different recovery strategies, and determines the optimal one that provides the best value for money. A business objective is a goal or a target that the organization wants to achieve through its IT systems and infrastructure, such as increasing the productivity, profitability, or customer satisfaction. A recovery strategy that is aligned with the cost/benefit analysis and business objectives can help to:
The other options are not the factors that the recovery strategies of a DRP must be aligned with, but rather factors that should be considered or addressed when developing or implementing the recovery strategies of a DRP. Hardware and software compatibility issues are factors that should be considered when developing the recovery strategies of a DRP, because they can affect the functionality and interoperability of the IT systems and infrastructure, and may require additional resources or adjustments to resolve them. Applications’ criticality and downtime tolerance are factors that should be addressed when implementing the recovery strategies of a DRP, because they can determine the priority and urgency of the recovery for different applications, and may require different levels of recovery objectives and resources. Budget constraints and requirements are factors that should be considered when developing the recovery strategies of a DRP, because they can limit the availability and affordability of the IT resources and funds for the recovery, and may require trade-offs or compromises to balance them.
What is the MOST important step during forensic analysis when trying to learn the purpose of an unknown application?
Disable all unnecessary services
Ensure chain of custody
Prepare another backup of the system
Isolate the system from the network
Isolating the system from the network is the most important step during forensic analysis when trying to learn the purpose of an unknown application. An unknown application is an application that is not recognized or authorized by the system or network administrator, and that may have been installed or executed without the user’s knowledge or consent. An unknown application may have various purposes, such as:
Forensic analysis is a process that involves examining and investigating the system or network for any evidence or traces of the unknown application, such as its origin, nature, behavior, and impact. Forensic analysis can provide several benefits, such as:
Isolating the system from the network is the most important step during forensic analysis when trying to learn the purpose of an unknown application, because it can ensure that the system is isolated and protected from any external or internal influences or interferences, and that the forensic analysis is conducted in a safe and controlled environment. Isolating the system from the network can also help to:
The other options are not the most important steps during forensic analysis when trying to learn the purpose of an unknown application, but rather steps that should be done after or along with isolating the system from the network. Disabling all unnecessary services is a step that should be done after isolating the system from the network, because it can ensure that the system is optimized and simplified for the forensic analysis, and that the system resources and functions are not consumed or affected by any irrelevant or redundant services. Ensuring chain of custody is a step that should be done along with isolating the system from the network, because it can ensure that the integrity and authenticity of the evidence are maintained and documented throughout the forensic process, and that the evidence can be traced and verified. Preparing another backup of the system is a step that should be done after isolating the system from the network, because it can ensure that the system data and configuration are preserved and replicated for the forensic analysis, and that the system can be restored and recovered in case of any damage or loss.
Which of the following does Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) support?
Multicast and broadcast messages
Coordination of IEEE 802.11 protocols
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) systems
Synchronization of multiple devices
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) supports multicast and broadcast messages by using a group temporal key that is shared by all the devices in the same wireless network. This key is used to encrypt and decrypt the messages that are sent to multiple recipients at once. TKIP also supports unicast messages by using a pairwise temporal key that is unique for each device and session. TKIP does not support coordination of IEEE 802.11 protocols, as it is a protocol itself that was designed to replace WEP. TKIP is compatible with WEP systems, but it does not support them, as it provides more security features than WEP. TKIP does not support synchronization of multiple devices, as it does not provide any clock or time synchronization mechanism . References: 1: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol - Wikipedia 2: Wi-Fi Security: Should You Use WPA2-AES, WPA2-TKIP, or Both? - How-To Geek
Internet Protocol (IP) source address spoofing is used to defeat
address-based authentication.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP).
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) hijacking.
Internet Protocol (IP) source address spoofing is used to defeat address-based authentication, which is a method of verifying the identity of a user or a system based on their IP address. IP source address spoofing involves forging the IP header of a packet to make it appear as if it came from a trusted or authorized source, and bypassing the authentication check. IP source address spoofing can be used for various malicious purposes, such as denial-of-service attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, or session hijacking34. References: 3: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 5274: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, page 153.
An advantage of link encryption in a communications network is that it
makes key management and distribution easier.
protects data from start to finish through the entire network.
improves the efficiency of the transmission.
encrypts all information, including headers and routing information.
An advantage of link encryption in a communications network is that it encrypts all information, including headers and routing information. Link encryption is a type of encryption that is applied at the data link layer of the OSI model, and encrypts the entire packet or frame as it travels from one node to another1. Link encryption can protect the confidentiality and integrity of the data, as well as the identity and location of the nodes. Link encryption does not make key management and distribution easier, as it requires each node to have a separate key for each link. Link encryption does not protect data from start to finish through the entire network, as it only encrypts the data while it is in transit, and decrypts it at each node. Link encryption does not improve the efficiency of the transmission, as it adds overhead and latency to the communication. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, page 419.
Which security action should be taken FIRST when computer personnel are terminated from their jobs?
Remove their computer access
Require them to turn in their badge
Conduct an exit interview
Reduce their physical access level to the facility
The first security action that should be taken when computer personnel are terminated from their jobs is to remove their computer access. Computer access is the ability to log in, use, or modify the computer systems, networks, or data of the organization3. Removing computer access can prevent the terminated personnel from accessing or harming the organization’s information assets, or from stealing or leaking sensitive or confidential data. Removing computer access can also reduce the risk of insider threats, such as sabotage, fraud, or espionage. Requiring them to turn in their badge, conducting an exit interview, and reducing their physical access level to the facility are also important security actions that should be taken when computer personnel are terminated from their jobs, but they are not as urgent or critical as removing their computer access. References: 3: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, 5th Edition, Chapter 5, page 249.
Which of the following is a security limitation of File Transfer Protocol (FTP)?
Passive FTP is not compatible with web browsers.
Anonymous access is allowed.
FTP uses Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) ports 20 and 21.
Authentication is not encrypted.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a protocol that enables the transfer of files between a client and a server over a network. FTP has a security limitation in that it does not encrypt the authentication process, meaning that the username and password are sent in clear text over the network. This exposes the credentials to interception and eavesdropping by unauthorized parties, who could then access the files or compromise the system . References: : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 533. : CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, page 155.
Which of the following is the FIRST step in the incident response process?
Determine the cause of the incident
Disconnect the system involved from the network
Isolate and contain the system involved
Investigate all symptoms to confirm the incident
Investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident is the first step in the incident response process. An incident is an event that violates or threatens the security, availability, integrity, or confidentiality of the IT systems or data. An incident response is a process that involves detecting, analyzing, containing, eradicating, recovering, and learning from an incident, using various methods and tools. An incident response can provide several benefits, such as:
Investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident is the first step in the incident response process, because it can ensure that the incident is verified and validated, and that the incident response is initiated and escalated. A symptom is a sign or an indication that an incident may have occurred or is occurring, such as an alert, a log, or a report. Investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident involves collecting and analyzing the relevant data and information from various sources, such as the IT systems, the network, the users, or the external parties, and determining whether an incident has actually happened or is happening, and how serious or urgent it is. Investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident can also help to:
The other options are not the first steps in the incident response process, but rather steps that should be done after or along with investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident. Determining the cause of the incident is a step that should be done after investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident, because it can ensure that the root cause and source of the incident are identified and analyzed, and that the incident response is directed and focused. Determining the cause of the incident involves examining and testing the affected IT systems and data, and tracing and tracking the origin and path of the incident, using various techniques and tools, such as forensics, malware analysis, or reverse engineering. Determining the cause of the incident can also help to:
Disconnecting the system involved from the network is a step that should be done along with investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident, because it can ensure that the system is isolated and protected from any external or internal influences or interferences, and that the incident response is conducted in a safe and controlled environment. Disconnecting the system involved from the network can also help to:
Isolating and containing the system involved is a step that should be done after investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident, because it can ensure that the incident is confined and restricted, and that the incident response is continued and maintained. Isolating and containing the system involved involves applying and enforcing the appropriate security measures and controls to limit or stop the activity and impact of the incident on the IT systems and data, such as firewall rules, access policies, or encryption keys. Isolating and containing the system involved can also help to:
Intellectual property rights are PRIMARY concerned with which of the following?
Owner’s ability to realize financial gain
Owner’s ability to maintain copyright
Right of the owner to enjoy their creation
Right of the owner to control delivery method
Intellectual property rights are primarily concerned with the owner’s ability to realize financial gain from their creation. Intellectual property is a category of intangible assets that are the result of human creativity and innovation, such as inventions, designs, artworks, literature, music, software, etc. Intellectual property rights are the legal rights that grant the owner the exclusive control over the use, reproduction, distribution, and modification of their intellectual property. Intellectual property rights aim to protect the owner’s interests and incentives, and to reward them for their contribution to the society and economy.
The other options are not the primary concern of intellectual property rights, but rather the secondary or incidental benefits or aspects of them. The owner’s ability to maintain copyright is a means of enforcing intellectual property rights, but not the end goal of them. The right of the owner to enjoy their creation is a personal or moral right, but not a legal or economic one. The right of the owner to control the delivery method is a specific or technical aspect of intellectual property rights, but not a general or fundamental one.
Which of the following types of technologies would be the MOST cost-effective method to provide a reactive control for protecting personnel in public areas?
Install mantraps at the building entrances
Enclose the personnel entry area with polycarbonate plastic
Supply a duress alarm for personnel exposed to the public
Hire a guard to protect the public area
Supplying a duress alarm for personnel exposed to the public is the most cost-effective method to provide a reactive control for protecting personnel in public areas. A duress alarm is a device that allows a person to signal for help in case of an emergency, such as an attack, a robbery, or a medical condition. A duress alarm can be activated by pressing a button, pulling a cord, or speaking a code word. A duress alarm can alert security personnel, law enforcement, or other responders to the location and nature of the emergency, and initiate appropriate actions. A duress alarm is a reactive control because it responds to an incident after it has occurred, rather than preventing it from happening.
The other options are not as cost-effective as supplying a duress alarm, as they involve more expensive or complex technologies or resources. Installing mantraps at the building entrances is a preventive control that restricts the access of unauthorized persons to the facility, but it also requires more space, maintenance, and supervision. Enclosing the personnel entry area with polycarbonate plastic is a preventive control that protects the personnel from physical attacks, but it also reduces the visibility and ventilation of the area. Hiring a guard to protect the public area is a deterrent control that discourages potential attackers, but it also involves paying wages, benefits, and training costs.
Which of the following actions will reduce risk to a laptop before traveling to a high risk area?
Examine the device for physical tampering
Implement more stringent baseline configurations
Purge or re-image the hard disk drive
Change access codes
Purging or re-imaging the hard disk drive of a laptop before traveling to a high risk area will reduce the risk of data compromise or theft in case the laptop is lost, stolen, or seized by unauthorized parties. Purging or re-imaging the hard disk drive will erase all the data and applications on the laptop, leaving only the operating system and the essential software. This will minimize the exposure of sensitive or confidential information that could be accessed by malicious actors. Purging or re-imaging the hard disk drive should be done using secure methods that prevent data recovery, such as overwriting, degaussing, or physical destruction.
The other options will not reduce the risk to the laptop as effectively as purging or re-imaging the hard disk drive. Examining the device for physical tampering will only detect if the laptop has been compromised after the fact, but will not prevent it from happening. Implementing more stringent baseline configurations will improve the security settings and policies of the laptop, but will not protect the data if the laptop is bypassed or breached. Changing access codes will make it harder for unauthorized users to log in to the laptop, but will not prevent them from accessing the data if they use other methods, such as booting from a removable media or removing the hard disk drive.
What is the MOST important consideration from a data security perspective when an organization plans to relocate?
Ensure the fire prevention and detection systems are sufficient to protect personnel
Review the architectural plans to determine how many emergency exits are present
Conduct a gap analysis of a new facilities against existing security requirements
Revise the Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity (DR/BC) plan
When an organization plans to relocate, the most important consideration from a data security perspective is to conduct a gap analysis of the new facilities against the existing security requirements. A gap analysis is a process that identifies and evaluates the differences between the current state and the desired state of a system or a process. In this case, the gap analysis would compare the security controls and measures implemented in the old and new locations, and identify any gaps or weaknesses that need to be addressed. The gap analysis would also help to determine the costs and resources needed to implement the necessary security improvements in the new facilities.
The other options are not as important as conducting a gap analysis, as they do not directly address the data security risks associated with relocation. Ensuring the fire prevention and detection systems are sufficient to protect personnel is a safety issue, not a data security issue. Reviewing the architectural plans to determine how many emergency exits are present is also a safety issue, not a data security issue. Revising the Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity (DR/BC) plan is a good practice, but it is not a preventive measure, rather a reactive one. A DR/BC plan is a document that outlines how an organization will recover from a disaster and resume its normal operations. A DR/BC plan should be updated regularly, not only when relocating.
Which of the following represents the GREATEST risk to data confidentiality?
Network redundancies are not implemented
Security awareness training is not completed
Backup tapes are generated unencrypted
Users have administrative privileges
Generating backup tapes unencrypted represents the greatest risk to data confidentiality, as it exposes the data to unauthorized access or disclosure if the tapes are lost, stolen, or intercepted. Backup tapes are often stored off-site or transported to remote locations, which increases the chances of them falling into the wrong hands. If the backup tapes are unencrypted, anyone who obtains them can read the data without any difficulty. Therefore, backup tapes should always be encrypted using strong algorithms and keys, and the keys should be protected and managed separately from the tapes.
The other options do not pose as much risk to data confidentiality as generating backup tapes unencrypted. Network redundancies are not implemented will affect the availability and reliability of the network, but not necessarily the confidentiality of the data. Security awareness training is not completed will increase the likelihood of human errors or negligence that could compromise the data, but not as directly as generating backup tapes unencrypted. Users have administrative privileges will grant users more access and control over the system and the data, but not as widely as generating backup tapes unencrypted.
An important principle of defense in depth is that achieving information security requires a balanced focus on which PRIMARY elements?
Development, testing, and deployment
Prevention, detection, and remediation
People, technology, and operations
Certification, accreditation, and monitoring
An important principle of defense in depth is that achieving information security requires a balanced focus on the primary elements of people, technology, and operations. People are the users, administrators, managers, and other stakeholders who are involved in the security process. They need to be aware, trained, motivated, and accountable for their security roles and responsibilities. Technology is the hardware, software, network, and other tools that are used to implement the security controls and measures. They need to be selected, configured, updated, and monitored according to the security standards and best practices. Operations are the policies, procedures, processes, and activities that are performed to achieve the security objectives and requirements. They need to be documented, reviewed, audited, and improved continuously to ensure their effectiveness and efficiency.
The other options are not the primary elements of defense in depth, but rather the phases, functions, or outcomes of the security process. Development, testing, and deployment are the phases of the security life cycle, which describes how security is integrated into the system development process. Prevention, detection, and remediation are the functions of the security management, which describes how security is maintained and improved over time. Certification, accreditation, and monitoring are the outcomes of the security evaluation, which describes how security is assessed and verified against the criteria and standards.
All of the following items should be included in a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) questionnaire EXCEPT questions that
determine the risk of a business interruption occurring
determine the technological dependence of the business processes
Identify the operational impacts of a business interruption
Identify the financial impacts of a business interruption
A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is a process that identifies and evaluates the potential effects of natural and man-made disasters on business operations. The BIA questionnaire is a tool that collects information from business process owners and stakeholders about the criticality, dependencies, recovery objectives, and resources of their processes. The BIA questionnaire should include questions that:
The BIA questionnaire should not include questions that determine the risk of a business interruption occurring, as this is part of the risk assessment process, which is a separate activity from the BIA. The risk assessment process identifies and analyzes the threats and vulnerabilities that could cause a business interruption, and estimates the likelihood and impact of such events. The risk assessment process also evaluates the existing controls and mitigation strategies, and recommends additional measures to reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
When assessing an organization’s security policy according to standards established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001 and 27002, when can management responsibilities be defined?
Only when assets are clearly defined
Only when standards are defined
Only when controls are put in place
Only procedures are defined
When assessing an organization’s security policy according to standards established by the ISO 27001 and 27002, management responsibilities can be defined only when standards are defined. Standards are the specific rules, guidelines, or procedures that support the implementation of the security policy. Standards define the minimum level of security that must be achieved by the organization, and provide the basis for measuring compliance and performance. Standards also assign roles and responsibilities to different levels of management and staff, and specify the reporting and escalation procedures.
Management responsibilities are the duties and obligations that managers have to ensure the effective and efficient execution of the security policy and standards. Management responsibilities include providing leadership, direction, support, and resources for the security program, establishing and communicating the security objectives and expectations, ensuring compliance with the legal and regulatory requirements, monitoring and reviewing the security performance and incidents, and initiating corrective and preventive actions when needed.
Management responsibilities cannot be defined without standards, as standards provide the framework and criteria for defining what managers need to do and how they need to do it. Management responsibilities also depend on the scope and complexity of the security policy and standards, which may vary depending on the size, nature, and context of the organization. Therefore, standards must be defined before management responsibilities can be defined.
The other options are not correct, as they are not prerequisites for defining management responsibilities. Assets are the resources that need to be protected by the security policy and standards, but they do not determine the management responsibilities. Controls are the measures that are implemented to reduce the security risks and achieve the security objectives, but they do not determine the management responsibilities. Procedures are the detailed instructions that describe how to perform the security tasks and activities, but they do not determine the management responsibilities.
The application of a security patch to a product previously validate at Common Criteria (CC) Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) 4 would
require an update of the Protection Profile (PP).
require recertification.
retain its current EAL rating.
reduce the product to EAL 3.
Common Criteria (CC) is an international standard for evaluating the security of IT products and systems. Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) is a numerical grade that indicates the level of assurance and rigor of the evaluation process. EAL ranges from 1 (lowest) to 7 (highest). A product that has been validated at EAL 4 has been methodically designed, tested, and reviewed, and provides a moderate level of independently assured security. The application of a security patch to a product previously validated at EAL 4 would require recertification, as the patch may introduce new vulnerabilities or affect the security functionality of the product. The recertification process would ensure that the patched product still meets the EAL 4 requirements and does not compromise the security claims of the original evaluation. Updating the Protection Profile (PP), retaining the current EAL rating, or reducing the product to EAL 3 are not valid options, as they do not reflect the impact of the security patch on the product’s security assurance.
After acquiring the latest security updates, what must be done before deploying to production systems?
Use tools to detect missing system patches
Install the patches on a test system
Subscribe to notifications for vulnerabilities
Assess the severity of the situation
After acquiring the latest security updates, the best practice is to install the patches on a test system before deploying them to the production systems. This is to ensure that the patches are compatible with the system configuration and do not cause any adverse effects or conflicts with the existing applications or services. The test system should be isolated from the production environment and should have the same or similar specifications and settings as the production system.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, page 336; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 6, page 297
A network scan found 50% of the systems with one or more critical vulnerabilities. Which of the following represents the BEST action?
Assess vulnerability risk and program effectiveness.
Assess vulnerability risk and business impact.
Disconnect all systems with critical vulnerabilities.
Disconnect systems with the most number of vulnerabilities.
The best action after finding 50% of the systems with one or more critical vulnerabilities is to assess the vulnerability risk and business impact. This means to evaluate the likelihood and severity of the vulnerabilities being exploited, as well as the potential consequences and costs for the business operations and objectives. This assessment can help prioritize the remediation efforts, allocate the resources, and justify the investments.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, page 343; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 6, page 304
A company was ranked as high in the following National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) functions: Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover. However, a low maturity grade was attributed to the Identify function. In which of the following the controls categories does this company need to improve when analyzing its processes individually?
Asset Management, Business Environment, Governance and Risk Assessment
Access Control, Awareness and Training, Data Security and Maintenance
Anomalies and Events, Security Continuous Monitoring and Detection Processes
Recovery Planning, Improvements and Communications
According to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, the control categories that the company needs to improve when analyzing its processes individually are Asset Management, Business Environment, Governance and Risk Assessment. These control categories are part of the Identify function, which is one of the five core functions of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. The Identify function is the function that provides the foundational understanding and awareness of the organization’s systems, assets, data, capabilities, and risks, as well as the role and contribution of the organization to the critical infrastructure and the society. The Identify function helps the organization to prioritize and align its cybersecurity activities and resources with its business objectives and requirements, as well as to establish and maintain its cybersecurity policies and standards. The Identify function consists of six control categories, which are the specific outcomes or goals that the organization should achieve for each function. The control categories for the Identify function are:
The company was ranked as high in the following NIST functions: Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover. However, a low maturity grade was attributed to the Identify function. This means that the company has a good level of capability and performance in implementing and executing the cybersecurity activities and controls that are related to the other four functions, but it has a low level of capability and performance in implementing and executing the cybersecurity activities and controls that are related to the Identify function. Therefore, the company needs to improve its processes and controls that are related to the Identify function, which are the Asset Management, Business Environment, Governance, Risk Assessment, Risk Management Strategy, and Supply Chain Risk Management control categories. By improving these control categories, the company can enhance its foundational understanding and awareness of its systems, assets, data, capabilities, and risks, as well as its role and contribution to the critical infrastructure and the society. The company can also better prioritize and align its cybersecurity activities and resources with its business objectives and requirements, as well as establish and maintain its cybersecurity policies and standards. Access Control, Awareness and Training, Data Security and Maintenance are not the control categories that the company needs to improve when analyzing its processes individually, as they are part of the Protect function, not the Identify function. The Protect function is the function that provides the appropriate safeguards and countermeasures to ensure the delivery of critical services and to limit or contain the impact of potential cybersecurity incidents. The Protect function consists of eight control categories, which are:
The company was ranked as high in the Protect function, which means that it has a good level of capability and performance in implementing and executing the cybersecurity activities and controls that are related to the Protect function. Therefore, the company does not need to improve its processes and controls that are related to the Protect function, which are the Access Control, Awareness and Training, Data Security, Information Protection Processes and Procedures, Maintenance, and Protective Technology control categories. Anomalies and Events, Security Continuous Monitoring and Detection Processes are not the control categories that the company needs to improve when analyzing its processes individually, as they are part of the Detect function, not the Identify function. The Detect function is the function that provides the appropriate activities and capabilities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity incident in a timely manner. The Detect function consists of three control categories, which are:
The company was ranked as high in the Detect function, which means that it has a good level of capability and performance in implementing and executing the cybersecurity activities and controls that are related to the Detect function. Therefore, the company does not need to improve its processes and controls that are related to the Detect function, which are the Anomalies and Events, Security Continuous Monitoring, and Detection Processes control categories. Recovery Planning, Improvements and Communications are not the control categories that the company needs to improve when analyzing its processes individually, as they are part of the Recover function, not the Identify function. The Recover function is the function that provides the appropriate activities and capabilities to restore the normal operations and functions of the organization as quickly as possible after a cybersecurity incident, as well as to prevent or reduce the recurrence or impact of future incidents. The Recover function consists of three control categories, which are:
The company was ranked as high in the Recover function, which means that it has a good level of capability and performance in implementing and executing the cybersecurity activities and controls that are related to the Recover function. Therefore, the company does not need to improve its processes and controls that are related to the Recover function, which are the Recovery Planning, Improvements, and Communications control categories.
The PRIMARY outcome of a certification process is that it provides documented
system weaknesses for remediation.
standards for security assessment, testing, and process evaluation.
interconnected systems and their implemented security controls.
security analyses needed to make a risk-based decision.
The primary outcome of a certification process is that it provides documented security analyses needed to make a risk-based decision. Certification is a process of evaluating and testing the security of a system or product against a set of criteria or standards. Certification provides evidence of the security posture and capabilities of the system or product, as well as the identified vulnerabilities, threats, and risks. Certification helps the decision makers, such as the system owners or accreditors, to determine whether the system or product meets the security requirements and can be authorized to operate in a specific environment12 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, p. 455; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 7: Security Operations, p. 867.
What is the GREATEST challenge to identifying data leaks?
Available technical tools that enable user activity monitoring.
Documented asset classification policy and clear labeling of assets.
Senior management cooperation in investigating suspicious behavior.
Law enforcement participation to apprehend and interrogate suspects.
The greatest challenge to identifying data leaks is having a documented asset classification policy and clear labeling of assets. Data leaks are the unauthorized or accidental disclosure or exposure of sensitive or confidential data, such as personal information, trade secrets, or intellectual property. Data leaks can cause serious damage or harm to the data owner, such as reputation loss, legal liability, or competitive disadvantage. The greatest challenge to identifying data leaks is having a documented asset classification policy and clear labeling of assets, which means that the organization has defined and implemented the rules and guidelines for categorizing and marking the data according to their sensitivity, value, or criticality. Having a documented asset classification policy and clear labeling of assets can help to identify data leaks by enabling the detection, tracking, and reporting of the data movements, access, or usage, and by alerting the data owner, custodian, or user of any unauthorized or abnormal data activities or incidents. The other options are not the greatest challenges, but rather the benefits or enablers of identifying data leaks. Available technical tools that enable user activity monitoring are not the greatest challenges, but rather the benefits, of identifying data leaks, as they can provide the means or mechanisms for collecting, analyzing, and auditing the data actions or behaviors of the users or devices. Senior management cooperation in investigating suspicious behavior is not the greatest challenge, but rather the enabler, of identifying data leaks, as it can provide the support or authority for conducting the data leak investigation and taking the appropriate actions or measures. Law enforcement participation to apprehend and interrogate suspects is not the greatest challenge, but rather the enabler, of identifying data leaks, as it can provide the assistance or collaboration for pursuing and prosecuting the data leak perpetrators or offenders. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, p. 29; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, p. 287.
Attack trees are MOST useful for which of the following?
Determining system security scopes
Generating attack libraries
Enumerating threats
Evaluating Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
Attack trees are most useful for enumerating threats. Attack trees are graphical models that represent the possible ways that an attacker can exploit a system or achieve a goal. Attack trees consist of nodes that represent the attacker’s actions or conditions, and branches that represent the logical relationships between the nodes. Attack trees can help to enumerate the threats that the system faces, as well as to analyze the likelihood, impact, and countermeasures of each threat. Attack trees are not useful for determining system security scopes, generating attack libraries, or evaluating DoS attacks, although they may be used as inputs or outputs for these tasks. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4: Security Operations, page 499; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4: Communication and Network Security, page 552.
Which type of test would an organization perform in order to locate and target exploitable defects?
Penetration
System
Performance
Vulnerability
Penetration testing is a type of test that an organization performs in order to locate and target exploitable defects in its information systems and networks. Penetration testing simulates a real-world attack scenario, where a tester, also known as a penetration tester or ethical hacker, tries to find and exploit the vulnerabilities in the system or network, using the same tools and techniques as a malicious attacker. The goal of penetration testing is to identify the weaknesses and gaps in the security posture of the organization, and to provide recommendations and solutions to mitigate or eliminate them. Penetration testing can help the organization improve its security awareness, compliance, and resilience, and prevent potential breaches or incidents.
Which of the following is the MOST important security goal when performing application interface testing?
Confirm that all platforms are supported and function properly
Evaluate whether systems or components pass data and control correctly to one another
Verify compatibility of software, hardware, and network connections
Examine error conditions related to external interfaces to prevent application details leakage
The most important security goal when performing application interface testing is to examine error conditions related to external interfaces to prevent application details leakage. Application interface testing is a type of testing that focuses on the interactions between different systems or components through their interfaces, such as APIs, web services, or protocols. Error conditions related to external interfaces can occur when the input, output, or communication is invalid, incomplete, or unexpected. These error conditions can cause the application to reveal sensitive or confidential information, such as error messages, stack traces, configuration files, or database queries, which can be exploited by attackers to gain access or compromise the system. Therefore, it is important to examine these error conditions and ensure that the application handles them properly and securely. Confirming that all platforms are supported and function properly, evaluating whether systems or components pass data and control correctly to one another, and verifying compatibility of software, hardware, and network connections are not security goals, but functional or performance goals of application interface testing. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8: Software Development Security, page 1000; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7: Software Development Security, page 922.
A security analyst for a large financial institution is reviewing network traffic related to an incident. The analyst determines the traffic is irrelevant to the investigation but in the process of the review, the analyst also finds that an applications data, which included full credit card cardholder data, is transferred in clear text between the server and user’s desktop. The analyst knows this violates the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS). Which of the following is the analyst’s next step?
Send the log file co-workers for peer review
Include the full network traffic logs in the incident report
Follow organizational processes to alert the proper teams to address the issue.
Ignore data as it is outside the scope of the investigation and the analyst’s role.
Section: Security Operations
An engineer in a software company has created a virus creation tool. The tool can generate thousands of polymorphic viruses. The engineer is planning to use the tool in a controlled environment to test the company's next generation virus scanning software. Which would BEST describe the behavior of the engineer and why?
The behavior is ethical because the tool will be used to create a better virus scanner.
The behavior is ethical because any experienced programmer could create such a tool.
The behavior is not ethical because creating any kind of virus is bad.
The behavior is not ethical because such a tool could be leaked on the Internet.
Creating a virus creation tool that can generate thousands of polymorphic viruses is not ethical, even if the intention is to use it in a controlled environment to test the company’s next generation virus scanning software. Such a tool could be leaked on the Internet, either intentionally or accidentally, and fall into the hands of malicious actors who could use it to create and spread harmful viruses that could compromise the security and privacy of millions of users and systems. The engineer should follow the code of ethics and professional conduct of the ISC2, which states that members and certificate holders shall protect society, the common good, necessary public trust and confidence, and the infrastructure . References: : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, page 18. : CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 1, page 11.
Which of the following is an appropriate source for test data?
Production data that is secured and maintained only in the production environment.
Test data that has no similarities to production datA.
Test data that is mirrored and kept up-to-date with production datA.
Production data that has been sanitized before loading into a test environment.
The most appropriate source for test data is production data that has been sanitized before loading into a test environment. Sanitization is the process of removing or modifying sensitive or confidential information from the data, such as personal identifiers, financial records, or trade secrets. Sanitized data preserves the characteristics and structure of the original data, but reduces the risk of exposing or compromising the data in the test environment. Production data that is secured and maintained only in the production environment is not a suitable source for test data, as it may not be accessible or available for testing purposes. Test data that has no similarities to production data is not a realistic or reliable source for test data, as it may not reflect the actual scenarios or conditions that the system will encounter in the production environment. Test data that is mirrored and kept up-to-date with production data is not a secure or ethical source for test data, as it may violate the privacy or confidentiality of the data owners or subjects, and expose the data to unauthorized access or modification in the test environment. References: 4: Data Sanitization: What It Is and How to Implement It55: Test Data Management: Best Practices and Methodologies
The three PRIMARY requirements for a penetration test are
A defined goal, limited time period, and approval of management
A general objective, unlimited time, and approval of the network administrator
An objective statement, disclosed methodology, and fixed cost
A stated objective, liability waiver, and disclosed methodology
The three primary requirements for a penetration test are a defined goal, a limited time period, and an approval of management. A penetration test is a type of security assessment that simulates a malicious attack on an information system or network, with the permission of the owner, to identify and exploit vulnerabilities and evaluate the security posture of the system or network. A penetration test requires a defined goal, which is the specific objective or scope of the test, such as testing a particular system, network, application, or function. A penetration test also requires a limited time period, which is the duration or deadline of the test, such as a few hours, days, or weeks. A penetration test also requires an approval of management, which is the formal authorization and consent from the senior management of the organization that owns the system or network to be tested, as well as the management of the organization that conducts the test. A general objective, unlimited time, and approval of the network administrator are not the primary requirements for a penetration test, as they may not provide a clear and realistic direction, scope, and authorization for the test.
A company whose Information Technology (IT) services are being delivered from a Tier 4 data center, is preparing a companywide Business Continuity Planning (BCP). Which of the following failures should the IT manager be concerned with?
Application
Storage
Power
Network
A company whose IT services are being delivered from a Tier 4 data center should be most concerned with application failures when preparing a companywide BCP. A BCP is a document that describes how an organization will continue its critical business functions in the event of a disruption or disaster. A BCP should include a risk assessment, a business impact analysis, a recovery strategy, and a testing and maintenance plan.
A Tier 4 data center is the highest level of data center classification, according to the Uptime Institute. A Tier 4 data center has the highest level of availability, reliability, and fault tolerance, as it has multiple and independent paths for power and cooling, and redundant and backup components for all systems. A Tier 4 data center has an uptime rating of 99.995%, which means it can only experience 0.4 hours of downtime per year. Therefore, the likelihood of a power, storage, or network failure in a Tier 4 data center is very low, and the impact of such a failure would be minimal, as the data center can quickly switch to alternative sources or routes.
However, a Tier 4 data center cannot prevent or mitigate application failures, which are caused by software bugs, configuration errors, or malicious attacks. Application failures can affect the functionality, performance, or security of the IT services, and cause data loss, corruption, or breach. Therefore, the IT manager should be most concerned with application failures when preparing a BCP, and ensure that the applications are properly designed, tested, updated, and monitored.
What is the BEST approach for controlling access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance?
Audit logs
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Two-factor authentication
Application of least privilege
Applying the principle of least privilege is the best approach for controlling access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance. The principle of least privilege is a security concept that states that every user or process should have the minimum amount of access rights and permissions that are necessary to perform their tasks or functions, and nothing more. The principle of least privilege can provide several benefits, such as:
Applying the principle of least privilege is the best approach for controlling access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance, because it can ensure that the employees can only access the information that is relevant and necessary for their tasks or functions, and that they cannot access or manipulate the information that is beyond their scope or authority. For example, if the highly sensitive information is related to a specific project or department, then only the employees who are involved in that project or department should have access to that information, and not the employees who have the same level of security clearance but are not involved in that project or department.
The other options are not the best approaches for controlling access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance, but rather approaches that have other purposes or effects. Audit logs are records that capture and store the information about the events and activities that occur within a system or a network, such as the access and usage of the sensitive data. Audit logs can provide a reactive and detective layer of security by enabling the monitoring and analysis of the system or network behavior, and facilitating the investigation and response of the incidents. However, audit logs cannot prevent or reduce the access or disclosure of the sensitive information, but rather provide evidence or clues after the fact. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a method that enforces the access rights and permissions of the users based on their roles or functions within the organization, rather than their identities or attributes. RBAC can provide a granular and dynamic layer of security by defining and assigning the roles and permissions according to the organizational structure and policies. However, RBAC cannot control the access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance and the same role or function within the organization, but rather rely on other criteria or mechanisms. Two-factor authentication is a technique that verifies the identity of the users by requiring them to provide two pieces of evidence or factors, such as something they know (e.g., password, PIN), something they have (e.g., token, smart card), or something they are (e.g., fingerprint, face). Two-factor authentication can provide a strong and preventive layer of security by preventing unauthorized access to the system or network by the users who do not have both factors. However, two-factor authentication cannot control the access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance and the same two factors, but rather rely on other criteria or mechanisms.
A manufacturing organization wants to establish a Federated Identity Management (FIM) system with its 20 different supplier companies. Which of the following is the BEST solution for the manufacturing organization?
Trusted third-party certification
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Security Assertion Markup language (SAML)
Cross-certification
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is the best solution for the manufacturing organization that wants to establish a Federated Identity Management (FIM) system with its 20 different supplier companies. FIM is a process that allows the sharing and recognition of identities across different organizations that have a trust relationship. FIM enables the users of one organization to access the resources or services of another organization without having to create or maintain multiple accounts or credentials. FIM can provide several benefits, such as:
SAML is a standard protocol that supports FIM by allowing the exchange of authentication and authorization information between different parties. SAML uses XML-based messages, called assertions, to convey the identity, attributes, and entitlements of a user to a service provider. SAML defines three roles for the parties involved in FIM:
SAML works as follows:
SAML is the best solution for the manufacturing organization that wants to establish a FIM system with its 20 different supplier companies, because it can enable the seamless and secure access to the resources or services across the different organizations, without requiring the users to create or maintain multiple accounts or credentials. SAML can also provide interoperability and compatibility between different platforms and technologies, as it is based on a standard and open protocol.
The other options are not the best solutions for the manufacturing organization that wants to establish a FIM system with its 20 different supplier companies, but rather solutions that have other limitations or drawbacks. Trusted third-party certification is a process that involves a third party, such as a certificate authority (CA), that issues and verifies digital certificates that contain the public key and identity information of a user or an entity. Trusted third-party certification can provide authentication and encryption for the communication between different parties, but it does not provide authorization or entitlement information for the access to the resources or services. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a protocol that allows the access and management of directory services, such as Active Directory, that store the identity and attribute information of users and entities. LDAP can provide a centralized and standardized way to store and retrieve identity and attribute information, but it does not provide a mechanism to exchange or federate the information across different organizations. Cross-certification is a process that involves two or more CAs that establish a trust relationship and recognize each other’s certificates. Cross-certification can extend the trust and validity of the certificates across different domains or organizations, but it does not provide a mechanism to exchange or federate the identity, attribute, or entitlement information.
Which of the following BEST describes an access control method utilizing cryptographic keys derived from a smart card private key that is embedded within mobile devices?
Derived credential
Temporary security credential
Mobile device credentialing service
Digest authentication
Derived credential is the best description of an access control method utilizing cryptographic keys derived from a smart card private key that is embedded within mobile devices. A smart card is a device that contains a microchip that stores a private key and a digital certificate that are used for authentication and encryption. A smart card is typically inserted into a reader that is attached to a computer or a terminal, and the user enters a personal identification number (PIN) to unlock the smart card and access the private key and the certificate. A smart card can provide a high level of security and convenience for the user, as it implements a two-factor authentication method that combines something the user has (the smart card) and something the user knows (the PIN).
However, a smart card may not be compatible or convenient for mobile devices, such as smartphones or tablets, that do not have a smart card reader or a USB port. To address this issue, a derived credential is a solution that allows the user to use a mobile device as an alternative to a smart card for authentication and encryption. A derived credential is a cryptographic key and a certificate that are derived from the smart card private key and certificate, and that are stored on the mobile device. A derived credential works as follows:
A derived credential can provide a secure and convenient way to use a mobile device as an alternative to a smart card for authentication and encryption, as it implements a two-factor authentication method that combines something the user has (the mobile device) and something the user is (the biometric feature). A derived credential can also comply with the standards and policies for the use of smart cards, such as the Personal Identity Verification (PIV) or the Common Access Card (CAC) programs.
The other options are not the best descriptions of an access control method utilizing cryptographic keys derived from a smart card private key that is embedded within mobile devices, but rather descriptions of other methods or concepts. Temporary security credential is a method that involves issuing a short-lived credential, such as a token or a password, that can be used for a limited time or a specific purpose. Temporary security credential can provide a flexible and dynamic way to grant access to the users or entities, but it does not involve deriving a cryptographic key from a smart card private key. Mobile device credentialing service is a concept that involves providing a service that can issue, manage, or revoke credentials for mobile devices, such as certificates, tokens, or passwords. Mobile device credentialing service can provide a centralized and standardized way to control the access of mobile devices, but it does not involve deriving a cryptographic key from a smart card private key. Digest authentication is a method that involves using a hash function, such as MD5, to generate a digest or a fingerprint of the user’s credentials, such as the username and password, and sending it to the server for verification. Digest authentication can provide a more secure way to authenticate the user than the basic authentication, which sends the credentials in plain text, but it does not involve deriving a cryptographic key from a smart card private key.
Users require access rights that allow them to view the average salary of groups of employees. Which control would prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary?
Limit access to predefined queries
Segregate the database into a small number of partitions each with a separate security level
Implement Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
Reduce the number of people who have access to the system for statistical purposes
Limiting access to predefined queries is the control that would prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they only require access rights that allow them to view the average salary of groups of employees. A query is a request for information from a database, which can be expressed in a structured query language (SQL) or a graphical user interface (GUI). A query can specify the criteria, conditions, and operations for selecting, filtering, sorting, grouping, and aggregating the data from the database. A predefined query is a query that has been created and stored in advance by the database administrator or the data owner, and that can be executed by the authorized users without any modification. A predefined query can provide several benefits, such as:
Limiting access to predefined queries is the control that would prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they only require access rights that allow them to view the average salary of groups of employees, because it can ensure that the users can only access the data that is relevant and necessary for their tasks, and that they cannot access or manipulate the data that is beyond their scope or authority. For example, a predefined query can be created and stored that calculates and displays the average salary of groups of employees based on certain criteria, such as department, position, or experience. The users who need to view this information can execute this predefined query, but they cannot modify it or create their own queries that might reveal the individual employee’s salary or other sensitive data.
The other options are not the controls that would prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they only require access rights that allow them to view the average salary of groups of employees, but rather controls that have other purposes or effects. Segregating the database into a small number of partitions each with a separate security level is a control that would improve the performance and security of the database by dividing it into smaller and manageable segments that can be accessed and processed independently and concurrently. However, this control would not prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they have access to the partition that contains the salary data, and if they can create or modify their own queries. Implementing Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is a control that would enforce the access rights and permissions of the users based on their roles or functions within the organization, rather than their identities or attributes. However, this control would not prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if their roles or functions require them to access the salary data, and if they can create or modify their own queries. Reducing the number of people who have access to the system for statistical purposes is a control that would reduce the risk and impact of unauthorized access or disclosure of the sensitive data by minimizing the exposure and distribution of the data. However, this control would not prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they are among the people who have access to the system, and if they can create or modify their own queries.
Which of the following could cause a Denial of Service (DoS) against an authentication system?
Encryption of audit logs
No archiving of audit logs
Hashing of audit logs
Remote access audit logs
Remote access audit logs could cause a Denial of Service (DoS) against an authentication system. A DoS attack is a type of attack that aims to disrupt or degrade the availability or performance of a system or a network by overwhelming it with excessive or malicious traffic or requests. An authentication system is a system that verifies the identity and credentials of the users or entities that want to access the system or network resources or services. An authentication system can use various methods or factors to authenticate the users or entities, such as passwords, tokens, certificates, biometrics, or behavioral patterns.
Remote access audit logs are records that capture and store the information about the events and activities that occur when the users or entities access the system or network remotely, such as via the internet, VPN, or dial-up. Remote access audit logs can provide a reactive and detective layer of security by enabling the monitoring and analysis of the remote access behavior, and facilitating the investigation and response of the incidents.
Remote access audit logs could cause a DoS against an authentication system, because they could consume a large amount of disk space, memory, or bandwidth on the authentication system, especially if the remote access is frequent, intensive, or malicious. This could affect the performance or functionality of the authentication system, and prevent or delay the legitimate users or entities from accessing the system or network resources or services. For example, an attacker could launch a DoS attack against an authentication system by sending a large number of fake or invalid remote access requests, and generating a large amount of remote access audit logs that fill up the disk space or memory of the authentication system, and cause it to crash or slow down.
The other options are not the factors that could cause a DoS against an authentication system, but rather the factors that could improve or protect the authentication system. Encryption of audit logs is a technique that involves using a cryptographic algorithm and a key to transform the audit logs into an unreadable or unintelligible format, that can only be reversed or decrypted by authorized parties. Encryption of audit logs can enhance the security and confidentiality of the audit logs by preventing unauthorized access or disclosure of the sensitive information in the audit logs. However, encryption of audit logs could not cause a DoS against an authentication system, because it does not affect the availability or performance of the authentication system, but rather the integrity or privacy of the audit logs. No archiving of audit logs is a practice that involves not storing or transferring the audit logs to a separate or external storage device or location, such as a tape, disk, or cloud. No archiving of audit logs can reduce the security and availability of the audit logs by increasing the risk of loss or damage of the audit logs, and limiting the access or retrieval of the audit logs. However, no archiving of audit logs could not cause a DoS against an authentication system, because it does not affect the availability or performance of the authentication system, but rather the availability or preservation of the audit logs. Hashing of audit logs is a technique that involves using a hash function, such as MD5 or SHA, to generate a fixed-length and unique value, called a hash or a digest, that represents the audit logs. Hashing of audit logs can improve the security and integrity of the audit logs by verifying the authenticity or consistency of the audit logs, and detecting any modification or tampering of the audit logs. However, hashing of audit logs could not cause a DoS against an authentication system, because it does not affect the availability or performance of the authentication system, but rather the integrity or verification of the audit logs.
Which of the following is a PRIMARY benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure?
Executive audiences will understand the outcomes of testing and most appropriate next steps for corrective actions to be taken
Technical teams will understand the testing objectives, testing strategies applied, and business risk associated with each vulnerability
Management teams will understand the testing objectives and reputational risk to the organization
Technical and management teams will better understand the testing objectives, results of each test phase, and potential impact levels
Technical and management teams will better understand the testing objectives, results of each test phase, and potential impact levels is the primary benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure. Security testing is a process that involves evaluating and verifying the security posture, vulnerabilities, and threats of a system or a network, using various methods and techniques, such as vulnerability assessment, penetration testing, code review, and compliance checks. Security testing can provide several benefits, such as:
A security testing report is a document that summarizes and communicates the findings and recommendations of the security testing process to the relevant stakeholders, such as the technical and management teams. A security testing report can have various formats and structures, depending on the scope, purpose, and audience of the report. However, a formalized security testing report format and structure is one that follows a standard and consistent template, such as the one proposed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the Special Publication 800-115, Technical Guide to Information Security Testing and Assessment. A formalized security testing report format and structure can have several components, such as:
Technical and management teams will better understand the testing objectives, results of each test phase, and potential impact levels is the primary benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, because it can ensure that the security testing report is clear, comprehensive, and consistent, and that it provides the relevant and useful information for the technical and management teams to make informed and effective decisions and actions regarding the system or network security.
The other options are not the primary benefits of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, but rather secondary or specific benefits for different audiences or purposes. Executive audiences will understand the outcomes of testing and most appropriate next steps for corrective actions to be taken is a benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, but it is not the primary benefit, because it is more relevant for the executive summary component of the report, which is a brief and high-level overview of the report, rather than the entire report. Technical teams will understand the testing objectives, testing strategies applied, and business risk associated with each vulnerability is a benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, but it is not the primary benefit, because it is more relevant for the methodology and results components of the report, which are more technical and detailed parts of the report, rather than the entire report. Management teams will understand the testing objectives and reputational risk to the organization is a benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, but it is not the primary benefit, because it is more relevant for the introduction and conclusion components of the report, which are more contextual and strategic parts of the report, rather than the entire report.
Which of the following is of GREATEST assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations?
Change management processes
User administration procedures
Operating System (OS) baselines
System backup documentation
Operating System (OS) baselines are of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations. OS baselines are standard or reference configurations that define the desired and secure state of an OS, including the settings, parameters, patches, and updates. OS baselines can provide several benefits, such as:
OS baselines are of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, because they can enable the auditors to evaluate and verify the current and actual state of the OS against the desired and secure state of the OS. OS baselines can also help the auditors to identify and report any gaps, issues, or risks in the OS configurations, and to recommend or implement any corrective or preventive actions.
The other options are not of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, but rather of assistance for other purposes or aspects. Change management processes are processes that ensure that any changes to the system configurations are planned, approved, implemented, and documented in a controlled and consistent manner. Change management processes can improve the security and reliability of the system configurations by preventing or reducing the errors, conflicts, or disruptions that might occur due to the changes. However, change management processes are not of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, because they do not define the desired and secure state of the system configurations, but rather the procedures and controls for managing the changes. User administration procedures are procedures that define the roles, responsibilities, and activities for creating, modifying, deleting, and managing the user accounts and access rights. User administration procedures can enhance the security and accountability of the user accounts and access rights by enforcing the principles of least privilege, separation of duties, and need to know. However, user administration procedures are not of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, because they do not define the desired and secure state of the system configurations, but rather the rules and tasks for administering the users. System backup documentation is documentation that records the information and details about the system backup processes, such as the backup frequency, type, location, retention, and recovery. System backup documentation can increase the availability and resilience of the system by ensuring that the system data and configurations can be restored in case of a loss or damage. However, system backup documentation is not of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, because it does not define the desired and secure state of the system configurations, but rather the backup and recovery of the system configurations.
A Virtual Machine (VM) environment has five guest Operating Systems (OS) and provides strong isolation. What MUST an administrator review to audit a user’s access to data files?
Host VM monitor audit logs
Guest OS access controls
Host VM access controls
Guest OS audit logs
Guest OS audit logs are what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files in a VM environment that has five guest OS and provides strong isolation. A VM environment is a system that allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine, each with its own OS and applications. A VM environment can provide several benefits, such as:
A guest OS is the OS that runs on a VM, which is different from the host OS that runs on the physical machine. A guest OS can have its own security controls and mechanisms, such as access controls, encryption, authentication, and audit logs. Audit logs are records that capture and store the information about the events and activities that occur within a system or a network, such as the access and usage of the data files. Audit logs can provide a reactive and detective layer of security by enabling the monitoring and analysis of the system or network behavior, and facilitating the investigation and response of the incidents.
Guest OS audit logs are what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files in a VM environment that has five guest OS and provides strong isolation, because they can provide the most accurate and relevant information about the user’s actions and interactions with the data files on the VM. Guest OS audit logs can also help the administrator to identify and report any unauthorized or suspicious access or disclosure of the data files, and to recommend or implement any corrective or preventive actions.
The other options are not what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files in a VM environment that has five guest OS and provides strong isolation, but rather what an administrator might review for other purposes or aspects. Host VM monitor audit logs are records that capture and store the information about the events and activities that occur on the host VM monitor, which is the software or hardware component that manages and controls the VMs on the physical machine. Host VM monitor audit logs can provide information about the performance, status, and configuration of the VMs, but they cannot provide information about the user’s access to data files on the VMs. Guest OS access controls are rules and mechanisms that regulate and restrict the access and permissions of the users and processes to the resources and services on the guest OS. Guest OS access controls can provide a proactive and preventive layer of security by enforcing the principles of least privilege, separation of duties, and need to know. However, guest OS access controls are not what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files, but rather what an administrator must configure and implement to protect the data files. Host VM access controls are rules and mechanisms that regulate and restrict the access and permissions of the users and processes to the VMs on the physical machine. Host VM access controls can provide a granular and dynamic layer of security by defining and assigning the roles and permissions according to the organizational structure and policies. However, host VM access controls are not what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files, but rather what an administrator must configure and implement to protect the VMs.
Which one of these risk factors would be the LEAST important consideration in choosing a building site for a new computer facility?
Vulnerability to crime
Adjacent buildings and businesses
Proximity to an airline flight path
Vulnerability to natural disasters
Proximity to an airline flight path is the least important consideration in choosing a building site for a new computer facility, as it poses the lowest risk factor compared to the other options. Proximity to an airline flight path may cause some noise or interference issues, but it is unlikely to result in a major disaster or damage to the computer facility, unless there is a rare case of a plane crash or a terrorist attack3. Vulnerability to crime, adjacent buildings and businesses, and vulnerability to natural disasters are more important considerations in choosing a building site for a new computer facility, as they can pose significant threats to the physical security, availability, and integrity of the facility and its assets. Vulnerability to crime can expose the facility to theft, vandalism, or sabotage. Adjacent buildings and businesses can affect the fire safety, power supply, or environmental conditions of the facility. Vulnerability to natural disasters can cause the facility to suffer from floods, earthquakes, storms, or fires. References: 3: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, 5th Edition, Chapter 10, page 543.
In which of the following programs is it MOST important to include the collection of security process data?
Quarterly access reviews
Security continuous monitoring
Business continuity testing
Annual security training
Security continuous monitoring is the program in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data. Security process data is the data that reflects the performance, effectiveness, and compliance of the security processes, such as the security policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines. Security process data can include metrics, indicators, logs, reports, and assessments. Security process data can provide several benefits, such as:
Security continuous monitoring is the program in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, because it is the program that involves maintaining the ongoing awareness of the security status, events, and activities of the system. Security continuous monitoring can enable the system to detect and respond to any security issues or incidents in a timely and effective manner, and to adjust and improve the security controls and processes accordingly. Security continuous monitoring can also help the system to comply with the security requirements and standards from the internal or external authorities or frameworks.
The other options are not the programs in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, but rather programs that have other objectives or scopes. Quarterly access reviews are programs that involve reviewing and verifying the user accounts and access rights on a quarterly basis. Quarterly access reviews can ensure that the user accounts and access rights are valid, authorized, and up to date, and that any inactive, expired, or unauthorized accounts or rights are removed or revoked. However, quarterly access reviews are not the programs in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, because they are not focused on the security status, events, and activities of the system, but rather on the user accounts and access rights. Business continuity testing is a program that involves testing and validating the business continuity plan (BCP) and the disaster recovery plan (DRP) of the system. Business continuity testing can ensure that the system can continue or resume its critical functions and operations in case of a disruption or disaster, and that the system can meet the recovery objectives and requirements. However, business continuity testing is not the program in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, because it is not focused on the security status, events, and activities of the system, but rather on the continuity and recovery of the system. Annual security training is a program that involves providing and updating the security knowledge and skills of the system users and staff on an annual basis. Annual security training can increase the security awareness and competence of the system users and staff, and reduce the human errors or risks that might compromise the system security. However, annual security training is not the program in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, because it is not focused on the security status, events, and activities of the system, but rather on the security education and training of the system users and staff.
To prevent inadvertent disclosure of restricted information, which of the following would be the LEAST effective process for eliminating data prior to the media being discarded?
Multiple-pass overwriting
Degaussing
High-level formatting
Physical destruction
The least effective process for eliminating data prior to the media being discarded is high-level formatting. High-level formatting is the process of preparing a storage device, such as a hard disk or a flash drive, for data storage by creating a file system and marking the bad sectors. However, high-level formatting does not erase the data that was previously stored on the device. The data can still be recovered using data recovery tools or forensic techniques. To prevent inadvertent disclosure of restricted information, more secure methods of data sanitization should be used, such as multiple-pass overwriting, degaussing, or physical destruction34. References: 3: Delete Sensitive Data before Discarding Your Media94: Best Practices for Media Destruction10
The use of strong authentication, the encryption of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) on database servers, application security reviews, and the encryption of data transmitted across networks provide
data integrity.
defense in depth.
data availability.
non-repudiation.
Defense in depth is a security strategy that involves applying multiple layers of protection to a system or network to prevent or mitigate attacks. The use of strong authentication, the encryption of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) on database servers, application security reviews, and the encryption of data transmitted across networks are examples of defense in depth measures that can enhance the security of the system or network.
A, C, and D are incorrect because they are not the best terms to describe the security strategy. Data integrity is a property of data that ensures its accuracy, consistency, and validity. Data availability is a property of data that ensures its accessibility and usability. Non-repudiation is a property of data that ensures its authenticity and accountability. While these properties are important for security, they are not the same as defense in depth.
Two companies wish to share electronic inventory and purchase orders in a supplier and client relationship. What is the BEST security solution for them?
Write a Service Level Agreement (SLA) for the two companies.
Set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) between the two companies.
Configure a firewall at the perimeter of each of the two companies.
Establish a File Transfer Protocol (FTP) connection between the two companies.
The best security solution for two companies that wish to share electronic inventory and purchase orders in a supplier and client relationship is to set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) between the two companies. A VPN is a secure and encrypted connection that allows the two companies to exchange data over a public network, such as the internet, as if they were on a private network. A VPN protects the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data, and prevents unauthorized access, interception, or modification by third parties. A VPN also provides authentication, authorization, and accounting of the users and devices that access the data . References: : What is a VPN and how does it work? Your guide to internet privacy and security : What is a VPN?
Which of the following is an attacker MOST likely to target to gain privileged access to a system?
Programs that write to system resources
Programs that write to user directories
Log files containing sensitive information
Log files containing system calls
An attacker is most likely to target programs that write to system resources to gain privileged access to a system. System resources are the hardware and software components that are essential for the operation and functionality of a system, such as the CPU, memory, disk, network, operating system, drivers, libraries, etc. Programs that write to system resources may have higher privileges or permissions than programs that write to user directories or log files. An attacker may exploit vulnerabilities or flaws in these programs to execute malicious code, escalate privileges, or bypass security controls. Programs that write to user directories or log files are less likely to be targeted by an attacker, as they may have lower privileges or permissions, and may not contain sensitive information or system calls. User directories are the folders or locations where users store their personal files or data. Log files are the records of events or activities that occur in a system or application.
What is the ultimate objective of information classification?
To assign responsibility for mitigating the risk to vulnerable systems
To ensure that information assets receive an appropriate level of protection
To recognize that the value of any item of information may change over time
To recognize the optimal number of classification categories and the benefits to be gained from their use
The ultimate objective of information classification is to ensure that information assets receive an appropriate level of protection in accordance with their importance and sensitivity to the organization. Information classification is the process of assigning labels or categories to information based on criteria such as confidentiality, integrity, availability, and value. Information classification helps the organization to identify the risks and threats to the information, and to apply the necessary controls and safeguards to protect it. Information classification also helps the organization to comply with the legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations related to the information12. References: 1: Information Classification - Why it matters?32: ISO 27001 & Information Classification: Free 4-Step Guide4
Which of the following assessment metrics is BEST used to understand a system's vulnerability to potential exploits?
Determining the probability that the system functions safely during any time period
Quantifying the system's available services
Identifying the number of security flaws within the system
Measuring the system's integrity in the presence of failure
Identifying the number of security flaws within the system is the best assessment metric to understand a system’s vulnerability to potential exploits. A security flaw is a weakness or a defect in the system’s design, implementation, or operation that could be exploited by an attacker to compromise the system’s confidentiality, integrity, or availability2. By identifying the number of security flaws within the system, the assessor can measure the system’s vulnerability, which is the degree to which the system is susceptible or exposed to attacks3. Determining the probability that the system functions safely during any time period, quantifying the system’s available services, and measuring the system’s integrity in the presence of failure are not assessment metrics that directly relate to the system’s vulnerability to potential exploits, as they are more concerned with the system’s reliability, availability, and resilience. References: 2: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 8, page 2173: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, 5th Edition, Chapter 8, page 461.
During an audit of system management, auditors find that the system administrator has not been trained. What actions need to be taken at once to ensure the integrity of systems?
A review of hiring policies and methods of verification of new employees
A review of all departmental procedures
A review of all training procedures to be undertaken
A review of all systems by an experienced administrator
During an audit of system management, if auditors find that the system administrator has not been trained, the immediate action that needs to be taken to ensure the integrity of systems is a review of all systems by an experienced administrator. This is to verify that the systems are configured, maintained, and secured properly, and that there are no errors, vulnerabilities, or breaches that could compromise the system’s availability, confidentiality, or integrity. A review of hiring policies, departmental procedures, or training procedures are not urgent actions, as they are more related to the long-term improvement of the system management process, rather than the current state of the systems . References: : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 829. : CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 8, page 267.
Logical access control programs are MOST effective when they are
approved by external auditors.
combined with security token technology.
maintained by computer security officers.
made part of the operating system.
Logical access control programs are most effective when they are made part of the operating system. Logical access control is the process of granting or denying access to information or resources based on the identity, role, or credentials of the user or device3. Logical access control programs, such as authentication, authorization, and auditing mechanisms, can be implemented at different levels of the system, such as the application, the database, or the network. However, the most effective level is the operating system, as it provides the lowest and most comprehensive layer of access control, and can enforce the principle of least privilege and the separation of duties for all users and processes. Approval by external auditors, combination with security token technology, and maintenance by computer security officers are not factors that affect the effectiveness of logical access control programs, as they are more related to the compliance, assurance, and administration of the access control policies. References: 3: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, 5th Edition, Chapter 5, page 247. : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, page 353.
Which of the following is considered best practice for preventing e-mail spoofing?
Spam filtering
Cryptographic signature
Uniform Resource Locator (URL) filtering
Reverse Domain Name Service (DNS) lookup
The best practice for preventing e-mail spoofing is to use cryptographic signatures. E-mail spoofing is a technique that involves forging the sender’s address or identity in an e-mail message, usually to trick the recipient into opening a malicious attachment, clicking on a phishing link, or disclosing sensitive information. Cryptographic signatures are digital signatures that are created by encrypting the e-mail message or a part of it with the sender’s private key, and attaching it to the e-mail message. Cryptographic signatures can be used to verify the authenticity and integrity of the sender and the message, and to prevent e-mail spoofing5 . References: 5: What is Email Spoofing? : How to Prevent Email Spoofing
When constructing an Information Protection Policy (IPP), it is important that the stated rules are necessary, adequate, and
flexible.
confidential.
focused.
achievable.
An Information Protection Policy (IPP) is a document that defines the objectives, scope, roles, responsibilities, and rules for protecting the information assets of an organization. An IPP should be aligned with the business goals and legal requirements, and should be communicated and enforced throughout the organization. When constructing an IPP, it is important that the stated rules are necessary, adequate, and achievable, meaning that they are relevant, sufficient, and realistic for the organization’s context and capabilities34. References: 3: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, page 234: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 1, page 15.
How can a forensic specialist exclude from examination a large percentage of operating system files residing on a copy of the target system?
Take another backup of the media in question then delete all irrelevant operating system files.
Create a comparison database of cryptographic hashes of the files from a system with the same operating system and patch level.
Generate a message digest (MD) or secure hash on the drive image to detect tampering of the media being examined.
Discard harmless files for the operating system, and known installed programs.
A forensic specialist can exclude from examination a large percentage of operating system files residing on a copy of the target system by creating a comparison database of cryptographic hashes of the files from a system with the same operating system and patch level. This method is also known as known file filtering or file signature analysis. It allows the forensic specialist to quickly identify and eliminate the files that are part of the standard operating system installation and focus on the files that are unique or relevant to the investigation. This makes the process of exclusion much faster and more accurate than manually deleting or discarding files12. References: 1: Computer Forensics: Forensic Techniques, Part 1 [Updated 2019]32: Point Checklist: cissp book4
Which of the following is a potential risk when a program runs in privileged mode?
It may serve to create unnecessary code complexity
It may not enforce job separation duties
It may create unnecessary application hardening
It may allow malicious code to be inserted
A potential risk when a program runs in privileged mode is that it may allow malicious code to be inserted. Privileged mode, also known as kernel mode or supervisor mode, is a mode of operation that grants the program full access and control over the hardware and software resources of the system, such as memory, disk, CPU, and devices. A program that runs in privileged mode can perform any action or instruction without any restriction or protection. This can be exploited by an attacker who can inject malicious code into the program, such as a rootkit, a backdoor, or a keylogger, and gain unauthorized access or control over the system . References: : What is Privileged Mode? : Privilege Escalation - OWASP Cheat Sheet Series
Which of the following statements is TRUE for point-to-point microwave transmissions?
They are not subject to interception due to encryption.
Interception only depends on signal strength.
They are too highly multiplexed for meaningful interception.
They are subject to interception by an antenna within proximity.
They are subject to interception by an antenna within proximity. Point-to-point microwave transmissions are line-of-sight media, which means that they can be intercepted by any antenna that is in the direct path of the signal. The interception does not depend on encryption, multiplexing, or signal strength, as long as the antenna is close enough to receive the signal.
Passive Infrared Sensors (PIR) used in a non-climate controlled environment should
reduce the detected object temperature in relation to the background temperature.
increase the detected object temperature in relation to the background temperature.
automatically compensate for variance in background temperature.
detect objects of a specific temperature independent of the background temperature.
Passive Infrared Sensors (PIR) are devices that detect motion by sensing the infrared radiation emitted by objects. In a non-climate controlled environment, the background temperature may vary due to weather, seasons, or other factors. This may affect the sensitivity and accuracy of the PIR sensors, as they may not be able to distinguish between the object and the background. Therefore, the PIR sensors should have a feature that automatically adjusts the threshold or baseline of the background temperature to avoid false alarms or missed detections.
A and B are incorrect because they are not feasible or desirable solutions. Reducing or increasing the detected object temperature in relation to the background temperature would require altering the physical properties of the object or the sensor, which may not be possible or practical. Moreover, this may also affect the performance or functionality of the object or the sensor.
D is incorrect because it is not realistic or reliable. Detecting objects of a specific temperature independent of the background temperature would require the PIR sensors to have a very high resolution and precision, which may not be available or affordable. Moreover, this may also limit the range and scope of the PIR sensors, as they may not be able to detect objects that have different temperatures or emit different amounts of infrared radiation.
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is generating alarms that a user account has over 100 failed login attempts per minute. A sniffer is placed on the network, and a variety of passwords for that user are noted. Which of the following is MOST likely occurring?
A dictionary attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack
A spoofing attack
A backdoor installation
A dictionary attack is a type of brute-force attack that attempts to guess a user’s password by trying a large number of possible words or phrases, often derived from a dictionary or a list of commonly used passwords. A dictionary attack can be detected by an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) if it generates a high number of failed login attempts per minute, as well as a variety of passwords for the same user. A sniffer can capture the network traffic and reveal the passwords being tried by the attacker34. References: 3: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, page 6574: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 6, page 197.
Alternate encoding such as hexadecimal representations is MOST often observed in which of the following forms of attack?
Smurf
Rootkit exploit
Denial of Service (DoS)
Cross site scripting (XSS)
Alternate encoding such as hexadecimal representations is most often observed in cross site scripting (XSS) attacks. XSS is a type of web application attack that involves injecting malicious code or scripts into a web page or a web application, usually through user input fields or parameters. The malicious code or script is then executed by the victim’s browser, and can perform various actions, such as stealing cookies, session tokens, or credentials, redirecting to malicious sites, or displaying fake content. Alternate encoding is a technique that is used by attackers to bypass input validation or filtering mechanisms, and to conceal or obfuscate the malicious code or script. Alternate encoding can use hexadecimal, decimal, octal, binary, or Unicode representations of the characters or symbols in the code or script . References: : What is Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)? : XSS Filter Evasion Cheat Sheet
The BEST method of demonstrating a company's security level to potential customers is
a report from an external auditor.
responding to a customer's security questionnaire.
a formal report from an internal auditor.
a site visit by a customer's security team.
The best method of demonstrating a company’s security level to potential customers is a report from an external auditor, who is an independent and qualified third party that evaluates the company’s security policies, procedures, controls, and practices against a set of standards or criteria, such as ISO 27001, NIST, or COBIT. A report from an external auditor provides an objective and credible assessment of the company’s security posture, and may also include recommendations for improvement or certification . References: : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, page 47. : CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 1, page 29.
Which of the following is the BEST mitigation from phishing attacks?
Network activity monitoring
Security awareness training
Corporate policy and procedures
Strong file and directory permissions
Security awareness training is the process of educating users on the potential threats and risks they may face online, and the best practices and behaviors they should adopt to protect themselves and the organization2. Security awareness training is the best mitigation from phishing attacks, as it can help users recognize and avoid malicious emails, links, or attachments that may compromise their credentials, data, or devices. Network activity monitoring, corporate policy and procedures, and strong file and directory permissions are also important security measures, but they are not as effective as security awareness training in preventing phishing attacks, as they rely on technical controls rather than human factors. References: 2: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, page 33.
Which one of the following transmission media is MOST effective in preventing data interception?
Microwave
Twisted-pair
Fiber optic
Coaxial cable
Fiber optic is the most effective transmission media in preventing data interception, as it uses light signals to transmit data over thin glass or plastic fibers1. Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, which means that they cannot be tapped or eavesdropped by external devices or signals. Fiber optic cables also have a low attenuation rate, which means that they can transmit data over long distances without losing much signal strength or quality. Microwave, twisted-pair, and coaxial cable are less effective transmission media in preventing data interception, as they use electromagnetic waves or electrical signals to transmit data over metal wires or air2. These media are susceptible to interference, noise, or tapping, which can compromise the confidentiality or integrity of the data. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, page 4062: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 4, page 85.
What is the MOST effective countermeasure to a malicious code attack against a mobile system?
Sandbox
Change control
Memory management
Public-Key Infrastructure (PKI)
A sandbox is a security mechanism that isolates a potentially malicious code or application from the rest of the system, preventing it from accessing or modifying any sensitive data or resources1. A sandbox can be implemented at the operating system, application, or network level, and can provide a safe environment for testing, debugging, or executing untrusted code. A sandbox is the most effective countermeasure to a malicious code attack against a mobile system, as it can prevent the code from spreading, stealing, or destroying any information on the device. Change control, memory management, and PKI are not directly related to preventing or mitigating malicious code attacks on mobile systems. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 507.
Including a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) in the design of a computer system is an example of a technique to what?
Interface with the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Improve the quality of security software
Prevent Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
Establish a secure initial state
Including a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) in the design of a computer system is an example of a technique to establish a secure initial state. A TPM is a hardware device that provides cryptographic functions and secure storage for keys, certificates, passwords, and other sensitive data. A TPM can also measure and verify the integrity of the system components, such as the BIOS, boot loader, operating system, and applications, before they are executed. This process is known as trusted boot or measured boot, and it ensures that the system is in a known and trusted state before allowing access to the user or network. A TPM can also enable features such as disk encryption, remote attestation, and platform authentication12. References: 1: What is a Trusted Platform Module (TPM)?32: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Fundamentals4
In a financial institution, who has the responsibility for assigning the classification to a piece of information?
Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
Originator or nominated owner of the information
Department head responsible for ensuring the protection of the information
In a financial institution, the responsibility for assigning the classification to a piece of information belongs to the originator or nominated owner of the information. The originator is the person who creates or generates the information, and the nominated owner is the person who is assigned the accountability and authority for the information by the management. The originator or nominated owner is the best person to determine the value and sensitivity of the information, and to assign the appropriate classification level based on the criteria and guidelines established by the organization. The originator or nominated owner is also responsible for reviewing and updating the classification as needed, and for ensuring that the information is handled and protected according to its classification56. References: 5: Information Classification Policy76: Information Classification and Handling Policy
What is the term commonly used to refer to a technique of authenticating one machine to another by forging packets from a trusted source?
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack
Smurfing
Session redirect
Spoofing
The term commonly used to refer to a technique of authenticating one machine to another by forging packets from a trusted source is spoofing. Spoofing is a type of attack that involves impersonating or masquerading as a legitimate entity, such as a user, a device, or a network, by altering or falsifying the source or destination address of a packet3. Spoofing can be used to bypass authentication, gain unauthorized access, or launch other attacks, such as denial-of-service or man-in-the-middle. Man-in-the-middle, smurfing, and session redirect are not terms that refer to a technique of authenticating one machine to another by forging packets from a trusted source, as they are related to different types of attacks or techniques. Man-in-the-middle is an attack that involves intercepting and modifying the communication between two parties. Smurfing is an attack that involves sending a large number of ICMP echo requests to a network broadcast address, using a spoofed source address of the intended victim. Session redirect is a technique that involves changing the destination address of a packet to redirect it to a different location. References: 3: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, 5th Edition, Chapter 4, page 199. : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, page 423.
What is the MOST important purpose of testing the Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)?
Evaluating the efficiency of the plan
Identifying the benchmark required for restoration
Validating the effectiveness of the plan
Determining the Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
The most important purpose of testing the Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) is to validate the effectiveness of the plan. A DRP is a document that outlines the procedures and steps to be followed in the event of a disaster that disrupts the normal operations of an organization. A DRP aims to minimize the impact of the disaster, restore the critical functions and systems, and resume the normal operations as soon as possible. Testing the DRP is essential to ensure that the plan is feasible, reliable, and up-to-date. Testing the DRP can reveal any errors, gaps, or weaknesses in the plan, and provide feedback and recommendations for improvement. Testing the DRP can also increase the confidence and readiness of the staff, and ensure compliance with the regulatory and contractual requirements97. References: 9: What Is Disaster Recovery Testing and Why Is It Important?107: Disaster Recovery Plan Testing in IT
What is the foundation of cryptographic functions?
Encryption
Cipher
Hash
Entropy
The foundation of cryptographic functions is entropy. Entropy is a measure of the randomness or unpredictability of a system or a process. Entropy is essential for cryptographic functions, such as encryption, decryption, hashing, or key generation, as it provides the security and the strength of the cryptographic algorithms and keys. Entropy can be derived from various sources, such as physical phenomena, user input, or software applications. Entropy can also be quantified in terms of bits, where higher entropy means higher randomness and higher security. Encryption, cipher, and hash are not the foundation of cryptographic functions, although they are related or important concepts or techniques. Encryption is the process of transforming plaintext or cleartext into ciphertext or cryptogram, using a cryptographic algorithm and a key, to protect the confidentiality and the integrity of the data. Encryption can be symmetric or asymmetric, depending on whether the same or different keys are used for encryption and decryption. Cipher is another term for a cryptographic algorithm, which is a mathematical function that performs encryption or decryption. Cipher can be classified into various types, such as substitution, transposition, stream, or block, depending on how they operate on the data. Hash is the process of generating a fixed-length and unique output, called a hash or a digest, from a variable-length and arbitrary input, using a one-way function, to verify the integrity and the authenticity of the data. Hash can be used for various purposes, such as digital signatures, message authentication codes, or password storage.
What is the second step in the identity and access provisioning lifecycle?
Provisioning
Review
Approval
Revocation
The identity and access provisioning lifecycle is the process of managing the creation, modification, and termination of user accounts and access rights in an organization. The second step in this lifecycle is approval, which means that the identity and access requests must be authorized by the appropriate managers or administrators before they are implemented. Approval ensures that the principle of least privilege is followed and that only authorized users have access to the required resources.
What does a Synchronous (SYN) flood attack do?
Forces Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connections into a reset state
Establishes many new Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connections
Empties the queue of pending Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) requests
Exceeds the limits for new Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connections
A SYN flood attack does exceed the limits for new TCP/IP connections. A SYN flood attack is a type of denial-of-service attack that sends a large number of SYN packets to a server, without completing the TCP three-way handshake. The server allocates resources for each SYN packet and waits for the final ACK packet, which never arrives. This consumes the server’s memory and processing power, and prevents it from accepting new legitimate connections. The other options are not accurate descriptions of what a SYN flood attack does. References: SYN flood - Wikipedia; SYN flood DDoS attack | Cloudflare.
Which of the following is a common characteristic of privacy?
Provision for maintaining an audit trail of access to the private data
Notice to the subject of the existence of a database containing relevant credit card data
Process for the subject to inspect and correct personal data on-site
Database requirements for integration of privacy data
A common characteristic of privacy is notice to the subject of the existence of a database containing relevant credit card data. Privacy is the right or the expectation of an individual or a group to control or limit the collection, use, disclosure, or retention of their personal or sensitive information by others. Privacy can involve various principles or tenets that are shared across different regulatory standards or frameworks, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PIPEDA. One of the common privacy principles or tenets is notice, which requires that the data subject or the individual whose information is collected or processed should be informed or notified of the following aspects:
Notice can provide some benefits for privacy, such as enhancing the transparency and the accountability of the data collection or processing activities, respecting the consent and the preferences of the data subject, and supporting the compliance and the enforcement of the privacy laws or regulations. Provision for maintaining an audit trail of access to the private data, process for the subject to inspect and correct personal data on-site, and database requirements for integration of privacy data are not common characteristics of privacy, although they may be related or important aspects of privacy. Provision for maintaining an audit trail of access to the private data is a technique that involves recording and storing the logs or the records of the events or the activities that occur on a database or a system that contains private data, such as who accessed, modified, or deleted the data, when, where, how, and why. Provision for maintaining an audit trail of access to the private data can provide some benefits for privacy, such as enhancing the visibility and the traceability of the data access or processing activities, preventing or detecting any unauthorized or improper access or processing, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. However, provision for maintaining an audit trail of access to the private data is not a common characteristic of privacy, as it is not a principle or a tenet that is shared across different regulatory standards or frameworks, and it may vary depending on the type or the nature of the private data. Process for the subject to inspect and correct personal data on-site is a technique that involves providing a mechanism or a procedure for the data subject to access and verify their personal data that is stored or processed on a database or a system, and to request or make any changes or corrections if needed, such as updating their name, address, or email. Process for the subject to inspect and correct personal data on-site can provide some benefits for privacy, such as enhancing the accuracy and the reliability of the personal data, respecting the rights and the interests of the data subject, and supporting the compliance and the enforcement of the privacy laws or regulations. However, process for the subject to inspect and correct personal data on-site is not a common characteristic of privacy, as it is not a principle or a tenet that is shared across different regulatory standards or frameworks, and it may vary depending on the type or the nature of the personal data. Database requirements for integration of privacy data are the specifications or the criteria that a database or a system that contains or processes privacy data should meet or comply with, such as the design, the architecture, the functionality, or the security of the database or the system. Database requirements for integration of privacy data can provide some benefits for privacy, such as enhancing the performance and the functionality of the database or the system, preventing or mitigating some types of attacks or vulnerabilities, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. However, database requirements for integration of privacy data are not a common characteristic of privacy, as they are not a principle or a tenet that is shared across different regulatory standards or frameworks, and they may vary depending on the type or the nature of the privacy data.
A company receives an email threat informing of an Imminent Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack
targeting its web application, unless ransom is paid. Which of the following techniques BEST addresses that threat?
Deploying load balancers to distribute inbound traffic across multiple data centers
Set Up Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) to filter out malicious traffic
Implementing reverse web-proxies to validate each new inbound connection
Coordinate with and utilize capabilities within Internet Service Provider (ISP)
The best technique to address the threat of an imminent DDoS attack targeting a web application is to coordinate with and utilize the capabilities within the ISP. A DDoS attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, service, or network by overwhelming the target or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of Internet traffic. A DDoS attack can cause severe damage to the availability, performance, and reputation of the web application, as well as incur financial losses and legal liabilities. Therefore, it is important to have a DDoS mitigation strategy in place to prevent or minimize the impact of such attacks. One of the most effective ways to mitigate DDoS attacks is to leverage the capabilities of the ISP, as they have more resources, bandwidth, and expertise to handle large volumes of traffic and filter out malicious packets. The ISP can also provide additional services such as traffic monitoring, alerting, reporting, and analysis, as well as assist with the investigation and prosecution of the attackers. The ISP can also work with other ISPs and network operators to coordinate the response and share information about the attack. The other options are not the best techniques to address the threat of an imminent DDoS attack, as they may not be sufficient, timely, or scalable to handle the attack. Deploying load balancers, setting up web application firewalls, and implementing reverse web-proxies are some of the measures that can be taken at the application level to improve the resilience and security of the web application, but they may not be able to cope with the magnitude and complexity of a DDoS attack, especially if the attack targets the network layer or the infrastructure layer. Moreover, these measures may require more time, cost, and effort to implement and maintain, and may not be feasible to deploy in a short notice. References: What is a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack?; What is a DDoS Attack? DDoS Meaning, Definition & Types | Fortinet; Denial-of-service attack - Wikipedia.
What is the PRIMARY goal of fault tolerance?
Elimination of single point of failure
Isolation using a sandbox
Single point of repair
Containment to prevent propagation
The primary goal of fault tolerance is to eliminate single point of failure, which is any component or resource that is essential for the operation or the functionality of a system or a network, and that can cause the entire system or network to fail or malfunction if it fails or malfunctions itself. Fault tolerance is the ability of a system or a network to suffer a fault but continue to operate, by adding redundant or backup components or resources that can take over or replace the failed or malfunctioning component or resource, without affecting the performance or the quality of the system or network. Fault tolerance can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the availability and the reliability of the system or network, preventing or mitigating some types of attacks or vulnerabilities, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. Fault tolerance can be implemented using various methods or techniques, such as:
Isolation using a sandbox, single point of repair, and containment to prevent propagation are not the primary goals of fault tolerance, although they may be related or possible outcomes or benefits of fault tolerance. Isolation using a sandbox is a security concept or technique that involves executing or testing a program or a code in a separate or a restricted environment, such as a virtual machine or a container, to protect the system or the network from any potential harm or damage that the program or the code may cause, such as malware, viruses, worms, or trojans. Isolation using a sandbox can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the confidentiality and the integrity of the system or the network, preventing or mitigating some types of attacks or vulnerabilities, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. However, isolation using a sandbox is not the primary goal of fault tolerance, as it is not a method or a technique of adding redundant or backup components or resources to the system or the network, and it does not address the availability or the reliability of the system or the network. Single point of repair is a security concept or technique that involves identifying or locating the component or the resource that is responsible for the failure or the malfunction of the system or the network, and that can restore or recover the system or the network if it is repaired or replaced, such as a disk, a server, or a router. Single point of repair can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the availability and the reliability of the system or the network, preventing or mitigating some types of attacks or vulnerabilities, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. However, single point of repair is not the primary goal of fault tolerance, as it is not a method or a technique of adding redundant or backup components or resources to the system or the network, and it does not prevent or eliminate the failure or the malfunction of the system or the network. Containment to prevent propagation is a security concept or technique that involves isolating or restricting the component or the resource that is affected or infected by a fault or an attack, such as a malware, a virus, a worm, or a trojan, to prevent or mitigate the spread or the transmission of the fault or the attack to other components or resources of the system or the network, such as by disconnecting, disabling, or quarantining the component or the resource. Containment to prevent propagation can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the confidentiality and the integrity of the system or the network, preventing or mitigating some types of attacks or vulnerabilities, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. However, containment to prevent propagation is not the primary goal of fault tolerance, as it is not a method or a technique of adding redundant or backup components or resources to the system or the network, and it does not ensure or improve the performance or the quality of the system or the network.
The security accreditation task of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process is completed at the end of which phase?
System acquisition and development
System operations and maintenance
System initiation
System implementation
The security accreditation task of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process is completed at the end of the system implementation phase. The SDLC is a framework that describes the stages and activities involved in the development, deployment, and maintenance of a system. The SDLC typically consists of the following phases: system initiation, system acquisition and development, system implementation, system operations and maintenance, and system disposal. The security accreditation task is the process of formally authorizing a system to operate in a specific environment, based on the security requirements, controls, and risks. The security accreditation task is part of the security certification and accreditation (C&A) process, which also includes the security certification task, which is the process of technically evaluating and testing the security controls and functionality of a system. The security accreditation task is completed at the end of the system implementation phase, which is the phase where the system is installed, configured, integrated, and tested in the target environment. The security accreditation task involves reviewing the security certification results and documentation, such as the security plan, the security assessment report, and the plan of action and milestones, and making a risk-based decision to grant, deny, or conditionally grant the authorization to operate (ATO) the system. The security accreditation task is usually performed by a senior official, such as the authorizing official (AO) or the designated approving authority (DAA), who has the authority and responsibility to accept the security risks and approve the system operation. The security accreditation task is not completed at the end of the system acquisition and development, system operations and maintenance, or system initiation phases. The system acquisition and development phase is the phase where the system requirements, design, and development are defined and executed, and the security controls are selected and implemented. The system operations and maintenance phase is the phase where the system is used and supported in the operational environment, and the security controls are monitored and updated. The system initiation phase is the phase where the system concept, scope, and objectives are established, and the security categorization and planning are performed.
What is the expected outcome of security awareness in support of a security awareness program?
Awareness activities should be used to focus on security concerns and respond to those concerns
accordingly
Awareness is not an activity or part of the training but rather a state of persistence to support the program
Awareness is training. The purpose of awareness presentations is to broaden attention of security.
Awareness is not training. The purpose of awareness presentation is simply to focus attention on security.
The expected outcome of security awareness in support of a security awareness program is that awareness is not training, but the purpose of awareness presentation is simply to focus attention on security. A security awareness program is a set of activities and initiatives that aim to raise the awareness and understanding of the security policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines among the employees, contractors, partners, or customers of an organization. A security awareness program can provide some benefits for security, such as improving the knowledge and the skills of the parties, changing the attitudes and the behaviors of the parties, and empowering the parties to make informed and secure decisions regarding the security activities. A security awareness program can involve various methods and techniques, such as posters, newsletters, emails, videos, quizzes, games, or rewards. Security awareness is not training, but the purpose of awareness presentation is simply to focus attention on security. Security awareness is the state or condition of being aware or conscious of the security issues and incidents, and the importance and implications of security. Security awareness is not the same as training, as it does not aim to teach or instruct the parties on how to perform specific tasks or functions related to security, but rather to inform and remind the parties of the security policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines, and their roles and responsibilities in complying and supporting them. The purpose of awareness presentation is simply to focus attention on security, as it does not provide detailed or comprehensive information or guidance on security, but rather to highlight or emphasize the key or relevant points or messages of security, and to motivate or persuade the parties to pay attention and care about security. Awareness activities should be used to focus on security concerns and respond to those concerns accordingly, awareness is not an activity or part of the training but rather a state of persistence to support the program, and awareness is training, the purpose of awareness presentations is to broaden attention of security are not the expected outcomes of security awareness in support of a security awareness program, although they may be related or possible statements. Awareness activities should be used to focus on security concerns and respond to those concerns accordingly is a statement that describes one of the possible objectives or functions of awareness activities, but it is not the expected outcome of security awareness, as it does not define or differentiate security awareness from training, and it does not specify the purpose of awareness presentation. Awareness is not an activity or part of the training but rather a state of persistence to support the program is a statement that partially defines security awareness, but it is not the expected outcome of security awareness, as it does not differentiate security awareness from training, and it does not specify the purpose of awareness presentation. Awareness is training, the purpose of awareness presentations is to broaden attention of security is a statement that contradicts the definition of security awareness, as it confuses security awareness with training, and it does not specify the purpose of awareness presentation.
Which of the following is the MOST important part of an awareness and training plan to prepare employees for emergency situations?
Having emergency contacts established for the general employee population to get information
Conducting business continuity and disaster recovery training for those who have a direct role in the recovery
Designing business continuity and disaster recovery training programs for different audiences
Publishing a corporate business continuity and disaster recovery plan on the corporate website
The most important part of an awareness and training plan to prepare employees for emergency situations is to design business continuity and disaster recovery training programs for different audiences. This means that the training content, format, frequency, and delivery methods should be tailored to the specific needs, roles, and responsibilities of the target audience, such as senior management, business unit managers, IT staff, recovery team members, or general employees. Different audiences may have different levels of awareness, knowledge, skills, and involvement in the business continuity and disaster recovery processes, and therefore require different types of training to ensure they are adequately prepared and informed. Designing business continuity and disaster recovery training programs for different audiences can help to increase the effectiveness, efficiency, and consistency of the training, as well as the engagement, motivation, and retention of the learners. Having emergency contacts established for the general employee population to get information, conducting business continuity and disaster recovery training for those who have a direct role in the recovery, and publishing a corporate business continuity and disaster recovery plan on the corporate website are all important parts of an awareness and training plan, but they are not as important as designing business continuity and disaster recovery training programs for different audiences. Having emergency contacts established for the general employee population to get information can help to provide timely and accurate communication and guidance during an emergency situation, but it does not necessarily prepare the employees for their roles and responsibilities before, during, and after the emergency. Conducting business continuity and disaster recovery training for those who have a direct role in the recovery can help to ensure that they are competent and confident to perform their tasks and duties in the event of a disruption, but it does not address the needs and expectations of other audiences who may also be affected by or involved in the business continuity and disaster recovery processes. Publishing a corporate business continuity and disaster recovery plan on the corporate website can help to make the plan accessible and transparent to the stakeholders, but it does not guarantee that the plan is understood, followed, or updated by the employees.
Which of the following is the MOST effective practice in managing user accounts when an employee is terminated?
Implement processes for automated removal of access for terminated employees.
Delete employee network and system IDs upon termination.
Manually remove terminated employee user-access to all systems and applications.
Disable terminated employee network ID to remove all access.
The most effective practice in managing user accounts when an employee is terminated is to implement processes for automated removal of access for terminated employees. This practice can ensure that the access rights of the terminated employee are revoked as soon as possible, preventing any unauthorized or malicious use of the account. Automated removal of access can be achieved by using software tools or scripts that can disable or delete the account, remove it from any groups or roles, and revoke any permissions or privileges associated with the account. Automated removal of access can also reduce the human errors or delays that may occur in manual processes, and provide an audit trail of the actions taken. Deleting employee network and system IDs upon termination, manually removing terminated employee user-access to all systems and applications, and disabling terminated employee network ID to remove all access are all possible ways to manage user accounts when an employee is terminated, but they are not as effective as automated removal of access. Deleting employee network and system IDs upon termination may cause problems with data retention, backup, or recovery, and may not remove all traces of the account from the systems. Manually removing terminated employee user-access to all systems and applications may be time-consuming, error-prone, or incomplete, and may depend on the cooperation and coordination of different administrators or departments. Disabling terminated employee network ID to remove all access may not be sufficient, as the account may still exist and be reactivated, or may have access to some resources that are not controlled by the network ID.
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack on a syslog server exploits weakness in which of the following protocols?
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
A DoS attack on a syslog server exploits weakness in TCP and UDP protocols. A syslog server is a server that collects and stores log messages from various devices on a network, such as routers, switches, firewalls, or servers. A syslog server uses either TCP or UDP protocols to receive log messages from the devices. A DoS attack on a syslog server can exploit the weakness of these protocols by sending a large volume of fake or malformed log messages to the syslog server, causing it to crash or become unresponsive. The other protocols are not relevant to a syslog server or a DoS attack. References: Denial-of-Service Attacks: History, Techniques & Prevention; What is a syslog server? | SolarWinds MSP.
Why is planning in Disaster Recovery (DR) an interactive process?
It details off-site storage plans
It identifies omissions in the plan
It defines the objectives of the plan
It forms part of the awareness process
Planning in Disaster Recovery (DR) is an interactive process because it identifies omissions in the plan. DR planning is the process of developing and implementing procedures and processes to ensure that an organization can quickly resume its critical functions after a disaster or a disruption. DR planning involves various steps, such as conducting a risk assessment, performing a business impact analysis, defining the recovery objectives and strategies, designing and developing the DR plan, testing and validating the DR plan, and maintaining and updating the DR plan. DR planning is an interactive process because it requires constant feedback and communication among the stakeholders, such as the management, the employees, the customers, the suppliers, and the regulators. DR planning also requires regular reviews and evaluations of the plan to identify and address any gaps, errors, or changes that may affect the effectiveness or the feasibility of the plan. DR planning is not an interactive process because it details off-site storage plans, defines the objectives of the plan, or forms part of the awareness process, although these may be related or important aspects of DR planning. Detailing off-site storage plans is a technique that involves storing copies of the essential data, documents, or equipment at a secure and remote location, such as a vault, a warehouse, or a cloud service. Detailing off-site storage plans can provide some benefits for DR planning, such as enhancing the availability and the integrity of the data, documents, or equipment, preventing data loss or corruption, and facilitating the recovery and the restoration process. However, detailing off-site storage plans is not the reason why DR planning is an interactive process, as it is not a feedback or a communication mechanism, and it does not identify or address any omissions in the plan. Defining the objectives of the plan is a step that involves establishing the goals and the priorities of the DR plan, such as the recovery time objective (RTO), the recovery point objective (RPO), the maximum tolerable downtime (MTD), or the minimum operating level (MOL). Defining the objectives of the plan can provide some benefits for DR planning, such as aligning the DR plan with the business needs and expectations, setting the scope and the boundaries of the DR plan, and measuring the performance and the outcomes of the DR plan. However, defining the objectives of the plan is not the reason why DR planning is an interactive process, as it is not a feedback or a communication mechanism, and it does not identify or address any omissions in the plan. Forming part of the awareness process is a technique that involves educating and informing the stakeholders about the DR plan, such as the purpose, the scope, the roles, the responsibilities, or the procedures of the DR plan. Forming part of the awareness process can provide some benefits for DR planning, such as improving the knowledge and the skills of the stakeholders, changing the attitudes and the behaviors of the stakeholders, and empowering the stakeholders to make informed and secure decisions regarding the DR plan. However, forming part of the awareness process is not the reason why DR planning is an interactive process, as it is not a feedback or a communication mechanism, and it does not identify or address any omissions in the plan.
What protocol is often used between gateway hosts on the Internet?
Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP)
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a protocol that is often used between gateway hosts on the Internet. A gateway host is a network device that connects two or more different networks, such as a router or a firewall. BGP is a routing protocol that exchanges routing information between autonomous systems (ASes), which are groups of networks under a single administrative control. BGP is used to determine the best path to reach a destination network on the Internet, based on various factors such as hop count, bandwidth, latency, and policy. BGP is also used to implement interdomain routing policies, such as traffic engineering, load balancing, and security. BGP is the de facto standard for Internet routing and is widely deployed by Internet service providers (ISPs) and large enterprises. The other options are not protocols that are often used between gateway hosts on the Internet. Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) is an obsolete protocol that was used to exchange routing information between ASes before BGP. Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a protocol that is used to exchange routing information within an AS, not between ASes. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a protocol that is used to send error and control messages between hosts and routers, not to exchange routing information. References: Border Gateway Protocol - Wikipedia; What is Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)? - Definition from WhatIs.com; What is BGP? | How BGP Routing Works | Cloudflare.
A security practitioner is tasked with securing the organization’s Wireless Access Points (WAP). Which of these is the MOST effective way of restricting this environment to authorized users?
Enable Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) encryption on the wireless access point
Disable the broadcast of the Service Set Identifier (SSID) name
Change the name of the Service Set Identifier (SSID) to a random value not associated with the organization
Create Access Control Lists (ACL) based on Media Access Control (MAC) addresses
The most effective way of restricting the wireless environment to authorized users is to enable Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) encryption on the wireless access point. WPA2 is a security protocol that provides confidentiality, integrity, and authentication for wireless networks. WPA2 uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to encrypt the data transmitted over the wireless network, and prevents unauthorized users from intercepting or modifying the traffic. WPA2 also uses a pre-shared key (PSK) or an Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to authenticate the users who want to join the wireless network, and prevents unauthorized users from accessing the network resources. WPA2 is the current standard for wireless security and is widely supported by most wireless devices. The other options are not as effective as WPA2 encryption for restricting the wireless environment to authorized users. Disabling the broadcast of the SSID name is a technique that hides the name of the wireless network from being displayed on the list of available networks, but it does not prevent unauthorized users from discovering the name by using a wireless sniffer or a brute force tool. Changing the name of the SSID to a random value not associated with the organization is a technique that reduces the likelihood of being targeted by an attacker who is looking for a specific network, but it does not prevent unauthorized users from joining the network if they know the name and the password. Creating ACLs based on MAC addresses is a technique that allows or denies access to the wireless network based on the physical address of the wireless device, but it does not prevent unauthorized users from spoofing a valid MAC address or bypassing the ACL by using a wireless bridge or a repeater. References: Secure Wireless Access Points - Fortinet; Configure Wireless Security Settings on a WAP - Cisco; Best WAP of 2024 | TechRadar.
When determining who can accept the risk associated with a vulnerability, which of the following is the MOST important?
Countermeasure effectiveness
Type of potential loss
Incident likelihood
Information ownership
Information ownership is the most important factor when determining who can accept the risk associated with a vulnerability. Information ownership is the concept that assigns the roles and responsibilities for the creation, maintenance, protection, and disposal of information assets within an organization. Information owners are the individuals or entities who have the authority and accountability for the information assets, and who can make decisions regarding the information lifecycle, classification, access, and usage. Information owners are also responsible for accepting or rejecting the risk associated with the information assets, and for ensuring that the risk is managed and communicated appropriately. Information owners can delegate some of their responsibilities to other roles, such as information custodians, information users, or information stewards, but they cannot delegate their accountability for the information assets and the associated risk. Countermeasure effectiveness, type of potential loss, and incident likelihood are not the most important factors when determining who can accept the risk associated with a vulnerability, although they are relevant or useful factors. Countermeasure effectiveness is the measure of how well a security control reduces or eliminates the risk. Countermeasure effectiveness can help to evaluate the cost-benefit and performance of the security control, and to determine the level of residual risk. Type of potential loss is the measure of the adverse impact or consequence that can result from a risk event. Type of potential loss can include financial, operational, reputational, legal, or strategic losses. Type of potential loss can help to assess the severity and priority of the risk, and to justify the investment and implementation of the security control. Incident likelihood is the measure of the probability or frequency of a risk event occurring. Incident likelihood can be influenced by various factors, such as the threat capability, the vulnerability exposure, the environmental conditions, or the historical data. Incident likelihood can help to estimate the level and trend of the risk, and to select the appropriate risk response and security control.
Assessing a third party’s risk by counting bugs in the code may not be the best measure of an attack surface
within the supply chain.
Which of the following is LEAST associated with the attack surface?
Input protocols
Target processes
Error messages
Access rights
Error messages are not part of the attack surface, which is the sum of all the points where an attacker can try to enter or extract data from a system. Error messages are the output of the system when something goes wrong, and they can reveal useful information to an attacker, such as the system version, configuration, or vulnerabilities. However, they are not directly associated with the attack surface. Input protocols, target processes, and access rights are all factors that can affect the attack surface, as they determine how the system interacts with the external environment and what resources are exposed or protected. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5: Security Engineering, page 587; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 375.
The core component of Role Based Access Control (RBAC) must be constructed of defined data elements.
Which elements are required?
Users, permissions, operations, and protected objects
Roles, accounts, permissions, and protected objects
Users, roles, operations, and protected objects
Roles, operations, accounts, and protected objects
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is a model of access control that assigns permissions to users based on their roles, rather than their individual identities. The core component of RBAC is the role, which is a collection of permissions that define what operations a user can perform on what protected objects. The required data elements for RBAC are:
What capability would typically be included in a commercially available software package designed for access control?
Password encryption
File encryption
Source library control
File authentication
Password encryption is a capability that would typically be included in a commercially available software package designed for access control. Password encryption is a technique that transforms the plain text passwords into unreadable ciphertexts, using a cryptographic algorithm and a key. Password encryption can help to protect the passwords from unauthorized access, disclosure, or modification, as well as to prevent password cracking or guessing attacks. File encryption, source library control, and file authentication are not capabilities related to access control, but to data protection, configuration management, and data integrity, respectively. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5: Security Engineering, page 605; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 386.
Which of the following provides the MOST comprehensive filtering of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) traffic?
Application proxy
Port filter
Network boundary router
Access layer switch
An application proxy provides the most comprehensive filtering of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) traffic. P2P traffic is a type of network traffic that involves direct communication and file sharing between peers, without the need for a central server. P2P traffic can be used for legitimate purposes, such as distributed computing, content delivery, or collaboration, but it can also be used for illegal or malicious purposes, such as piracy, malware distribution, or denial-of-service attacks. P2P traffic can also consume a lot of bandwidth and degrade the performance of other network applications. Therefore, it may be desirable to filter or block P2P traffic on a network. An application proxy is a type of firewall that operates at the application layer of the OSI model, and acts as an intermediary between the client and the server. An application proxy can inspect the content and the behavior of the network traffic, and apply granular filtering rules based on the specific application protocol, such as HTTP, FTP, or SMTP. An application proxy can also perform authentication, encryption, caching, and logging functions. An application proxy can provide the most comprehensive filtering of P2P traffic, as it can identify and block the P2P applications and protocols, regardless of the port number or the payload. An application proxy can also prevent P2P traffic from bypassing the firewall by using encryption or tunneling techniques. The other options are not as effective as an application proxy for filtering P2P traffic. A port filter is a type of firewall that operates at the transport layer of the OSI model, and blocks or allows traffic based on the source and destination port numbers. A port filter cannot inspect the content or the behavior of the traffic, and cannot distinguish between different applications that use the same port number. A port filter can also be easily evaded by P2P traffic that uses random or well-known port numbers, such as port 80 for HTTP. A network boundary router is a router that connects a network to another network, such as the Internet. A network boundary router can perform some basic filtering functions, such as access control lists (ACLs) or packet filtering, but it cannot inspect the content or the behavior of the traffic, and cannot apply granular filtering rules based on the specific application protocol. A network boundary router can also be easily evaded by P2P traffic that uses encryption or tunneling techniques. An access layer switch is a switch that connects end devices, such as PCs, printers, or servers, to the network. An access layer switch can perform some basic filtering functions, such as MAC address filtering or port security, but it cannot inspect the content or the behavior of the traffic, and cannot apply granular filtering rules based on the specific application protocol. An access layer switch can also be easily evaded by P2P traffic that uses encryption or tunneling techniques. References: Why and how to control peer-to-peer traffic | Network World; Detection and Management of P2P Traffic in Networks using Artificial Neural Networksa | Journal of Network and Systems Management; Blocking P2P And File Sharing - Cisco Meraki Documentation.
As part of the security assessment plan, the security professional has been asked to use a negative testing strategy on a new website. Which of the following actions would be performed?
Use a web scanner to scan for vulnerabilities within the website.
Perform a code review to ensure that the database references are properly addressed.
Establish a secure connection to the web server to validate that only the approved ports are open.
Enter only numbers in the web form and verify that the website prompts the user to enter a valid input.
A negative testing strategy is a type of software testing that aims to verify how the system handles invalid or unexpected inputs, errors, or conditions. A negative testing strategy can help identify potential bugs, vulnerabilities, or failures that could compromise the functionality, security, or usability of the system. One example of a negative testing strategy is to enter only numbers in a web form that expects a text input, such as a name or an email address, and verify that the website prompts the user to enter a valid input. This can help ensure that the website has proper input validation and error handling mechanisms, and that it does not accept or process any malicious or malformed data. A web scanner, a code review, and a secure connection are not examples of a negative testing strategy, as they do not involve providing invalid or unexpected inputs to the system.
At a MINIMUM, audits of permissions to individual or group accounts should be scheduled
annually
to correspond with staff promotions
to correspond with terminations
continually
The minimum frequency for audits of permissions to individual or group accounts is continually. Audits of permissions are the processes of reviewing and verifying the user accounts and access rights on a system or a network, and ensuring that they are appropriate, necessary, and compliant with the policies and standards. Audits of permissions can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the accuracy and the reliability of the user accounts and access rights, identifying and removing any excessive, obsolete, or unauthorized access rights, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. Audits of permissions should be performed continually, which means that they should be conducted on a regular and consistent basis, without any interruption or delay. Continual audits of permissions can help to maintain the security and the integrity of the system or the network, by detecting and addressing any changes or issues that may affect the user accounts and access rights, such as role changes, transfers, promotions, or terminations. Continual audits of permissions can also help to ensure the effectiveness and the feasibility of the audit process, by reducing the workload and the complexity of the audit tasks, and by providing timely and relevant feedback and results. Annually, to correspond with staff promotions, and to correspond with terminations are not the minimum frequencies for audits of permissions to individual or group accounts, although they may be related or possible frequencies. Annually means that the audits of permissions are performed once a year, which may not be sufficient or adequate to maintain the security and the integrity of the system or the network, as the user accounts and access rights may change or become outdated more frequently than that, due to various factors, such as role changes, transfers, promotions, or terminations. Annually audits of permissions may also increase the workload and the complexity of the audit process, as they may involve a large number of user accounts and access rights to review and verify, and they may not provide timely and relevant feedback and results. To correspond with staff promotions means that the audits of permissions are performed whenever a staff member is promoted to a higher or a different position within the organization, which may affect their user accounts and access rights. To correspond with staff promotions audits of permissions can help to ensure that the user accounts and access rights are aligned with the current roles or functions of the staff members, and that they follow the principle of least privilege. However, to correspond with staff promotions audits of permissions may not be sufficient or adequate to maintain the security and the integrity of the system or the network, as the user accounts and access rights may change or become outdated due to other factors, such as role changes, transfers, or terminations, and they may not be performed on a regular and consistent basis. To correspond with terminations means that the audits of permissions are performed whenever a staff member leaves the organization, which may affect their user accounts and access rights. To correspond with terminations audits of permissions can help to ensure that the user accounts and access rights are revoked or removed from the system or the network, and that they prevent any unauthorized or improper access or use. However, to correspond with terminations audits of permissions may not be sufficient or adequate to maintain the security and the integrity of the system or the network, as the user accounts and access rights may change or become outdated due to other factors, such as role changes, transfers, or promotions, and they may not be performed on a regular and consistent basis.
What MUST each information owner do when a system contains data from multiple information owners?
Provide input to the Information System (IS) owner regarding the security requirements of the data
Review the Security Assessment report (SAR) for the Information System (IS) and authorize the IS to
operate.
Develop and maintain the System Security Plan (SSP) for the Information System (IS) containing the data
Move the data to an Information System (IS) that does not contain data owned by other information
owners
The information owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility for the data stored, processed, or transmitted by an Information System (IS). When a system contains data from multiple information owners, each information owner must provide input to the IS owner regarding the security requirements of the data, such as the classification, sensitivity, retention, and disposal of the data. The IS owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility for the operation and maintenance of the IS. The IS owner must ensure that the security requirements of the data are met and that the IS complies with the applicable laws and regulations. Reviewing the Security Assessment Report (SAR), developing and maintaining the System Security Plan (SSP), and moving the data to another IS are not the responsibilities of the information owner, but they may involve the information owner’s participation or approval. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, page 48; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, page 40.
Due to system constraints, a group of system administrators must share a high-level access set of credentials.
Which of the following would be MOST appropriate to implement?
Increased console lockout times for failed logon attempts
Reduce the group in size
A credential check-out process for a per-use basis
Full logging on affected systems
The most appropriate measure to implement when a group of system administrators must share a high-level access set of credentials due to system constraints is a credential check-out process for a per-use basis. This means that the system administrators must request and obtain the credentials from a secure source each time they need to use them, and return them after they finish their tasks. This can help to reduce the risk of unauthorized access, misuse, or compromise of the credentials, as well as to enforce accountability and traceability of the system administrators’ actions. Increasing console lockout times, reducing the group size, and enabling full logging are not as effective as a credential check-out process, as they do not address the root cause of the problem, which is the sharing of the credentials. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5: Security Engineering, page 633; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 412.
An Information Technology (IT) professional attends a cybersecurity seminar on current incident response methodologies.
What code of ethics canon is being observed?
Provide diligent and competent service to principals
Protect society, the commonwealth, and the infrastructure
Advance and protect the profession
Act honorable, honesty, justly, responsibly, and legally
Attending a cybersecurity seminar to learn about current incident response methodologies aligns with the ethical canon of advancing and protecting the profession. It involves enhancing one’s knowledge and skills, contributing to the growth and integrity of the field, and staying abreast of the latest developments and best practices in information security. References: ISC² Code of Ethics
An organization adopts a new firewall hardening standard. How can the security professional verify that the technical staff correct implemented the new standard?
Perform a compliance review
Perform a penetration test
Train the technical staff
Survey the technical staff
A compliance review is a process of checking whether the systems and processes meet the established standards, policies, and regulations. A compliance review can help to verify that the technical staff has correctly implemented the new firewall hardening standard, as well as to identify and correct any deviations or violations. A penetration test, a training session, or a survey are not as effective as a compliance review, as they may not cover all the aspects of the firewall hardening standard or provide sufficient evidence of compliance. References: CISSP Exam Outline
Which of the following would BEST support effective testing of patch compatibility when patches are applied to an organization’s systems?
Standardized configurations for devices
Standardized patch testing equipment
Automated system patching
Management support for patching
Standardized configurations for devices can help to reduce the complexity and variability of the systems that need to be patched, and thus facilitate the testing of patch compatibility. Standardized configurations can also help to ensure that the patches are applied consistently and correctly across the organization. Standardized patch testing equipment, automated system patching, and management support for patching are also important factors for effective patch management, but they are not directly related to testing patch compatibility. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5: Security Engineering, page 605; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 386.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
An organization experiencing a negative financial impact is forced to reduce budgets and the number of Information Technology (IT) operations staff performing basic logical access security administration functions. Security processes have been tightly integrated into normal IT operations and are not separate and distinct roles.
Which of the following will indicate where the IT budget is BEST allocated during this time?
Policies
Frameworks
Metrics
Guidelines
The best indicator of where the IT budget is best allocated during this time is the metrics. The metrics are the measurements or the indicators of the performance, the effectiveness, the efficiency, or the quality of the IT processes, activities, or outcomes. The metrics can help to allocate the IT budget in a rational, objective, and evidence-based manner, as they can show the value, the impact, or the return of the IT investments, and they can identify the gaps, the risks, or the opportunities for the IT improvement or enhancement. The metrics can also help to justify, communicate, or report the IT budget allocation to the senior management or the stakeholders, and to align the IT budget allocation with the business needs and requirements. Policies, frameworks, and guidelines are not the best indicators of where the IT budget is best allocated during this time, as they are related to the documents or the models that define, guide, or standardize the IT processes, activities, or outcomes, not the measurements or the indicators of the IT performance, effectiveness, efficiency, or quality. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 38. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 53.
Which of the following provides the MOST protection against data theft of sensitive information when a laptop is stolen?
Set up a BIOS and operating system password
Encrypt the virtual drive where confidential files can be stored
Implement a mandatory policy in which sensitive data cannot be stored on laptops, but only on the corporate network
Encrypt the entire disk and delete contents after a set number of failed access attempts
Encrypting the entire disk and deleting the contents after a set number of failed access attempts provides the most protection against data theft of sensitive information when a laptop is stolen. This method ensures that the data is unreadable without the correct decryption key, and that the data is erased if someone tries to guess the key or bypass the encryption. Setting up a BIOS and operating system password, encrypting the virtual drive, or implementing a policy are less effective methods, as they can be circumvented by physical access, booting from another device, or copying the data to another location. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5: Identity and Access Management, p. 269; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 5: Identity and Access Management (IAM), p. 521.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A new employee is given a laptop computer with full administrator access. This employee does not have a personal computer at home and has a child that uses the computer to send and receive e-mail, search the web, and use instant messaging. The organization’s Information Technology (IT) department discovers that a peer-to-peer program has been installed on the computer using the employee's access.
Which of the following documents explains the proper use of the organization's assets?
Human resources policy
Acceptable use policy
Code of ethics
Access control policy
The document that explains the proper use of the organization’s assets is the acceptable use policy. An acceptable use policy is a document that defines the rules and guidelines for the appropriate and responsible use of the organization’s information systems and resources, such as computers, networks, or devices. An acceptable use policy can help to prevent or reduce the misuse, abuse, or damage of the organization’s assets, and to protect the security, privacy, and reputation of the organization and its users. An acceptable use policy can also specify the consequences or penalties for violating the policy, such as disciplinary actions, termination, or legal actions. A human resources policy, a code of ethics, and an access control policy are not the documents that explain the proper use of the organization’s assets, as they are related to the management, values, or authorization of the organization’s employees or users, not the usage or responsibility of the organization’s information systems or resources. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 47. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 62.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
In a Multilevel Security (MLS) system, the following sensitivity labels are used in increasing levels of sensitivity: restricted, confidential, secret, top secret. Table A lists the clearance levels for four users, while Table B lists the security classes of four different files.
In a Bell-LaPadula system, which user has the MOST restrictions when writing data to any of the four files?
User A
User B
User C
User D
In a Bell-LaPadula system, a user has the most restrictions when writing data to any of the four files if they have the lowest clearance level. This is because of the star property (*property) of the Bell-LaPadula model, which states that a subject with a given security clearance may write data to an object if and only if the object’s security level is greater than or equal to the subject’s security level. This rule is also known as the no write-down rule, as it prevents the leakage of information from a higher level to a lower level. In this question, User A has a Restricted clearance, which is the lowest level among the four users. Therefore, User A has the most restrictions when writing data to any of the four files, as they can only write data to File 1, which has the same security level as their clearance. User B, User C, and User D have less restrictions when writing data to any of the four files, as they can write data to more than one file, depending on their clearance levels and the security classes of the files. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 498. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 514.
Which of the following is the MOST difficult to enforce when using cloud computing?
Data access
Data backup
Data recovery
Data disposal
The most difficult thing to enforce when using cloud computing is data disposal. Data disposal is the process of permanently deleting or destroying the data that is no longer needed or authorized, in a secure and compliant manner. Data disposal is challenging when using cloud computing, because the data may be stored or replicated in multiple locations, devices, or servers, and the cloud provider may not have the same policies, procedures, or standards as the cloud customer. Data disposal may also be affected by the legal or regulatory requirements of different jurisdictions, or the contractual obligations of the cloud service agreement. Data access, data backup, and data recovery are not the most difficult things to enforce when using cloud computing, as they can be achieved by using encryption, authentication, authorization, replication, or restoration techniques, and by specifying the service level agreements and the roles and responsibilities of the cloud provider and the cloud customer. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3, Security Architecture and Engineering, page 337. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3, Security Architecture and Engineering, page 353.
A security manager has noticed an inconsistent application of server security controls resulting in vulnerabilities on critical systems. What is the MOST likely cause of this issue?
A lack of baseline standards
Improper documentation of security guidelines
A poorly designed security policy communication program
Host-based Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS) policies are ineffective
The most likely cause of the inconsistent application of server security controls resulting in vulnerabilities on critical systems is a lack of baseline standards. Baseline standards are the minimum level of security controls and measures that must be applied to the servers or other assets to ensure their protection and compliance. Baseline standards help to establish a consistent and uniform security posture across the organization, and to prevent or reduce the exposure to threats and risks. If there is a lack of baseline standards, the server security controls may vary in quality, effectiveness, or completeness, resulting in vulnerabilities on critical systems. Improper documentation of security guidelines, a poorly designed security policy communication program, and ineffective Host-based Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS) policies are not the most likely causes of this issue, as they do not directly affect the application of server security controls or the existence of baseline standards. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 35. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 48.
Which of the following is a process within a Systems Engineering Life Cycle (SELC) stage?
Requirements Analysis
Development and Deployment
Production Operations
Utilization Support
Requirements analysis is a process within the Systems Engineering Life Cycle (SELC) stage of Concept Development. It involves defining the problem, identifying the stakeholders, eliciting the requirements, analyzing the requirements, and validating the requirements. Requirements analysis is essential for ensuring that the system meets the needs and expectations of the users and customers. References: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 3: Security Architecture and Engineering, p. 295; CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4: Security Architecture and Design, p. 149.
Identify the component that MOST likely lacks digital accountability related to information access.
Click on the correct device in the image below.
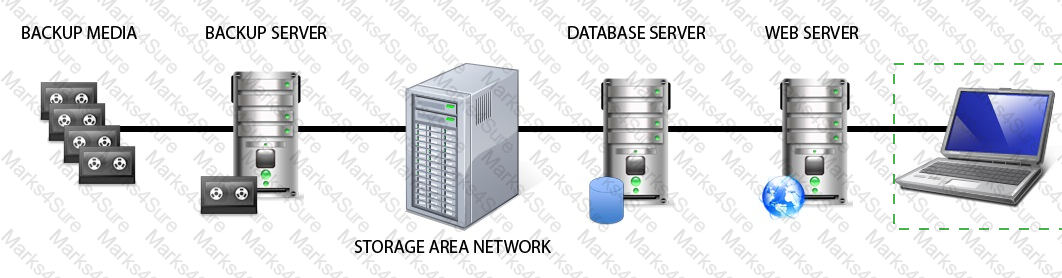
Storage Area Network (SAN): SANs are designed for centralized storage and access control mechanisms can be implemented to track users and their activities.
A large university needs to enable student access to university resources from their homes. Which of the following provides the BEST option for low maintenance and ease of deployment?
Provide students with Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) Virtual Private Network (VPN) client software.
Use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN technology.
Use Secure Shell (SSH) with public/private keys.
Require students to purchase home router capable of VPN.
The best option for low maintenance and ease of deployment to enable student access to university resources from their homes is to use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN technology. SSL VPN is a type of virtual private network that uses the SSL protocol to provide secure and remote access to the network resources over the internet. SSL VPN does not require the installation or configuration of any special client software or hardware on the student’s device, as it can use the web browser as the client interface. SSL VPN can also support various types of devices, operating systems, and applications, and can provide granular access control and encryption for the network traffic. Providing students with Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) VPN client software, using Secure Shell (SSH) with public/private keys, and requiring students to purchase home router capable of VPN are not the best options for low maintenance and ease of deployment, as they involve more complexity, cost, and compatibility issues for the students and the university. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 507. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 523.
During an investigation of database theft from an organization's web site, it was determined that the Structured Query Language (SQL) injection technique was used despite input validation with client-side scripting. Which of the following provides the GREATEST protection against the same attack occurring again?
Encrypt communications between the servers
Encrypt the web server traffic
Implement server-side filtering
Filter outgoing traffic at the perimeter firewall
The action that provides the greatest protection against the same attack occurring again is to implement server-side filtering. Server-side filtering is the process of validating and sanitizing the user input on the server side, before passing it to the database or application. Server-side filtering can prevent SQL injection attacks, which are the attacks that exploit the vulnerability of the database or application to execute malicious SQL commands or queries. SQL injection attacks can result in data theft, corruption, or deletion, as well as unauthorized access or privilege escalation. The other options are not as effective as server-side filtering, as they either do not prevent SQL injection attacks (A and B), or do not address the root cause of the vulnerability (D). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 481; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8, page 581.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
Desktop computers in an organization were sanitized for re-use in an equivalent security environment. The data was destroyed in accordance with organizational policy and all marking and other external indications of the sensitivity of the data that was formerly stored on the magnetic drives were removed.
Organizational policy requires the deletion of user data from Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) devices before disposal. It may not be possible to delete the user data if the device is malfunctioning. Which destruction method below provides the BEST assurance that the data has been removed?
Knurling
Grinding
Shredding
Degaussing
The best destruction method that provides the assurance that the data has been removed from a malfunctioning PDA device is shredding. Shredding is a method of physically destroying the media, such as flash memory cards, by cutting or tearing them into small pieces that make the data unrecoverable. Shredding can be effective in removing the data from a PDA device that cannot be deleted by software or firmware methods, as it does not depend on the functionality of the device or the media. Shredding can also prevent the reuse or the recycling of the media or the device, as it renders them unusable. Knurling, grinding, and degaussing are not the best destruction methods that provide the assurance that the data has been removed from a malfunctioning PDA device, as they are related to the methods of altering the surface, the shape, or the magnetic field of the media, not the methods of cutting or tearing the media into small pieces. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 889. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 905.
Which of the following is a BEST practice when traveling internationally with laptops containing Personally Identifiable Information (PII)?
Use a thumb drive to transfer information from a foreign computer.
Do not take unnecessary information, including sensitive information.
Connect the laptop only to well-known networks like the hotel or public Internet cafes.
Request international points of contact help scan the laptop on arrival to ensure it is protected.
The best practice when traveling internationally with laptops containing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is to do not take unnecessary information, including sensitive information. PII is any information that can be used to identify, contact, or locate a specific individual, such as name, address, phone number, email, social security number, or biometric data. PII is subject to various privacy and security laws and regulations, and must be protected from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or theft. When traveling internationally with laptops containing PII, the best practice is to minimize the amount and type of PII that is stored or processed on the laptop, and to take only the information that is absolutely necessary for the business purpose. This can reduce the risk of losing, exposing, or compromising the PII, and the potential legal or reputational consequences. Using a thumb drive to transfer information from a foreign computer, connecting the laptop only to well-known networks like the hotel or public Internet cafes, and requesting international points of contact help scan the laptop on arrival to ensure it is protected are not the best practices when traveling internationally with laptops containing PII, as they may still expose the PII to various threats, such as malware, interception, or tampering, and may not comply with the privacy and security requirements of different countries or regions. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 43. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 56.
Which of the following actions MUST be taken if a vulnerability is discovered during the maintenance stage in a System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
Make changes following principle and design guidelines.
Stop the application until the vulnerability is fixed.
Report the vulnerability to product owner.
Monitor the application and review code.
The action that must be taken if a vulnerability is discovered during the maintenance stage in a SDLC is to make changes following principle and design guidelines. Principle and design guidelines are the rules and standards that define the security objectives, requirements, and specifications of the system. They also provide the criteria and methods for evaluating and testing the security of the system. By making changes following principle and design guidelines, the organization can ensure that the vulnerability is fixed in a secure and consistent manner, and that the system maintains its functionality and quality. The other options are not actions that must be taken, as they either do not fix the vulnerability (B and D), or do not follow the principle and design guidelines ©. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 461; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8, page 553.
Which of the following assures that rules are followed in an identity management architecture?
Policy database
Digital signature
Policy decision point
Policy enforcement point
The component that assures that rules are followed in an identity management architecture is the policy enforcement point. A policy enforcement point is a device or software that implements and enforces the security policies and rules defined by the policy decision point. A policy decision point is a device or software that evaluates and makes decisions about the access requests and privileges of the users or devices based on the security policies and rules. A policy enforcement point can be a firewall, a router, a switch, a proxy, or an application that controls the access to the network or system resources. A policy database, a digital signature, and a policy decision point are not the components that assure that rules are followed in an identity management architecture, as they are related to the storage, verification, or definition of the security policies and rules, not the implementation or enforcement of them. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 664. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 680.
What is the MOST effective method for gaining unauthorized access to a file protected with a long complex password?
Brute force attack
Frequency analysis
Social engineering
Dictionary attack
The most effective method for gaining unauthorized access to a file protected with a long complex password is social engineering. Social engineering is a type of attack that exploits the human factor or the psychological weaknesses of the target, such as trust, curiosity, greed, or fear, to manipulate them into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords, or performing malicious actions, such as opening malicious attachments or clicking malicious links. Social engineering can bypass the technical security controls, such as encryption or authentication, and can be more efficient and successful than other methods that rely on brute force or guesswork. Brute force attack, frequency analysis, and dictionary attack are not the most effective methods for gaining unauthorized access to a file protected with a long complex password, as they require a lot of time, resources, and computing power, and they can be thwarted by the use of strong passwords, password policies, or password managers. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, Security Assessment and Testing, page 813. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 6, Security Assessment and Testing, page 829.
Which of the following MUST system and database administrators be aware of and apply when configuring systems used for storing personal employee data?
Secondary use of the data by business users
The organization's security policies and standards
The business purpose for which the data is to be used
The overall protection of corporate resources and data
The thing that system and database administrators must be aware of and apply when configuring systems used for storing personal employee data is the organization’s security policies and standards. Security policies and standards are the documents that define the rules, guidelines, and procedures that govern the security of the organization’s information systems and data. Security policies and standards help to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the information systems and data, and to comply with the legal or regulatory requirements. System and database administrators must be aware of and apply the organization’s security policies and standards when configuring systems used for storing personal employee data, as they are responsible for implementing and maintaining the security controls and measures that protect the personal employee data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or theft. Secondary use of the data by business users, the business purpose for which the data is to be used, and the overall protection of corporate resources and data are not the things that system and database administrators must be aware of and apply when configuring systems used for storing personal employee data, as they are related to the usage, purpose, or scope of the data, not the security of the data. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 35. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 48.
Which of the following is a critical factor for implementing a successful data classification program?
Executive sponsorship
Information security sponsorship
End-user acceptance
Internal audit acceptance
The critical factor for implementing a successful data classification program is executive sponsorship. Executive sponsorship is the support and commitment from the senior management of the organization for the data classification program. Executive sponsorship can provide the necessary resources, authority, and guidance for the data classification program, and ensure that the program aligns with the organization’s goals, policies, and culture. Executive sponsorship can also influence and motivate the data owners, custodians, and users to participate and comply with the data classification program. The other options are not as critical as executive sponsorship, as they either do not have the same level of influence or authority (B, C, and D), or do not directly contribute to the data classification program (D). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 2, page 66; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 2, page 72.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A new employee is given a laptop computer with full administrator access. This employee does not have a personal computer at home and has a child that uses the computer to send and receive e-mail, search the web, and use instant messaging. The organization’s Information Technology (IT) department discovers that a peer-to-peer program has been installed on the computer using the employee's access.
Which of the following methods is the MOST effective way of removing the Peer-to-Peer (P2P) program from the computer?
Run software uninstall
Re-image the computer
Find and remove all installation files
Delete all cookies stored in the web browser cache
The most effective way of removing the P2P program from the computer is to re-image the computer. Re-imaging the computer means to restore the computer to its original or desired state, by erasing or overwriting the existing data or software on the computer, and by installing a new or a backup image of the operating system and the applications on the computer. Re-imaging the computer can ensure that the P2P program and any other unwanted or harmful programs or files are completely removed from the computer, and that the computer is clean and secure. Run software uninstall, find and remove all installation files, and delete all cookies stored in the web browser cache are not the most effective ways of removing the P2P program from the computer, as they may not remove all the traces or components of the P2P program from the computer, or they may not address the other potential issues or risks that the P2P program may have caused on the computer. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 906. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 922.
An organization's data policy MUST include a data retention period which is based on
application dismissal.
business procedures.
digital certificates expiration.
regulatory compliance.
An organization’s data policy must include a data retention period that is based on regulatory compliance. Regulatory compliance is the adherence to the laws, regulations, and standards that apply to the organization’s industry, sector, or jurisdiction. Regulatory compliance may dictate how long the organization must retain certain types of data, such as financial records, health records, or tax records, and how the data must be stored, protected, and disposed of. The organization must follow the regulatory compliance requirements for data retention to avoid legal liabilities, fines, or sanctions. The other options are not the basis for data retention period, as they either do not relate to the data policy (A and C), or do not have the same level of authority or obligation (B). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 2, page 68; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 2, page 74.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
An organization experiencing a negative financial impact is forced to reduce budgets and the number of Information Technology (IT) operations staff performing basic logical access security administration functions. Security processes have been tightly integrated into normal IT operations and are not separate and distinct roles.
When determining appropriate resource allocation, which of the following is MOST important to monitor?
Number of system compromises
Number of audit findings
Number of staff reductions
Number of additional assets
The most important factor to monitor when determining appropriate resource allocation is the number of system compromises. The number of system compromises is the count or the frequency of the security incidents or breaches that affect the confidentiality, the integrity, or the availability of the system data or functionality, and that are caused by the unauthorized or the malicious access or activity. The number of system compromises can help to determine appropriate resource allocation, as it can indicate the level of security risk or threat that the system faces, and the level of security protection or improvement that the system needs. The number of system compromises can also help to evaluate the effectiveness or the efficiency of the current resource allocation, and to identify the areas or the domains that require more or less resources. Number of audit findings, number of staff reductions, and number of additional assets are not the most important factors to monitor when determining appropriate resource allocation, as they are related to the results or the outcomes of the audit process, the changes or the impacts of the staff size, or the additions or the expansions of the system resources, not the security incidents or breaches that affect the system data or functionality. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 863. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 879.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A new employee is given a laptop computer with full administrator access. This employee does not have a personal computer at home and has a child that uses the computer to send and receive e-mail, search the web, and use instant messaging. The organization’s Information Technology (IT) department discovers that a peer-to-peer program has been installed on the computer using the employee's access.
Which of the following could have MOST likely prevented the Peer-to-Peer (P2P) program from being installed on the computer?
Removing employee's full access to the computer
Supervising their child's use of the computer
Limiting computer's access to only the employee
Ensuring employee understands their business conduct guidelines
The best way to prevent the P2P program from being installed on the computer is to remove the employee’s full access to the computer. Full access or administrator access means that the user has the highest level of privilege or permission to perform any action or operation on the computer, such as installing, modifying, or deleting any software or file. By removing the employee’s full access to the computer, and assigning them a lower level of access, such as user or guest, the organization can restrict the employee’s ability to install unauthorized or potentially harmful programs, such as P2P programs, on the computer. Supervising their child’s use of the computer, limiting computer’s access to only the employee, and ensuring employee understands their business conduct guidelines are not the best ways to prevent the P2P program from being installed on the computer, as they are related to the monitoring, control, or awareness of the computer usage, not the restriction or limitation of the computer access. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 660. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 676.
What is the MAIN feature that onion routing networks offer?
Non-repudiation
Traceability
Anonymity
Resilience
The main feature that onion routing networks offer is anonymity. Anonymity is the state of being unknown or unidentifiable by hiding or masking the identity or the location of the sender or the receiver of a communication. Onion routing is a technique that enables anonymous communication over a network, such as the internet, by encrypting and routing the messages through multiple layers of intermediate nodes, called onion routers. Onion routing can protect the privacy and security of the users or the data, and can prevent censorship, surveillance, or tracking by third parties. Non-repudiation, traceability, and resilience are not the main features that onion routing networks offer, as they are related to the proof, tracking, or recovery of the communication, not the anonymity of the communication. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 467. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 483.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is necessary in many systems given common types of password attacks. Which of the following is a correct list of password attacks?
Masquerading, salami, malware, polymorphism
Brute force, dictionary, phishing, keylogger
Zeus, netbus, rabbit, turtle
Token, biometrics, IDS, DLP
The correct list of password attacks is brute force, dictionary, phishing, and keylogger. Password attacks are the attacks that aim to guess, crack, or steal the passwords or the credentials of the users or the systems, and to gain unauthorized or malicious access to the information or the resources. Password attacks can include the following methods: - Brute force is a method that tries all possible combinations of characters or symbols until the correct password is found. - Dictionary is a method that uses a list of common or likely words or phrases as the input for guessing the password. - Phishing is a method that uses fraudulent emails or websites that impersonate legitimate entities or parties, and that trick the users into revealing their passwords or credentials. - Keylogger is a method that uses a software or a hardware device that records the keystrokes of the users, and that captures or transmits their passwords or credentials. Masquerading, salami, malware, and polymorphism are not password attacks, as they are related to the impersonation, manipulation, infection, or mutation of the data or the systems, not the guessing, cracking, or stealing of the passwords or the credentials. Zeus, netbus, rabbit, and turtle are not password attacks, as they are the names of specific types of malware, such as trojans, worms, or viruses, not the methods of attacking the passwords or the credentials. Token, biometrics, IDS, and DLP are not password attacks, as they are the types of security controls or technologies, such as authentication, identification, detection, or prevention, not the attacks on the passwords or the credentials. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 684. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 700.
Which of the following is a MAJOR consideration in implementing a Voice over IP (VoIP) network?
Use of a unified messaging.
Use of separation for the voice network.
Use of Network Access Control (NAC) on switches.
Use of Request for Comments (RFC) 1918 addressing.
The use of Network Access Control (NAC) on switches is a major consideration in implementing a Voice over IP (VoIP) network. NAC is a mechanism that enforces security policies on the network devices, such as switches, routers, firewalls, and servers. NAC can prevent unauthorized or compromised devices from accessing the network, or limit their access to specific segments or resources. NAC can also monitor and remediate the devices for compliance with the security policies, such as patch level, antivirus status, or configuration settings. NAC can enhance the security and performance of a VoIP network, as well as reduce the operational costs and risks. References: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 4: Communication and Network Security, p. 473; CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6: Communication and Network Security, p. 353.
According to best practice, which of the following groups is the MOST effective in performing an information security compliance audit?
In-house security administrators
In-house Network Team
Disaster Recovery (DR) Team
External consultants
According to best practice, the most effective group in performing an information security compliance audit is external consultants. External consultants are independent and objective third parties that can provide unbiased and impartial assessment of the organization’s compliance with the security policies, standards, and regulations. External consultants can also bring expertise, experience, and best practices from other organizations and industries, and offer recommendations for improvement. The other options are not as effective as external consultants, as they either have a conflict of interest or lack of independence (A and B), or do not have the primary role or responsibility of conducting compliance audits ©. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 240; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, page 302.
Which of the following is critical for establishing an initial baseline for software components in the operation and maintenance of applications?
Application monitoring procedures
Configuration control procedures
Security audit procedures
Software patching procedures
Configuration control procedures are critical for establishing an initial baseline for software components in the operation and maintenance of applications. Configuration control procedures are the processes and activities that ensure the integrity, consistency, and traceability of the software components throughout the SDLC. Configuration control procedures include identifying, documenting, storing, reviewing, approving, and updating the software components, as well as managing the changes and versions of the components. By establishing an initial baseline, the organization can have a reference point for measuring and evaluating the performance, quality, and security of the software components, and for applying and tracking the changes and updates to the components. The other options are not as critical as configuration control procedures, as they either do not establish an initial baseline (A and C), or do not apply to all software components (D). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 468; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8, page 568.
Which of the following is the BEST countermeasure to brute force login attacks?
Changing all canonical passwords
Decreasing the number of concurrent user sessions
Restricting initial password delivery only in person
Introducing a delay after failed system access attempts
The best countermeasure to brute force login attacks is to introduce a delay after failed system access attempts. A brute force login attack is a type of attack that tries to guess the username and password of a system or account by using a large number of possible combinations, usually with the help of automated tools or scripts. A delay after failed system access attempts is a security mechanism that imposes a waiting time or a penalty before allowing another login attempt, after a certain number of unsuccessful attempts. This can slow down or discourage the brute force login attack, as it increases the time and effort required to find the correct credentials. Changing all canonical passwords, decreasing the number of concurrent user sessions, and restricting initial password delivery only in person are not the best countermeasures to brute force login attacks, as they do not directly address the frequency or speed of the login attempts or the use of automated tools or scripts. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 685. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 701.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A new employee is given a laptop computer with full administrator access. This employee does not have a personal computer at home and has a child that uses the computer to send and receive e-mail, search the web, and use instant messaging. The organization’s Information Technology (IT) department discovers that a peer-to-peer program has been installed on the computer using the employee's access.
Which of the following solutions would have MOST likely detected the use of peer-to-peer programs when the computer was connected to the office network?
Anti-virus software
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
Anti-spyware software
Integrity checking software
The best solution to detect the use of P2P programs when the computer was connected to the office network is an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS). An IPS is a device or a software that monitors, analyzes, and blocks the network traffic based on the predefined rules or policies, and that can prevent or stop any unauthorized or malicious access or activity on the network, such as P2P programs. An IPS can detect the use of P2P programs by inspecting the network packets, identifying the P2P protocols or signatures, and blocking or dropping the P2P traffic. Anti-virus software, anti-spyware software, and integrity checking software are not the best solutions to detect the use of P2P programs when the computer was connected to the office network, as they are related to the protection, removal, or verification of the software or files on the computer, not the monitoring, analysis, or blocking of the network traffic. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 512. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 528.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A security practitioner detects client-based attacks on the organization’s network. A plan will be necessary to address these concerns.
What MUST the plan include in order to reduce client-side exploitation?
Approved web browsers
Network firewall procedures
Proxy configuration
Employee education
The plan must include employee education in order to reduce client-side exploitation. Employee education is a process of providing the employees with the necessary knowledge, skills, and awareness to follow the security policies and procedures, and to prevent or avoid the common security threats or risks, such as client-side exploitation. Client-side exploitation is a type of attack that targets the vulnerabilities or weaknesses of the client applications or systems, such as web browsers, email clients, or media players, and that can compromise the client data or functionality, or allow the attacker to gain access to the network or the server. Employee education can help to reduce client-side exploitation by teaching the employees how to recognize and avoid the malicious or suspicious links, attachments, or downloads, how to update and patch their client applications or systems, how to use the security tools or features, such as antivirus or firewall, and how to report or respond to any security incidents or breaches. Approved web browsers, network firewall procedures, and proxy configuration are not the plan components that must be included in order to reduce client-side exploitation, as they are related to the technical or administrative controls or measures, not the human or behavioral factors, that can affect the client-side security. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 47. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 62.
An organization decides to implement a partial Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) with only the servers having digital certificates. What is the security benefit of this implementation?
Clients can authenticate themselves to the servers.
Mutual authentication is available between the clients and servers.
Servers are able to issue digital certificates to the client.
Servers can authenticate themselves to the client.
A Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a system that provides the services and mechanisms for creating, managing, distributing, using, storing, and revoking digital certificates, which are electronic documents that bind a public key to an identity. A digital certificate can be used to authenticate the identity of an entity, such as a person, a device, or a server, that possesses the corresponding private key. An organization can implement a partial PKI with only the servers having digital certificates, which means that only the servers can prove their identity to the clients, but not vice versa. The security benefit of this implementation is that servers can authenticate themselves to the client, which can prevent impersonation, spoofing, or man-in-the-middle attacks by malicious servers. Clients can authenticate themselves to the servers, mutual authentication is available between the clients and servers, and servers are able to issue digital certificates to the client are not the security benefits of this implementation, as they require the clients to have digital certificates as well. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, Cryptography and Symmetric Key Algorithms, page 615. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, Cryptography and Symmetric Key Algorithms, page 631.
What is the BEST method to detect the most common improper initialization problems in programming languages?
Use and specify a strong character encoding.
Use automated static analysis tools that target this type of weakness.
Perform input validation on any numeric inputs by assuring that they are within the expected range.
Use data flow analysis to minimize the number of false positives.
The best method to detect the most common improper initialization problems in programming languages is to use automated static analysis tools that target this type of weakness. Improper initialization is a type of programming error that occurs when a variable or a data structure is not assigned a valid initial value before it is used. This can lead to undefined behavior, memory corruption, or security vulnerabilities. Automated static analysis tools are software tools that can scan, analyze, and test the source code of a program for errors, flaws, or vulnerabilities, without executing the program. By using automated static analysis tools that target improper initialization problems, the programmer can identify and fix the potential issues before they cause any harm or damage. Use and specify a strong character encoding, perform input validation on any numeric inputs by assuring that they are within the expected range, and use data flow analysis to minimize the number of false positives are not the best methods to detect the most common improper initialization problems in programming languages, as they do not directly address the root cause of the problem or provide the same level of coverage and accuracy as automated static analysis tools. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, Software Development Security, page 1018. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8, Software Development Security, page 1040.
If an attacker in a SYN flood attack uses someone else's valid host address as the source address, the system under attack will send a large number of Synchronize/Acknowledge (SYN/ACK) packets to the
default gateway.
attacker's address.
local interface being attacked.
specified source address.
A SYN flood attack is a type of denial-of-service attack that exploits the three-way handshake mechanism of the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The attacker sends a large number of TCP packets with the SYN flag set, indicating a request to establish a connection, to the target system, using a spoofed source address. The target system responds with a TCP packet with the SYN and ACK flags set, indicating an acknowledgment of the request, and waits for a final TCP packet with the ACK flag set, indicating the completion of the handshake, from the source address. However, since the source address is fake, the final ACK packet never arrives, and the target system keeps the connection half-open, consuming its resources and preventing legitimate connections. Therefore, the system under attack will send a large number of SYN/ACK packets to the specified source address, which is the spoofed address used by the attacker. The default gateway, the attacker’s address, and the local interface being attacked are not the destinations of the SYN/ACK packets in a SYN flood attack. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 460. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 476.
What is the PRIMARY reason for ethics awareness and related policy implementation?
It affects the workflow of an organization.
It affects the reputation of an organization.
It affects the retention rate of employees.
It affects the morale of the employees.
The primary reason for ethics awareness and related policy implementation is to affect the reputation of an organization positively, by demonstrating its commitment to ethical principles, values, and standards in its business practices, services, and products. Ethics awareness and policy implementation can also help the organization avoid legal liabilities, fines, or sanctions for unethical conduct, and foster trust and loyalty among its customers, partners, and employees. The other options are not as important as affecting the reputation, as they either do not directly relate to ethics (A), or are secondary outcomes of ethics (C and D). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, page 19; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, page 28.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A large organization uses unique identifiers and requires them at the start of every system session. Application access is based on job classification. The organization is subject to periodic independent reviews of access controls and violations. The organization uses wired and wireless networks and remote access. The organization also uses secure connections to branch offices and secure backup and recovery strategies for selected information and processes.
In addition to authentication at the start of the user session, best practice would require re-authentication
periodically during a session.
for each business process.
at system sign-off.
after a period of inactivity.
The best practice would require re-authentication after a period of inactivity, in addition to authentication at the start of the user session. Authentication is a process of verifying the identity or the credentials of a user or a device that requests access to a system or a resource. Re-authentication is a process of repeating the authentication after a certain condition or event, such as a change of location, a change of role, a change of privilege, or a period of inactivity. Re-authentication can help to enhance the security and the accountability of the access control, as it can prevent or detect the unauthorized or malicious use of the user or the device credentials, and it can ensure that the user or the device is still active and valid. Re-authenticating after a period of inactivity can help to prevent the unauthorized or malicious access by someone who may have gained physical access to the user or the device session, such as a co-worker, a visitor, or a thief. Re-authenticating periodically during a session, for each business process, or at system sign-off are not the best practices, as they may not be necessary or effective for the security or the accountability of the access control, and they may cause inconvenience or frustration to the user or the device. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 685. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 701.
Place the following information classification steps in sequential order.
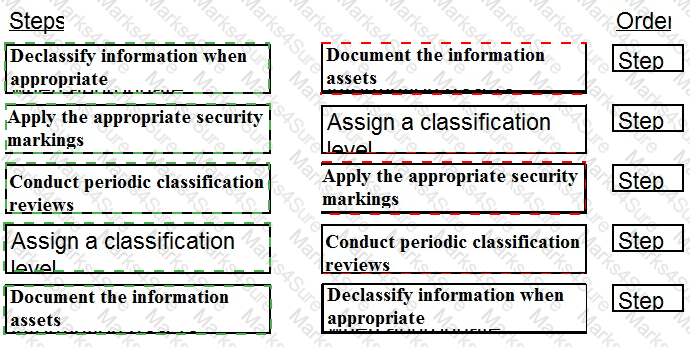
The following information classification steps should be placed in sequential order as follows:
Information classification is a process or a method of categorizing the information assets based on their sensitivity, criticality, or value, and applying the appropriate security controls or measures to protect them. Information classification can help to ensure the confidentiality, the integrity, and the availability of the information assets, and to support the security, the compliance, or the business objectives of the organization. The information classification steps are the activities or the tasks that are involved in the information classification process, and they should be performed in a sequential order, as follows:
An organization operates a legacy Industrial Control System (ICS) to support its core business service, which carrot be replaced. Its management MUST be performed remotely through an administrative console software, which in tum depends on an old version of the Java Runtime Environment (JPE) known to be vulnerable to a number of attacks, How is this risk BEST managed?
Isolate the full ICS by moving It onto its own network segment
Air-gap and harden the host used for management purposes
Convince the management to decommission the ICS and mitigate to a modem technology
Deploy a restrictive proxy between all clients and the vulnerable management station
Air-gapping and hardening the host used for management purposes is the best way to manage the risk of a legacy Industrial Control System (ICS) that depends on a vulnerable version of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). Air-gapping means disconnecting the host from any network or internet connection, so that it can only be accessed physically. Hardening means applying security patches, disabling unnecessary services, and configuring security settings to reduce the attack surface of the host. This way, the risk of remote exploitation of the JRE vulnerability is minimized, and the host is protected from other potential threats. Isolating the full ICS by moving it onto its own network segment may reduce the exposure of the system, but it does not eliminate the possibility of network-based attacks. Convincing the management to decommission the ICS and migrate to a modern technology may be the ideal solution, but it may not be feasible or cost-effective, especially if the ICS cannot be replaced. Deploying a restrictive proxy between all clients and the vulnerable management station may also help to filter and monitor the network traffic, but it does not address the root cause of the vulnerability, and it may introduce additional complexity and overhead to the system. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 447. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 321.
Why would a system be structured to isolate different classes of information from one another and segregate them by user jurisdiction?
The organization can avoid e-discovery processes in the event of litigation.
The organization's infrastructure is clearly arranged and scope of responsibility is simplified.
The organization can vary its system policies to comply with conflicting national laws.
The organization is required to provide different services to various third-party organizations.
A system that is structured to isolate different classes of information from one another and segregate them by user jurisdiction can help the organization to vary its system policies to comply with conflicting national laws. Different classes of information may have different levels of sensitivity, confidentiality, or classification, and may require different security measures and controls to protect them. Different user jurisdictions may have different legal or regulatory requirements, standards, or expectations for the information, and may impose different obligations or restrictions on the organization. By isolating and segregating the information by class and jurisdiction, the organization can tailor its system policies to meet the specific needs and demands of each class and jurisdiction, and avoid any conflicts or violations of the national laws. The other options are not the reasons why a system would be structured to isolate different classes of information from one another and segregate them by user jurisdiction, as they either do not relate to the system structure, do not involve different classes or jurisdictions, or do not address the national laws. References: CISSP - Certified Information Systems Security Professional, Domain 1. Security and Risk Management, 1.6 Understand legal and regulatory issues that pertain to information security in a global context, 1.6.1 Understand and adhere to laws, regulations, and compliance requirements, 1.6.1.2 Data sovereignty; CISSP Exam Outline, Domain 1. Security and Risk Management, 1.6 Understand legal and regulatory issues that pertain to information security in a global context, 1.6.1 Understand and adhere to laws, regulations, and compliance requirements, 1.6.1.2 Data sovereignty
Digital certificates used transport Layer security (TLS) support which of the following?
Server identify and data confidentially
Information input validation
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Non-reputation controls and data encryption
Digital certificates used in Transport Layer Security (TLS) support non-repudiation controls and data encryption. TLS is a protocol that provides secure communication over the internet, by using encryption, authentication, and integrity mechanisms. Digital certificates are electronic documents that contain the public key and identity information of an entity, such as a server, a client, or a user. Digital certificates are issued and verified by a trusted third party, called a certificate authority (CA). Digital certificates are used in TLS to support two features: non-repudiation controls and data encryption. Non-repudiation controls are the measures that prevent an entity from denying or disputing the validity or authenticity of a communication or transaction. Data encryption is the process of transforming data into an unreadable form, using a secret key, to protect the confidentiality of the data. Digital certificates support non-repudiation controls by using digital signatures, which are the encrypted hashes of the data, signed with the private key of the sender. Digital signatures can prove the origin, identity, and integrity of the data, and prevent the sender from denying or altering the data. Digital certificates support data encryption by using public key encryption, which is a type of encryption that uses a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. Public key encryption can encrypt the data with the public key of the receiver, and decrypt the data with the private key of the receiver. Public key encryption can ensure that only the intended receiver can access the data, and protect the data from unauthorized interception or modification. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Engineering, page 125; [Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Engineering, page 187]
The core component of Role Based Access control (RBAC) must be constructed of defined data elements. Which elements are required?
Users, permissions, operators, and protected objects
Users, rotes, operations, and protected objects
Roles, accounts, permissions, and protected objects
Roles, operations, accounts, and protected objects
The core component of Role Based Access Control (RBAC) must be constructed of defined data elements. The elements that are required are users, roles, operations, and protected objects. RBAC is a model of access control that assigns permissions to roles, rather than to individual users. A role is a logical grouping of users that share common responsibilities or functions within an organization. An operation is an action that can be performed on a protected object. A protected object is a resource or entity that is subject to access control, such as a file, a database, or a network device. RBAC defines the relationships between users, roles, operations, and protected objects, and enforces the access rules based on these relationships. Users, permissions, operators, and protected objects; roles, accounts, permissions, and protected objects; and roles, operations, accounts, and protected objects are not the correct elements that are required for the core component of RBAC, although they may be related or derived from the core elements. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5: Identity and Access Management, page 536. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5: Identity and Access Management, page 355.
When designing a Cyber-Physical System (CPS), which of the following should be a security practitioner's first consideration?
Detection of sophisticated attackers
Resiliency of the system
Topology of the network used for the system
Risk assessment of the system
A risk assessment is the first step in designing a secure CPS, as it helps to identify the threats, vulnerabilities, impacts, and likelihoods of the system. A risk assessment also helps to prioritize the security requirements and controls for the system, based on the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization. Detection, resiliency, and topology are important aspects of CPS security, but they depend on the outcome of the risk assessment. References: CISSP CBK Reference, 5th Edition, Chapter 1, page 29; CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 8th Edition, Chapter 1, page 23
Which of the following is the BEST statement for a professional to include as port of business continuity (BC) procedure?
A full data backup must be done upon management request.
An incremental data backup must be done upon management request.
A full data backup must be done based on the needs of the business.
In incremental data backup must be done after each system change.
The best statement for a professional to include as part of a business continuity (BC) procedure is that a full data backup must be done based on the needs of the business. A business continuity procedure is a set of steps or actions that should be followed to ensure the continuity of critical business functions and processes in the event of a disruption or disaster. A full data backup is a type of backup that copies all the data from a system or resource to another storage medium, such as a tape, a disk, or a cloud. A full data backup provides the most complete and reliable recovery option, as it restores the system or resource to its original state. A full data backup must be done based on the needs of the business, meaning that it should consider the factors such as the recovery time objective (RTO), the recovery point objective (RPO), the frequency of data changes, the importance of data, the cost of backup, and the available resources. A full data backup must not be done upon management request, as this may not reflect the actual needs of the business, and may result in unnecessary or insufficient backup. An incremental data backup is a type of backup that copies only the data that has changed since the last backup, whether it was a full or an incremental backup. An incremental data backup saves time and space, but it requires more steps and dependencies to restore the system or resource. An incremental data backup must not be done upon management request or after each system change, as this may not meet the needs of the business, and may cause inconsistency or redundancy in the backup. References:
A software developer installs a game on their organization-provided smartphone. Upon installing the game, the software developer is prompted to allow the game access to call logs, Short Message Service (SMS) messaging, and Global Positioning System (GPS) location data. What has the game MOST likely introduced to the smartphone?
Alerting
Vulnerability
Geo-fencing
Monitoring
The game has most likely introduced a vulnerability to the smartphone. A vulnerability is a type of weakness or flaw in a system or a device, such as a smartphone, that can be exploited or leveraged by a threat or an attacker, to cause harm or damage to the system or the device, or to compromise the security, functionality, or usability of the system or the device. A vulnerability can be caused by various factors, such as the design, the configuration, the implementation, or the operation of the system or the device, or the software, the hardware, or the firmware that run on the system or the device. A game is a type of software application that can be installed or run on a system or a device, such as a smartphone, to provide entertainment, education, or simulation for the user or the player. A game can also introduce a vulnerability to the system or the device, if the game is not designed, developed, or tested properly or securely, or if the game requires or requests access to unnecessary or sensitive information or resources on the system or the device, such as the call logs, the SMS messaging, or the GPS location data. A game that introduces a vulnerability to the system or the device can expose the system or the device to potential attacks, such as unauthorized access, data leakage, or malware infection56. References: CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3, page 228; CISSP Practice Exam – FREE 20 Questions and Answers, Question 14.
An organization implements Network Access Control (NAC) ay Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.1x and discovers the printers do not support the IEEE 802.1x standard. Which of the following is the BEST resolution?
Implement port security on the switch ports for the printers.
Implement a virtual local area network (VLAN) for the printers.
Do nothing; IEEE 802.1x is irrelevant to printers.
Install an IEEE 802. 1x bridge for the printers.
The best resolution for an organization that implements Network Access Control (NAC) using IEEE 802.1x and discovers the printers do not support the IEEE 802.1x standard is to install an IEEE 802.1x bridge for the printers. IEEE 802.1x is a standard that provides port-based authentication for network devices, such as switches, routers, or wireless access points. IEEE 802.1x allows only authorized devices to access the network, based on their credentials or certificates. However, some devices, such as printers, may not support IEEE 802.1x or have the required credentials or certificates. In this case, an IEEE 802.1x bridge can be used to connect the printers to the network. An IEEE 802.1x bridge is a device that acts as a proxy for the printers and performs the IEEE 802.1x authentication on their behalf. The bridge can also isolate the printers from the rest of the network and apply security policies to them. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Chapter 4: Communication and Network Security, Section: IEEE 802.1x, pp. 264-265.
Which of the following is the MOST important rule for digital investigations?
Ensure event logs are rotated.
Ensure original data is never modified.
Ensure individual privacy is protected.
Ensure systems are powered on.
The most important rule for digital investigations is to ensure that the original data is never modified. Digital investigations are the processes of collecting, preserving, analyzing, and presenting digital evidence from various sources, such as computers, mobile devices, networks, or cloud services. Digital evidence is any data that can support or refute a hypothesis or claim related to a criminal or civil case. Digital evidence is often fragile, volatile, and easily altered or destroyed, either intentionally or unintentionally. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the original data is never modified during the digital investigation, to maintain its integrity and authenticity, and to avoid compromising its validity and admissibility in court. To ensure that the original data is never modified, the following steps should be followed:
What is the PRIMARY purpose of auditing, as it relates to the security review cycle?
To ensure the organization's controls and pokies are working as intended
To ensure the organization can still be publicly traded
To ensure the organization's executive team won't be sued
To ensure the organization meets contractual requirements
Auditing is the process of examining and evaluating the organization’s security controls and policies, such as access control, encryption, backup, incident response, or disaster recovery, to determine if they are working as intended, and if they are compliant with the organization’s objectives, standards, and regulations. Auditing is an essential part of the security review cycle, which is the process of continuously monitoring, assessing, and improving the organization’s security posture. The primary purpose of auditing, as it relates to the security review cycle, is to ensure the organization’s controls and policies are working as intended, and to identify and report any gaps, weaknesses, or violations that may affect the organization’s security. Auditing does not necessarily ensure the organization can still be publicly traded, as this depends on other factors, such as the financial performance, the market demand, or the legal compliance of the organization. Auditing does not necessarily ensure the organization’s executive team won’t be sued, as this depends on other factors, such as the nature, severity, or responsibility of the security incidents or breaches that may occur in the organization. Auditing does not necessarily ensure the organization meets contractual requirements, as this depends on the specific terms and conditions of the contracts that the organization has with its customers, partners, or suppliers. References: Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, page 339. CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8: Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning, page 476.
What is the MAIN reason to ensure the appropriate retention periods are enforced for data stored on electronic media?
To reduce the carbon footprint by eliminating paper
To create an inventory of data assets stored on disk for backup and recovery
To declassify information that has been improperly classified
To reduce the risk of loss, unauthorized access, use, modification, and disclosure
Data stored on electronic media, such as hard disks, flash drives, or optical disks, are subject to various security risks, such as loss, unauthorized access, use, modification, or disclosure. These risks can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the data, as well as the reputation, compliance, or liability of the organization or the data owner. Therefore, the main reason to ensure the appropriate retention periods are enforced for data stored on electronic media is to reduce these risks. Retention periods are the duration of time that the data must be kept or preserved on the electronic media, based on the value, sensitivity, or legal requirements of the data. Enforcing the appropriate retention periods can help to minimize the exposure or vulnerability of the data to the security risks, as well as to optimize the storage capacity and performance of the electronic media. Reducing the carbon footprint by eliminating paper, creating an inventory of data assets stored on disk for backup and recovery, or declassifying information that has been improperly classified are not the main reasons to ensure the appropriate retention periods are enforced for data stored on electronic media, as they are more related to environmental, operational, or compliance objectives. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4: Data Security, page 179; CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests, Third Edition, Domain 2: Asset Security, Question 2.14, page 80.
An external attacker has compromised an organization’s network security perimeter and installed a sniffer onto an inside computer. Which of the following is the MOST effective layer of security the organization could have implemented to mitigate the attacker’s ability to gain further information?
Implement packet filtering on the network firewalls
Install Host Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
Require strong authentication for administrators
Implement logical network segmentation at the switches
Implementing logical network segmentation at the switches is the most effective layer of security the organization could have implemented to mitigate the attacker’s ability to gain further information. Logical network segmentation is the process of dividing a network into smaller subnetworks or segments based on criteria such as function, location, or security level. Logical network segmentation can be implemented at the switches, which are devices that operate at the data link layer of the OSI model and forward data packets based on the MAC addresses. Logical network segmentation can provide several benefits, such as:
Logical network segmentation can mitigate the attacker’s ability to gain further information by limiting the visibility and access of the sniffer to the segment where it is installed. A sniffer is a tool that captures and analyzes the data packets that are transmitted over a network. A sniffer can be used for legitimate purposes, such as troubleshooting, testing, or monitoring the network, or for malicious purposes, such as eavesdropping, stealing, or modifying the data. A sniffer can only capture the data packets that are within its broadcast domain, which is the set of devices that can communicate with each other without a router. By implementing logical network segmentation at the switches, the organization can create multiple broadcast domains and isolate the sensitive or critical data from the compromised segment. This way, the attacker can only see the data packets that belong to the same segment as the sniffer, and not the data packets that belong to other segments. This can prevent the attacker from gaining further information or accessing other resources on the network.
The other options are not the most effective layers of security the organization could have implemented to mitigate the attacker’s ability to gain further information, but rather layers that have other limitations or drawbacks. Implementing packet filtering on the network firewalls is not the most effective layer of security, because packet filtering only examines the network layer header of the data packets, such as the source and destination IP addresses, and does not inspect the payload or the content of the data. Packet filtering can also be bypassed by using techniques such as IP spoofing or fragmentation. Installing Host Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) is not the most effective layer of security, because HIDS only monitors and detects the activities and events on a single host, and does not prevent or respond to the attacks. HIDS can also be disabled or evaded by the attacker if the host is compromised. Requiring strong authentication for administrators is not the most effective layer of security, because authentication only verifies the identity of the users or processes, and does not protect the data in transit or at rest. Authentication can also be defeated by using techniques such as phishing, keylogging, or credential theft.
Which of the following is the BEST network defense against unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks in progress?
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Stateful firewalls
Network Behavior Analysis (NBA) tools
Network Behavior Analysis (NBA) tools are the best network defense against unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks in progress. NBA tools are devices or software that monitor and analyze the network traffic and activities, and detect any anomalies or deviations from the normal or expected behavior. NBA tools use various techniques, such as statistical analysis, machine learning, artificial intelligence, or heuristics, to establish a baseline of the network behavior, and to identify any outliers or indicators of compromise. NBA tools can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the best network defense against unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks in progress, but rather network defenses that have other limitations or drawbacks. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are devices or software that monitor and block the network traffic and activities that match the predefined signatures or rules of known attacks. IPS can provide a proactive and preventive layer of security, but they cannot detect or stop unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks that do not match any signatures or rules, or that can evade or disable the IPS. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are devices or software that monitor and alert the network traffic and activities that match the predefined signatures or rules of known attacks. IDS can provide a reactive and detective layer of security, but they cannot detect or alert unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks that do not match any signatures or rules, or that can evade or disable the IDS. Stateful firewalls are devices or software that filter and control the network traffic and activities based on the state and context of the network sessions, such as the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, protocol types, and sequence numbers. Stateful firewalls can provide a granular and dynamic layer of security, but they cannot filter or control unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks that use valid or spoofed network sessions, or that can exploit or bypass the firewall rules.
What is the purpose of an Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing attack?
To send excessive amounts of data to a process, making it unpredictable
To intercept network traffic without authorization
To disguise the destination address from a target’s IP filtering devices
To convince a system that it is communicating with a known entity
The purpose of an Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing attack is to convince a system that it is communicating with a known entity. IP spoofing is a technique that involves creating and sending IP packets with a forged source IP address, which is usually the IP address of a trusted or authorized host. IP spoofing can be used for various malicious purposes, such as:
The purpose of IP spoofing is to convince a system that it is communicating with a known entity, because it allows the attacker to evade detection, avoid responsibility, and exploit trust relationships.
The other options are not the main purposes of IP spoofing, but rather the possible consequences or methods of IP spoofing. To send excessive amounts of data to a process, making it unpredictable is a possible consequence of IP spoofing, as it can cause a DoS or DDoS attack. To intercept network traffic without authorization is a possible method of IP spoofing, as it can be used to hijack or intercept a TCP session. To disguise the destination address from a target’s IP filtering devices is not a valid option, as IP spoofing involves forging the source address, not the destination address.
An input validation and exception handling vulnerability has been discovered on a critical web-based system. Which of the following is MOST suited to quickly implement a control?
Add a new rule to the application layer firewall
Block access to the service
Install an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
Patch the application source code
Adding a new rule to the application layer firewall is the most suited to quickly implement a control for an input validation and exception handling vulnerability on a critical web-based system. An input validation and exception handling vulnerability is a type of vulnerability that occurs when a web-based system does not properly check, filter, or sanitize the input data that is received from the users or other sources, or does not properly handle the errors or exceptions that are generated by the system. An input validation and exception handling vulnerability can lead to various attacks, such as:
An application layer firewall is a device or software that operates at the application layer of the OSI model and inspects the application layer payload or the content of the data packets. An application layer firewall can provide various functions, such as:
Adding a new rule to the application layer firewall is the most suited to quickly implement a control for an input validation and exception handling vulnerability on a critical web-based system, because it can prevent or reduce the impact of the attacks by filtering or blocking the malicious or invalid input data that exploit the vulnerability. For example, a new rule can be added to the application layer firewall to:
Adding a new rule to the application layer firewall can be done quickly and easily, without requiring any changes or patches to the web-based system, which can be time-consuming and risky, especially for a critical system. Adding a new rule to the application layer firewall can also be done remotely and centrally, without requiring any physical access or installation on the web-based system, which can be inconvenient and costly, especially for a distributed system.
The other options are not the most suited to quickly implement a control for an input validation and exception handling vulnerability on a critical web-based system, but rather options that have other limitations or drawbacks. Blocking access to the service is not the most suited option, because it can cause disruption and unavailability of the service, which can affect the business operations and customer satisfaction, especially for a critical system. Blocking access to the service can also be a temporary and incomplete solution, as it does not address the root cause of the vulnerability or prevent the attacks from occurring again. Installing an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is not the most suited option, because IDS only monitors and detects the attacks, and does not prevent or respond to them. IDS can also generate false positives or false negatives, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the detection. IDS can also be overwhelmed or evaded by the attacks, which can affect the effectiveness and efficiency of the detection. Patching the application source code is not the most suited option, because it can take a long time and require a lot of resources and testing to identify, fix, and deploy the patch, especially for a complex and critical system. Patching the application source code can also introduce new errors or vulnerabilities, which can affect the functionality and security of the system. Patching the application source code can also be difficult or impossible, if the system is proprietary or legacy, which can affect the feasibility and compatibility of the patch.
Which of the following is used by the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to determine packet formats?
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
Link Control Protocol (LCP)
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
Packet Transfer Protocol (PTP)
Link Control Protocol (LCP) is used by the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to determine packet formats. PPP is a data link layer protocol that provides a standard method for transporting network layer packets over point-to-point links, such as serial lines, modems, or dial-up connections. PPP supports various network layer protocols, such as IP, IPX, or AppleTalk, and it can encapsulate them in a common frame format. PPP also provides features such as authentication, compression, error detection, and multilink aggregation. LCP is a subprotocol of PPP that is responsible for establishing, configuring, maintaining, and terminating the point-to-point connection. LCP negotiates and agrees on various options and parameters for the PPP link, such as the maximum transmission unit (MTU), the authentication method, the compression method, the error detection method, and the packet format. LCP uses a series of messages, such as configure-request, configure-ack, configure-nak, configure-reject, terminate-request, terminate-ack, code-reject, protocol-reject, echo-request, echo-reply, and discard-request, to communicate and exchange information between the PPP peers.
The other options are not used by PPP to determine packet formats, but rather for other purposes. Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol that allows the creation of virtual private networks (VPNs) over public networks, such as the Internet. L2TP encapsulates PPP frames in IP datagrams and sends them across the tunnel between two L2TP endpoints. L2TP does not determine the packet format of PPP, but rather uses it as a payload. Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) is an authentication protocol that is used by PPP to verify the identity of the remote peer before allowing access to the network. CHAP uses a challenge-response mechanism that involves a random number (nonce) and a hash function to prevent replay attacks. CHAP does not determine the packet format of PPP, but rather uses it as a transport. Packet Transfer Protocol (PTP) is not a valid option, as there is no such protocol with this name. There is a Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE), which is a protocol that encapsulates PPP frames in Ethernet frames and allows the use of PPP over Ethernet networks. PPPoE does not determine the packet format of PPP, but rather uses it as a payload.
At what level of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model is data at rest on a Storage Area Network (SAN) located?
Link layer
Physical layer
Session layer
Application layer
Data at rest on a Storage Area Network (SAN) is located at the physical layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that describes how data is transmitted and processed across different layers of a network. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The physical layer is the lowest layer of the OSI model, and it is responsible for the transmission and reception of raw bits over a physical medium, such as cables, wires, or optical fibers. The physical layer defines the physical characteristics of the medium, such as voltage, frequency, modulation, connectors, etc. The physical layer also deals with the physical topology of the network, such as bus, ring, star, mesh, etc.
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated and block-level data storage. A SAN consists of storage devices, such as disks, tapes, or arrays, that are connected to servers or clients via a network infrastructure, such as switches, routers, or hubs. A SAN allows multiple servers or clients to share the same storage devices, and it provides high performance, availability, scalability, and security for data storage. Data at rest on a SAN is located at the physical layer of the OSI model, because it is stored as raw bits on the physical medium of the storage devices, and it is accessed by the servers or clients through the physical medium of the network infrastructure.
Which of the following operates at the Network Layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model?
Packet filtering
Port services filtering
Content filtering
Application access control
Packet filtering operates at the network layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that describes how data is transmitted and processed across different layers of a network. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The network layer is the third layer from the bottom of the OSI model, and it is responsible for routing and forwarding data packets between different networks or subnets. The network layer uses logical addresses, such as IP addresses, to identify the source and destination of the data packets, and it uses protocols, such as IP, ICMP, or ARP, to perform the routing and forwarding functions.
Packet filtering is a technique that controls the access to a network or a host by inspecting the incoming and outgoing data packets and applying a set of rules or policies to allow or deny them. Packet filtering can be performed by devices, such as routers, firewalls, or proxies, that operate at the network layer of the OSI model. Packet filtering typically examines the network layer header of the data packets, such as the source and destination IP addresses, the protocol type, or the fragmentation flags, and compares them with the predefined rules or policies. Packet filtering can also examine the transport layer header of the data packets, such as the source and destination port numbers, the TCP flags, or the sequence numbers, and compare them with the rules or policies. Packet filtering can provide a basic level of security and performance for a network or a host, but it also has some limitations, such as the inability to inspect the payload or the content of the data packets, the vulnerability to spoofing or fragmentation attacks, or the complexity and maintenance of the rules or policies.
The other options are not techniques that operate at the network layer of the OSI model, but rather at other layers. Port services filtering is a technique that controls the access to a network or a host by inspecting the transport layer header of the data packets and applying a set of rules or policies to allow or deny them based on the port numbers or the services. Port services filtering operates at the transport layer of the OSI model, which is the fourth layer from the bottom. Content filtering is a technique that controls the access to a network or a host by inspecting the application layer payload or the content of the data packets and applying a set of rules or policies to allow or deny them based on the keywords, URLs, file types, or other criteria. Content filtering operates at the application layer of the OSI model, which is the seventh and the topmost layer. Application access control is a technique that controls the access to a network or a host by inspecting the application layer identity or the credentials of the users or the processes and applying a set of rules or policies to allow or deny them based on the roles, permissions, or other attributes. Application access control operates at the application layer of the OSI model, which is the seventh and the topmost layer.
Which of the following factors contributes to the weakness of Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol?
WEP uses a small range Initialization Vector (IV)
WEP uses Message Digest 5 (MD5)
WEP uses Diffie-Hellman
WEP does not use any Initialization Vector (IV)
WEP uses a small range Initialization Vector (IV) is the factor that contributes to the weakness of Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol. WEP is a security protocol that provides encryption and authentication for wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi. WEP uses the RC4 stream cipher to encrypt the data packets, and the CRC-32 checksum to verify the data integrity. WEP also uses a shared secret key, which is concatenated with a 24-bit Initialization Vector (IV), to generate the keystream for the RC4 encryption. WEP has several weaknesses and vulnerabilities, such as:
WEP has been deprecated and replaced by more secure protocols, such as Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) or Wi-Fi Protected Access II (WPA2), which use stronger encryption and authentication methods, such as the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), or the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP).
The other options are not factors that contribute to the weakness of WEP, but rather factors that are irrelevant or incorrect. WEP does not use Message Digest 5 (MD5), which is a hash function that produces a 128-bit output from a variable-length input. WEP does not use Diffie-Hellman, which is a method for generating a shared secret key between two parties. WEP does use an Initialization Vector (IV), which is a 24-bit value that is concatenated with the secret key.
In a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) stack, which layer is responsible for negotiating and establishing a connection with another node?
Transport layer
Application layer
Network layer
Session layer
The transport layer of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) stack is responsible for negotiating and establishing a connection with another node. The TCP/IP stack is a simplified version of the OSI model, and it consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and link. The transport layer is the third layer of the TCP/IP stack, and it is responsible for providing reliable and efficient end-to-end data transfer between two nodes on a network. The transport layer uses protocols, such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or User Datagram Protocol (UDP), to segment, sequence, acknowledge, and reassemble the data packets, and to handle error detection and correction, flow control, and congestion control. The transport layer also provides connection-oriented or connectionless services, depending on the protocol used.
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, which means that it establishes a logical connection between two nodes before exchanging data, and it maintains the connection until the data transfer is complete. TCP uses a three-way handshake to negotiate and establish a connection with another node. The three-way handshake works as follows:
UDP is a connectionless protocol, which means that it does not establish or maintain a connection between two nodes, but rather sends data packets independently and without any guarantee of delivery, order, or integrity. UDP does not use a handshake or any other mechanism to negotiate and establish a connection with another node, but rather relies on the application layer to handle any connection-related issues.
Which of the following BEST describes the responsibilities of a data owner?
Ensuring quality and validation through periodic audits for ongoing data integrity
Maintaining fundamental data availability, including data storage and archiving
Ensuring accessibility to appropriate users, maintaining appropriate levels of data security
Determining the impact the information has on the mission of the organization
The best description of the responsibilities of a data owner is determining the impact the information has on the mission of the organization. A data owner is a person or entity that has the authority and accountability for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of a set of data. A data owner is also responsible for defining the purpose, value, and classification of the data, as well as the security requirements and controls for the data. A data owner should be able to determine the impact the information has on the mission of the organization, which means assessing the potential consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing the data. The impact of the information on the mission of the organization is one of the main criteria for data classification, which helps to establish the appropriate level of protection and handling for the data.
The other options are not the best descriptions of the responsibilities of a data owner, but rather the responsibilities of other roles or functions related to data management. Ensuring quality and validation through periodic audits for ongoing data integrity is a responsibility of a data steward, who is a person or entity that oversees the quality, consistency, and usability of the data. Maintaining fundamental data availability, including data storage and archiving is a responsibility of a data custodian, who is a person or entity that implements and maintains the technical and physical security of the data. Ensuring accessibility to appropriate users, maintaining appropriate levels of data security is a responsibility of a data controller, who is a person or entity that determines the purposes and means of processing the data.
Which of the following is an initial consideration when developing an information security management system?
Identify the contractual security obligations that apply to the organizations
Understand the value of the information assets
Identify the level of residual risk that is tolerable to management
Identify relevant legislative and regulatory compliance requirements
When developing an information security management system (ISMS), an initial consideration is to understand the value of the information assets that the organization owns or processes. An information asset is any data, information, or knowledge that has value to the organization and supports its mission, objectives, and operations. Understanding the value of the information assets helps to determine the appropriate level of protection and investment for them, as well as the potential impact and consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing them. Understanding the value of the information assets also helps to identify the stakeholders, owners, and custodians of the information assets, and their roles and responsibilities in the ISMS.
The other options are not initial considerations, but rather subsequent or concurrent considerations when developing an ISMS. Identifying the contractual security obligations that apply to the organizations is a consideration that depends on the nature, scope, and context of the information assets, as well as the relationships and agreements with the external parties. Identifying the level of residual risk that is tolerable to management is a consideration that depends on the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization, as well as the risk assessment and analysis of the information assets. Identifying relevant legislative and regulatory compliance requirements is a consideration that depends on the legal and ethical obligations and expectations of the organization, as well as the jurisdiction and industry of the information assets.
Which one of the following affects the classification of data?
Assigned security label
Multilevel Security (MLS) architecture
Minimum query size
Passage of time
The passage of time is one of the factors that affects the classification of data. Data classification is the process of assigning a level of sensitivity or criticality to data based on its value, impact, and legal requirements. Data classification helps to determine the appropriate security controls and handling procedures for the data. However, data classification is not static, but dynamic, meaning that it can change over time depending on various factors. One of these factors is the passage of time, which can affect the relevance, usefulness, or sensitivity of the data. For example, data that is classified as confidential or secret at one point in time may become obsolete, outdated, or declassified at a later point in time, and thus require a lower level of protection. Conversely, data that is classified as public or unclassified at one point in time may become more valuable, sensitive, or regulated at a later point in time, and thus require a higher level of protection. Therefore, data classification should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect the changes in the data over time.
The other options are not factors that affect the classification of data, but rather the outcomes or components of data classification. Assigned security label is the result of data classification, which indicates the level of sensitivity or criticality of the data. Multilevel Security (MLS) architecture is a system that supports data classification, which allows different levels of access to data based on the clearance and need-to-know of the users. Minimum query size is a parameter that can be used to enforce data classification, which limits the amount of data that can be retrieved or displayed at a time.
An organization has doubled in size due to a rapid market share increase. The size of the Information Technology (IT) staff has maintained pace with this growth. The organization hires several contractors whose onsite time is limited. The IT department has pushed its limits building servers and rolling out workstations and has a backlog of account management requests.
Which contract is BEST in offloading the task from the IT staff?
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Identity as a Service (IDaaS)
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Identity as a Service (IDaaS) is the best contract in offloading the task of account management from the IT staff. IDaaS is a cloud-based service that provides identity and access management (IAM) functions, such as user authentication, authorization, provisioning, deprovisioning, password management, single sign-on (SSO), and multifactor authentication (MFA). IDaaS can help the organization to streamline and automate the account management process, reduce the workload and costs of the IT staff, and improve the security and compliance of the user accounts. IDaaS can also support the contractors who have limited onsite time, as they can access the organization’s resources remotely and securely through the IDaaS provider.
The other options are not as effective as IDaaS in offloading the task of account management from the IT staff, as they do not provide IAM functions. Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud-based service that provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications, but it does not manage the user accounts for the applications. Desktop as a Service (DaaS) is a cloud-based service that provides virtual desktops for users to access applications and data, but it does not manage the user accounts for the virtual desktops. Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based service that provides software applications for users to use, but it does not manage the user accounts for the software applications.
Which of the following is MOST important when assigning ownership of an asset to a department?
The department should report to the business owner
Ownership of the asset should be periodically reviewed
Individual accountability should be ensured
All members should be trained on their responsibilities
When assigning ownership of an asset to a department, the most important factor is to ensure individual accountability for the asset. Individual accountability means that each person who has access to or uses the asset is responsible for its protection and proper handling. Individual accountability also implies that each person who causes or contributes to a security breach or incident involving the asset can be identified and held liable. Individual accountability can be achieved by implementing security controls such as authentication, authorization, auditing, and logging.
The other options are not as important as ensuring individual accountability, as they do not directly address the security risks associated with the asset. The department should report to the business owner is a management issue, not a security issue. Ownership of the asset should be periodically reviewed is a good practice, but it does not prevent misuse or abuse of the asset. All members should be trained on their responsibilities is a preventive measure, but it does not guarantee compliance or enforcement of the responsibilities.
When implementing a data classification program, why is it important to avoid too much granularity?
The process will require too many resources
It will be difficult to apply to both hardware and software
It will be difficult to assign ownership to the data
The process will be perceived as having value
When implementing a data classification program, it is important to avoid too much granularity, because the process will require too many resources. Data classification is the process of assigning a level of sensitivity or criticality to data based on its value, impact, and legal requirements. Data classification helps to determine the appropriate security controls and handling procedures for the data. However, data classification is not a simple or straightforward process, as it involves many factors, such as the nature, context, and scope of the data, the stakeholders, the regulations, and the standards. If the data classification program has too many levels or categories of data, it will increase the complexity, cost, and time of the process, and reduce the efficiency and effectiveness of the data protection. Therefore, data classification should be done with a balance between granularity and simplicity, and follow the principle of proportionality, which means that the level of protection should be proportional to the level of risk.
The other options are not the main reasons to avoid too much granularity in data classification, but rather the potential challenges or benefits of data classification. It will be difficult to apply to both hardware and software is a challenge of data classification, as it requires consistent and compatible methods and tools for labeling and protecting data across different types of media and devices. It will be difficult to assign ownership to the data is a challenge of data classification, as it requires clear and accountable roles and responsibilities for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of data. The process will be perceived as having value is a benefit of data classification, as it demonstrates the commitment and awareness of the organization to protect its data assets and comply with its obligations.
Which of the following is an effective control in preventing electronic cloning of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) based access cards?
Personal Identity Verification (PIV)
Cardholder Unique Identifier (CHUID) authentication
Physical Access Control System (PACS) repeated attempt detection
Asymmetric Card Authentication Key (CAK) challenge-response
Asymmetric Card Authentication Key (CAK) challenge-response is an effective control in preventing electronic cloning of RFID based access cards. RFID based access cards are contactless cards that use radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to communicate with a reader and grant access to a physical or logical resource. RFID based access cards are vulnerable to electronic cloning, which is the process of copying the data and identity of a legitimate card to a counterfeit card, and using it to impersonate the original cardholder and gain unauthorized access. Asymmetric CAK challenge-response is a cryptographic technique that prevents electronic cloning by using public key cryptography and digital signatures to verify the authenticity and integrity of the card and the reader. Asymmetric CAK challenge-response works as follows:
Asymmetric CAK challenge-response prevents electronic cloning because the private keys of the card and the reader are never transmitted or exposed, and the signatures are unique and non-reusable for each transaction. Therefore, a cloned card cannot produce a valid signature without knowing the private key of the original card, and a rogue reader cannot impersonate a legitimate reader without knowing its private key.
The other options are not as effective as asymmetric CAK challenge-response in preventing electronic cloning of RFID based access cards. Personal Identity Verification (PIV) is a standard for federal employees and contractors to use smart cards for physical and logical access, but it does not specify the cryptographic technique for RFID based access cards. Cardholder Unique Identifier (CHUID) authentication is a technique that uses a unique number and a digital certificate to identify the card and the cardholder, but it does not prevent replay attacks or verify the reader’s identity. Physical Access Control System (PACS) repeated attempt detection is a technique that monitors and alerts on multiple failed or suspicious attempts to access a resource, but it does not prevent the cloning of the card or the impersonation of the reader.
In a data classification scheme, the data is owned by the
system security managers
business managers
Information Technology (IT) managers
end users
In a data classification scheme, the data is owned by the business managers. Business managers are the persons or entities that have the authority and accountability for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of a set of data. Business managers are also responsible for defining the purpose, value, and classification of the data, as well as the security requirements and controls for the data. Business managers should be able to determine the impact the information has on the mission of the organization, which means assessing the potential consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing the data. The impact of the information on the mission of the organization is one of the main criteria for data classification, which helps to establish the appropriate level of protection and handling for the data.
The other options are not the data owners in a data classification scheme, but rather the other roles or functions related to data management. System security managers are the persons or entities that oversee the security of the information systems and networks that store, process, and transmit the data. They are responsible for implementing and maintaining the technical and physical security of the data, as well as monitoring and auditing the security performance and incidents. Information Technology (IT) managers are the persons or entities that manage the IT resources and services that support the business processes and functions that use the data. They are responsible for ensuring the availability, reliability, and scalability of the IT infrastructure and applications, as well as providing technical support and guidance to the users and stakeholders. End users are the persons or entities that access and use the data for their legitimate purposes and needs. They are responsible for complying with the security policies and procedures for the data, as well as reporting any security issues or violations.
When in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) MUST software security functional requirements be defined?
After the system preliminary design has been developed and the data security categorization has been performed
After the vulnerability analysis has been performed and before the system detailed design begins
After the system preliminary design has been developed and before the data security categorization begins
After the business functional analysis and the data security categorization have been performed
Software security functional requirements must be defined after the business functional analysis and the data security categorization have been performed in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). The SDLC is a process that involves planning, designing, developing, testing, deploying, operating, and maintaining a system, using various models and methodologies, such as waterfall, spiral, agile, or DevSecOps. The SDLC can be divided into several phases, each with its own objectives and activities, such as:
Software security functional requirements are the specific and measurable security features and capabilities that the system must provide to meet the security objectives and requirements. Software security functional requirements are derived from the business functional analysis and the data security categorization, which are two tasks that are performed in the system initiation phase of the SDLC. The business functional analysis is the process of identifying and documenting the business functions and processes that the system must support and enable, such as the inputs, outputs, workflows, and tasks. The data security categorization is the process of determining the security level and impact of the system and its data, based on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability criteria, and applying the appropriate security controls and measures. Software security functional requirements must be defined after the business functional analysis and the data security categorization have been performed, because they can ensure that the system design and development are consistent and compliant with the security objectives and requirements, and that the system security is aligned and integrated with the business functions and processes.
The other options are not the phases of the SDLC when the software security functional requirements must be defined, but rather phases that involve other tasks or activities related to the system design and development. After the system preliminary design has been developed and the data security categorization has been performed is not the phase when the software security functional requirements must be defined, but rather the phase when the system architecture and components are designed, based on the system scope and objectives, and the data security categorization is verified and validated. After the vulnerability analysis has been performed and before the system detailed design begins is not the phase when the software security functional requirements must be defined, but rather the phase when the system design and components are evaluated and tested for the security effectiveness and compliance, and the system detailed design is developed, based on the system architecture and components. After the system preliminary design has been developed and before the data security categorization begins is not the phase when the software security functional requirements must be defined, but rather the phase when the system architecture and components are designed, based on the system scope and objectives, and the data security categorization is initiated and planned.
What is the BEST approach to addressing security issues in legacy web applications?
Debug the security issues
Migrate to newer, supported applications where possible
Conduct a security assessment
Protect the legacy application with a web application firewall
Migrating to newer, supported applications where possible is the best approach to addressing security issues in legacy web applications. Legacy web applications are web applications that are outdated, unsupported, or incompatible with the current technologies and standards. Legacy web applications may have various security issues, such as:
Migrating to newer, supported applications where possible is the best approach to addressing security issues in legacy web applications, because it can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the best approaches to addressing security issues in legacy web applications, but rather approaches that can mitigate or remediate the security issues, but not eliminate or prevent them. Debugging the security issues is an approach that can mitigate the security issues in legacy web applications, but not the best approach, because it involves identifying and fixing the errors or defects in the code or logic of the web applications, which may be difficult or impossible to do for the legacy web applications that are outdated or unsupported. Conducting a security assessment is an approach that can remediate the security issues in legacy web applications, but not the best approach, because it involves evaluating and testing the security effectiveness and compliance of the web applications, using various techniques and tools, such as audits, reviews, scans, or penetration tests, and identifying and reporting any security weaknesses or gaps, which may not be sufficient or feasible to do for the legacy web applications that are incompatible or obsolete. Protecting the legacy application with a web application firewall is an approach that can mitigate the security issues in legacy web applications, but not the best approach, because it involves deploying and configuring a web application firewall, which is a security device or software that monitors and filters the web traffic between the web applications and the users or clients, and blocks or allows the web requests or responses based on the predefined rules or policies, which may not be effective or efficient to do for the legacy web applications that have weak or outdated encryption or authentication mechanisms.
A Java program is being developed to read a file from computer A and write it to computer B, using a third computer C. The program is not working as expected. What is the MOST probable security feature of Java preventing the program from operating as intended?
Least privilege
Privilege escalation
Defense in depth
Privilege bracketing
The most probable security feature of Java preventing the program from operating as intended is least privilege. Least privilege is a principle that states that a subject (such as a user, a process, or a program) should only have the minimum amount of access or permissions that are necessary to perform its function or task. Least privilege can help to reduce the attack surface and the potential damage of a system or network, by limiting the exposure and impact of a subject in case of a compromise or misuse.
Java implements the principle of least privilege through its security model, which consists of several components, such as:
In this question, the Java program is being developed to read a file from computer A and write it to computer B, using a third computer C. This means that the Java program needs to have the permissions to perform the file I/O and the network communication operations, which are considered as sensitive or risky actions by the Java security model. However, if the Java program is running on computer C with the default or the minimal security permissions, such as in the Java Security Sandbox, then it will not be able to perform these operations, and the program will not work as expected. Therefore, the most probable security feature of Java preventing the program from operating as intended is least privilege, which limits the access or permissions of the Java program based on its source, signer, or policy.
The other options are not the security features of Java preventing the program from operating as intended, but rather concepts or techniques that are related to security in general or in other contexts. Privilege escalation is a technique that allows a subject to gain higher or unauthorized access or permissions than what it is supposed to have, by exploiting a vulnerability or a flaw in a system or network. Privilege escalation can help an attacker to perform malicious actions or to access sensitive resources or data, by bypassing the security controls or restrictions. Defense in depth is a concept that states that a system or network should have multiple layers or levels of security, to provide redundancy and resilience in case of a breach or an attack. Defense in depth can help to protect a system or network from various threats and risks, by using different types of security measures and controls, such as the physical, the technical, or the administrative ones. Privilege bracketing is a technique that allows a subject to temporarily elevate or lower its access or permissions, to perform a specific function or task, and then return to its original or normal level. Privilege bracketing can help to reduce the exposure and impact of a subject, by minimizing the time and scope of its higher or lower access or permissions.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction?
Lack of software documentation
License agreements requiring release of modified code
Expiration of the license agreement
Costs associated with support of the software
The primary risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction is license agreements requiring release of modified code. Open source software is software that uses publicly available source code, which can be seen, modified, and distributed by anyone. Open source software has some advantages, such as being affordable and flexible, but it also has some disadvantages, such as being potentially insecure or unsupported.
One of the main disadvantages of using open source software in a commercial software construction is the license agreements that govern the use and distribution of the open source software. License agreements are legal contracts that specify the rights and obligations of the parties involved in the software, such as the original authors, the developers, and the users. License agreements can vary in terms of their terms and conditions, such as the scope, the duration, or the fees of the software.
Some of the common types of license agreements for open source software are:
The primary risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction is license agreements requiring release of modified code, which are usually associated with copyleft licenses. This means that if a commercial software construction uses or incorporates open source software that is licensed under a copyleft license, then it must also release its own source code and any modifications or derivatives of it, under the same or compatible copyleft license. This can pose a significant risk for the commercial software construction, as it may lose its competitive advantage, intellectual property, or revenue, by disclosing its source code and allowing others to use, modify, or distribute it.
The other options are not the primary risks with using open source software in a commercial software construction, but rather secondary or minor risks that may or may not apply to the open source software. Lack of software documentation is a secondary risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction, as it may affect the quality, usability, or maintainability of the open source software, but it does not necessarily affect the rights or obligations of the commercial software construction. Expiration of the license agreement is a minor risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction, as it may affect the availability or continuity of the open source software, but it is unlikely to happen, as most open source software licenses are perpetual or indefinite. Costs associated with support of the software is a secondary risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction, as it may affect the reliability, security, or performance of the open source software, but it can be mitigated or avoided by choosing the open source software that has adequate or alternative support options.
The configuration management and control task of the certification and accreditation process is incorporated in which phase of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
System acquisition and development
System operations and maintenance
System initiation
System implementation
The configuration management and control task of the certification and accreditation process is incorporated in the system acquisition and development phase of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC). The SDLC is a process that involves planning, designing, developing, testing, deploying, operating, and maintaining a system, using various models and methodologies, such as waterfall, spiral, agile, or DevSecOps. The SDLC can be divided into several phases, each with its own objectives and activities, such as:
The certification and accreditation process is a process that involves assessing and verifying the security and compliance of a system, and authorizing and approving the system operation and maintenance, using various standards and frameworks, such as NIST SP 800-37 or ISO/IEC 27001. The certification and accreditation process can be divided into several tasks, each with its own objectives and activities, such as:
The configuration management and control task of the certification and accreditation process is incorporated in the system acquisition and development phase of the SDLC, because it can ensure that the system design and development are consistent and compliant with the security objectives and requirements, and that the system changes are controlled and documented. Configuration management and control is a process that involves establishing and maintaining the baseline and the inventory of the system components and resources, such as hardware, software, data, or documentation, and tracking and recording any modifications or updates to the system components and resources, using various techniques and tools, such as version control, change control, or configuration audits. Configuration management and control can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the phases of the SDLC that incorporate the configuration management and control task of the certification and accreditation process, but rather phases that involve other tasks of the certification and accreditation process. System operations and maintenance is a phase of the SDLC that incorporates the security monitoring task of the certification and accreditation process, because it can ensure that the system operation and maintenance are consistent and compliant with the security objectives and requirements, and that the system security is updated and improved. System initiation is a phase of the SDLC that incorporates the security categorization and security planning tasks of the certification and accreditation process, because it can ensure that the system scope and objectives are defined and aligned with the security objectives and requirements, and that the security plan and policy are developed and documented. System implementation is a phase of the SDLC that incorporates the security assessment and security authorization tasks of the certification and accreditation process, because it can ensure that the system deployment and installation are evaluated and verified for the security effectiveness and compliance, and that the system operation and maintenance are authorized and approved based on the risk and impact analysis and the security objectives and requirements.
Which of the following is a web application control that should be put into place to prevent exploitation of Operating System (OS) bugs?
Check arguments in function calls
Test for the security patch level of the environment
Include logging functions
Digitally sign each application module
Testing for the security patch level of the environment is the web application control that should be put into place to prevent exploitation of Operating System (OS) bugs. OS bugs are errors or defects in the code or logic of the OS that can cause the OS to malfunction or behave unexpectedly. OS bugs can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, disrupt business operations, or steal or leak sensitive data. Testing for the security patch level of the environment is the web application control that should be put into place to prevent exploitation of OS bugs, because it can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the web application controls that should be put into place to prevent exploitation of OS bugs, but rather web application controls that can prevent or mitigate other types of web application attacks or issues. Checking arguments in function calls is a web application control that can prevent or mitigate buffer overflow attacks, which are attacks that exploit the vulnerability of the web application code that does not properly check the size or length of the input data that is passed to a function or a variable, and overwrite the adjacent memory locations with malicious code or data. Including logging functions is a web application control that can prevent or mitigate unauthorized access or modification attacks, which are attacks that exploit the lack of or weak authentication or authorization mechanisms of the web applications, and access or modify the web application data or functionality without proper permission or verification. Digitally signing each application module is a web application control that can prevent or mitigate code injection or tampering attacks, which are attacks that exploit the vulnerability of the web application code that does not properly validate or sanitize the input data that is executed or interpreted by the web application, and inject or modify the web application code with malicious code or data.
Which of the following is the BEST method to prevent malware from being introduced into a production environment?
Purchase software from a limited list of retailers
Verify the hash key or certificate key of all updates
Do not permit programs, patches, or updates from the Internet
Test all new software in a segregated environment
Testing all new software in a segregated environment is the best method to prevent malware from being introduced into a production environment. Malware is any malicious software that can harm or compromise the security, availability, integrity, or confidentiality of a system or data. Malware can be introduced into a production environment through various sources, such as software downloads, updates, patches, or installations. Testing all new software in a segregated environment involves verifying and validating the functionality and security of the software before deploying it to the production environment, using a separate system or network that is isolated and protected from the production environment. Testing all new software in a segregated environment can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the best methods to prevent malware from being introduced into a production environment, but rather methods that can reduce or mitigate the risk of malware, but not eliminate it. Purchasing software from a limited list of retailers is a method that can reduce the risk of malware from being introduced into a production environment, but not prevent it. This method involves obtaining software only from trusted and reputable sources, such as official vendors or distributors, that can provide some assurance of the quality and security of the software. However, this method does not guarantee that the software is free of malware, as it may still contain hidden or embedded malware, or it may be tampered with or compromised during the delivery or installation process. Verifying the hash key or certificate key of all updates is a method that can reduce the risk of malware from being introduced into a production environment, but not prevent it. This method involves checking the authenticity and integrity of the software updates, patches, or installations, by comparing the hash key or certificate key of the software with the expected or published value, using cryptographic techniques and tools. However, this method does not guarantee that the software is free of malware, as it may still contain malware that is not detected or altered by the hash key or certificate key, or it may be subject to a man-in-the-middle attack or a replay attack that can intercept or modify the software or the key. Not permitting programs, patches, or updates from the Internet is a method that can reduce the risk of malware from being introduced into a production environment, but not prevent it. This method involves restricting or blocking the access or download of software from the Internet, which is a common and convenient source of malware, by applying and enforcing the appropriate security policies and controls, such as firewall rules, antivirus software, or web filters. However, this method does not guarantee that the software is free of malware, as it may still be obtained or infected from other sources, such as removable media, email attachments, or network shares.
When developing a business case for updating a security program, the security program owner MUST do
which of the following?
Identify relevant metrics
Prepare performance test reports
Obtain resources for the security program
Interview executive management
When developing a business case for updating a security program, the security program owner must identify relevant metrics that can help to measure and evaluate the performance and the effectiveness of the security program, as well as to justify and support the investment and the return of the security program. A business case is a document or a presentation that provides the rationale or the argument for initiating or continuing a project or a program, such as a security program, by analyzing and comparing the costs and the benefits, the risks and the opportunities, and the alternatives and the recommendations of the project or the program. A business case can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the visibility and the accountability of the security program, preventing or detecting any unauthorized or improper activities or changes, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. A business case can involve various elements and steps, such as:
Identifying relevant metrics is a key element or step of developing a business case for updating a security program, as it can help to measure and evaluate the performance and the effectiveness of the security program, as well as to justify and support the investment and the return of the security program. Metrics are measures or indicators that can quantify or qualify the attributes or the outcomes of a process or an activity, such as the security program, and that can provide the information or the feedback that can facilitate the decision making or the improvement of the process or the activity. Metrics can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the accuracy and the reliability of the security program, preventing or detecting fraud or errors, and supporting the audit and the compliance activities. Identifying relevant metrics can involve various tasks or duties, such as:
Preparing performance test reports, obtaining resources for the security program, and interviewing executive management are not the tasks or duties that the security program owner must do when developing a business case for updating a security program, although they may be related or possible tasks or duties. Preparing performance test reports is a task or a technique that can be used by the security program owner, the security program team, or the security program auditor, to verify or validate the functionality and the quality of the security program, according to the standards and the criteria of the security program, and to detect and report any errors, bugs, or vulnerabilities in the security program. Obtaining resources for the security program is a task or a technique that can be used by the security program owner, the security program sponsor, or the security program manager, to acquire or allocate the necessary or the sufficient resources for the security program, such as the financial, human, or technical resources, and to manage or optimize the use or the distribution of the resources for the security program. Interviewing executive management is a task or a technique that can be used by the security program owner, the security program team, or the security program auditor, to collect and analyze the information and the feedback about the security program, from the executive management, who are the primary users or recipients of the security program, and who have the authority and the accountability to implement or execute the security program.
Which of the following is a responsibility of the information owner?
Ensure that users and personnel complete the required security training to access the Information System
(IS)
Defining proper access to the Information System (IS), including privileges or access rights
Managing identification, implementation, and assessment of common security controls
Ensuring the Information System (IS) is operated according to agreed upon security requirements
One of the responsibilities of the information owner is to define proper access to the Information System (IS), including privileges or access rights. This involves determining who can access the data, what they can do with the data, and under what conditions they can access the data. The information owner must also approve or deny the access requests and periodically review the access rights. Ensuring that users and personnel complete the required security training, managing the common security controls, and ensuring the IS is operated according to the security requirements are not the responsibilities of the information owner, but they may involve the information owner’s collaboration or consultation. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, page 48; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, page 40.
A company seizes a mobile device suspected of being used in committing fraud. What would be the BEST method used by a forensic examiner to isolate the powered-on device from the network and preserve the evidence?
Put the device in airplane mode
Suspend the account with the telecommunication provider
Remove the SIM card
Turn the device off
The best method used by a forensic examiner to isolate the powered-on device from the network and preserve the evidence is to put the device in airplane mode. Airplane mode is a feature that disables the wireless communication functions of the device, such as cellular, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or GPS. Putting the device in airplane mode can isolate the device from the network and prevent any remote access, modification, deletion, or wiping of the data on the device. Putting the device in airplane mode can also preserve the evidence by maintaining the current state of the device, such as the battery level, the signal strength, the date and time, or the notifications. Putting the device in airplane mode can also avoid any legal or ethical issues that may arise from intercepting or monitoring the network traffic of the device. Suspend the account with the telecommunication provider, remove the SIM card, and turn the device off are not the best methods used by a forensic examiner to isolate the powered-on device from the network and preserve the evidence, although they may be possible or alternative options. Suspend the account with the telecommunication provider is a method that involves contacting the service provider and requesting them to disable the service or the account associated with the device. Suspend the account with the telecommunication provider can isolate the device from the cellular network, but it may not isolate the device from other wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Suspend the account with the telecommunication provider may also require a court order or a warrant, and it may alert the owner or the user of the device. Remove the SIM card is a method that involves physically removing the subscriber identity module (SIM) card from the device. The SIM card is a small chip that stores the information and the credentials of the user and the service provider, and it enables the device to connect to the cellular network. Remove the SIM card can isolate the device from the cellular network, but it may not isolate the device from other wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Remove the SIM card may also alter or damage the data on the SIM card or the device, and it may require special tools or skills. Turn the device off is a method that involves powering off the device completely. Turn the device off can isolate the device from all wireless networks, such as cellular, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or GPS. Turn the device off may also prevent any further data loss or corruption on the device. However, turn the device off may also cause some data to be erased or overwritten, such as the data in the volatile memory (RAM) or the temporary files. Turn the device off may also trigger some security mechanisms, such as encryption, password, or biometric lock, that may prevent or hinder the access to the data on the device.
“Stateful” differs from “Static” packet filtering firewalls by being aware of which of the following?
Difference between a new and an established connection
Originating network location
Difference between a malicious and a benign packet payload
Originating application session
Stateful firewalls differ from static packet filtering firewalls by being aware of the difference between a new and an established connection. A stateful firewall is a firewall that keeps track of the state of network connections and transactions, and uses this information to make filtering decisions. A stateful firewall maintains a state table that records the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, protocols, and sequence numbers of each connection. A stateful firewall can distinguish between a new connection, which requires a three-way handshake to be completed, and an established connection, which has already completed the handshake and is ready to exchange data. A stateful firewall can also detect when a connection is terminated or idle, and remove it from the state table. A stateful firewall can provide more security and efficiency than a static packet filtering firewall, which only examines the header of each packet and compares it to a set of predefined rules. A static packet filtering firewall does not keep track of the state of connections, and cannot differentiate between new and established connections. A static packet filtering firewall may allow or block packets based on the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols, but it cannot inspect the payload or the sequence numbers of the packets. A static packet filtering firewall may also be vulnerable to spoofing or flooding attacks, as it cannot verify the authenticity or validity of the packets. The other options are not aspects that stateful firewalls are aware of, but static packet filtering firewalls are not. Both types of firewalls can check the originating network location of the packets, but they cannot check the difference between a malicious and a benign packet payload, or the originating application session of the packets. References: Stateless vs Stateful Packet Filtering Firewalls - GeeksforGeeks; Stateful vs Stateless Firewall: Differences and Examples - Fortinet; Stateful Inspection Firewalls Explained - Palo Alto Networks.
Checking routing information on e-mail to determine it is in a valid format and contains valid information is an example of which of the following anti-spam approaches?
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) blacklist
Reverse Domain Name System (DNS) lookup
Hashing algorithm
Header analysis
Header analysis is an example of an anti-spam approach that checks the routing information on e-mail to determine if it is in a valid format and contains valid information. The routing information, or the header, is the part of the e-mail that contains the sender, the recipient, the subject, the date, and the path of the e-mail. Header analysis can detect spam by looking for inconsistencies, anomalies, or falsifications in the header, such as mismatched domains, spoofed addresses, forged timestamps, or invalid characters34. References: 3: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, page 6744: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 6, page 205.
Which of the following management process allows ONLY those services required for users to accomplish
their tasks, change default user passwords, and set servers to retrieve antivirus updates?
Configuration
Identity
Compliance
Patch
The management process that allows only those services required for users to accomplish their tasks, change default user passwords, and set servers to retrieve antivirus updates is configuration. Configuration is the process of setting and adjusting the parameters and options of a system or a network, such as hardware, software, or services, to meet the requirements and objectives of the organization. Configuration can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the performance and the functionality of the system or the network, preventing or mitigating some types of attacks or vulnerabilities, and supporting the audit and compliance activities. Configuration can involve various techniques and tools, such as configuration management, configuration control, configuration auditing, or configuration baselines. Configuration can allow only those services required for users to accomplish their tasks, change default user passwords, and set servers to retrieve antivirus updates, by using the following methods:
Which of the following is the PRIMARY benefit of implementing data-in-use controls?
If the data is lost, it must be decrypted to be opened.
If the data is lost, it will not be accessible to unauthorized users.
When the data is being viewed, it can only be printed by authorized users.
When the data is being viewed, it must be accessed using secure protocols.
Data-in-use controls are security measures that protect data while it is being processed or manipulated by an application or a user. Examples of data-in-use controls include encryption, masking, tokenization, and digital rights management. The primary benefit of implementing data-in-use controls is that they prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data in the event of data loss, theft, or leakage. If the data is lost, it will not be accessible to unauthorized users because it will be encrypted, masked, tokenized, or protected by digital rights. The other options are not benefits of data-in-use controls, but rather benefits of data-at-rest controls, data-in-transit controls, or access controls. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3, page 142; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3, page 118
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation?
To verify that only employees have access to the facility.
To identify present hazards requiring remediation.
To monitor staff movement throughout the facility.
To provide a safe environment for employees.
According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide, the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation is to provide a safe environment for employees. Physical security personnel are the human or the personnel components or elements of the physical security system or the network, which is the system or the network that prevents or deters the unauthorized or unintended access or entry to the resources, data, or information, such as the locks, keys, doors, or windows of the premises or the facilities, or the badges, cards, or tags of the subjects or the entities. Physical security personnel may perform various functions or tasks, such as the guarding, patrolling, or monitoring of the premises or the facilities, or the verifying, identifying, or authenticating of the subjects or the entities. Employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation helps to provide a safe environment for employees, as it enhances or supplements the security or the protection of the premises or the facilities, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the premises or the facilities, by adding or applying an additional layer or level of security or protection, as well as a human or a personal touch or factor, to the physical security system or the network. Providing a safe environment for employees helps to ensure the safety or the well-being of the employees, as well as the productivity or the performance of the employees, as it reduces or eliminates the risks or the threats that may harm or damage the employees, such as the theft, vandalism, or violence of the employees. To verify that only employees have access to the facility is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. Verifying that only employees have access to the facility is the process of checking or confirming that the subjects or the entities that enter or access the facility are the employees or the authorized users or clients of the facility, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the card access, the biometrics, or the physical security personnel of the facility. Verifying that only employees have access to the facility helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the facility, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the facility, as it prevents or limits the unauthorized or unintended access or entry to the facility, which may lead to the attacks or threats that may harm or damage the facility, such as the theft, vandalism, or violence of the facility. Verifying that only employees have access to the facility may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as physical security personnel may perform the function or the task of verifying, identifying, or authenticating the subjects or the entities that enter or access the facility, by using or applying the card access, the biometrics, or other methods or mechanisms of the facility. However, verifying that only employees have access to the facility is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as it is not the main or the most important reason or objective for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. To identify present hazards requiring remediation is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. Identifying present hazards requiring remediation is the process of detecting or discovering the existing or the current hazards or dangers that may affect or impair the facility, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the facility, such as the fire, flood, or earthquake of the facility, as well as the actions or the measures that are needed or required to fix or resolve the hazards or dangers, such as the evacuation, recovery, or contingency of the facility. Identifying present hazards requiring remediation helps to ensure the safety or the well-being of the facility, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the facility, as it reduces or eliminates the impact or the consequence of the hazards or dangers that may harm or damage the facility, such as the fire, flood, or earthquake of the facility. Identifying present hazards requiring remediation may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as physical security personnel may perform the function or the task of detecting or discovering the existing or the current hazards or dangers that may affect or impair the facility, as well as the actions or the measures that are needed or required to fix or resolve the hazards or dangers, by using or applying the appropriate tools or techniques, such as the sensors, alarms, or cameras of the facility. However, identifying present hazards requiring remediation is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as it is not the main or the most important reason or objective for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. To monitor staff movement throughout the facility is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. Monitoring staff movement throughout the facility is the process of observing or tracking the activities or the behaviors of the staff or the employees that work or operate in the facility, such as the entry, exit, or location of the staff or the employees, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the card access, the biometrics, or the physical security personnel of the facility. Monitoring staff movement throughout the facility helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the facility, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the facility, as it prevents or limits the unauthorized or unintended access or entry to the facility, which may lead to the attacks or threats that may harm or damage the facility, such as the theft, vandalism, or violence of the facility. Monitoring staff movement throughout the facility may also help to ensure the productivity or the performance of the staff or the employees, as it prevents or limits the misuse or abuse of the facility, such as the idle, waste, or fraud of the facility. Monitoring staff movement throughout the facility may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as physical security personnel may perform the function or the task of observing or tracking the activities or the behaviors of the staff or the employees that work or operate in the facility, by using or applying the card access, the biometrics, or other methods or mechanisms of the facility. However, monitoring staff movement throughout the facility is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as it is not the main or the most important reason or objective for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation.
To protect auditable information, which of the following MUST be configured to only allow read access?
Logging configurations
Transaction log files
User account configurations
Access control lists (ACL)
To protect auditable information, transaction log files must be configured to only allow read access. Transaction log files are files that record and store the details or the history of the transactions or the activities that occur within a system or a database, such as the date, the time, the user, the action, or the outcome. Transaction log files are important for auditing purposes, as they can provide the evidence or the proof of the transactions or the activities that occur within a system or a database, and they can also support the recovery or the restoration of the system or the database in case of a failure or a corruption. To protect auditable information, transaction log files must be configured to only allow read access, which means that only authorized users or devices can view or access the transaction log files, but they cannot modify, delete, or overwrite the transaction log files. This can prevent or reduce the risk of tampering, alteration, or destruction of the auditable information, and it can also ensure the integrity, the accuracy, or the reliability of the auditable information.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, page 197; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, page 354
When writing security assessment procedures, what is the MAIN purpose of the test outputs and reports?
To force the software to fail and document the process
To find areas of compromise in confidentiality and integrity
To allow for objective pass or fail decisions
To identify malware or hidden code within the test results
According to the CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests3, the main purpose of the test outputs and reports when writing security assessment procedures is to find areas of compromise in confidentiality and integrity. Security assessment is the process of evaluating the security posture and effectiveness of a system, network, or application, by identifying and measuring the vulnerabilities, threats, and risks that may affect its security objectives. Security assessment procedures are the steps and methods that define how the security assessment will be conducted, such as the scope, the tools, the techniques, the criteria, and the deliverables. The test outputs and reports are the results and documentation of the security assessment, which provide the evidence and analysis of the security issues and findings. The main purpose of the test outputs and reports is to find areas of compromise in confidentiality and integrity, which are two of the core security principles that aim to protect the data and the system from unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, or destruction. The test outputs and reports may also help to find areas of compromise in availability, accountability, authenticity, or non-repudiation, which are other security principles that may be relevant for the system under assessment. The test outputs and reports are not meant to force the software to fail and document the process, although this may be a side effect of some security testing techniques, such as penetration testing or fuzz testing. The test outputs and reports are not meant to allow for objective pass or fail decisions, although they may provide some recommendations or suggestions for improving the security posture and mitigating the risks. The test outputs and reports are not meant to identify malware or hidden code within the test results, although they may detect some signs or indicators of malicious or unauthorized activities or components.
Which of the following BEST describes the purpose of performing security certification?
To identify system threats, vulnerabilities, and acceptable level of risk
To formalize the confirmation of compliance to security policies and standards
To formalize the confirmation of completed risk mitigation and risk analysis
To verify that system architecture and interconnections with other systems are effectively implemented
The best description of the purpose of performing security certification is to formalize the confirmation of compliance to security policies and standards. Security certification is the process of evaluating and validating the security posture and compliance of a system or network against a set of predefined criteria, such as security policies, standards, regulations, or best practices. Security certification results in a formal statement or document that attests the level of security and compliance achieved by the system or network.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3, page 147; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3, page 123
Which Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) phenomenon associated with bundled cable runs can create information leakage?
Transference
Covert channel
Bleeding
Cross-talk
Cross-talk is a type of Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) phenomenon that occurs when signals from one cable or circuit interfere with signals from another cable or circuit. Cross-talk can create information leakage by allowing an attacker to eavesdrop on or modify the transmitted data. Cross-talk can be caused by electromagnetic induction, capacitive coupling, or common impedance coupling. Cross-talk can be reduced by using shielded cables, twisted pairs, or optical fibers123. References:
During the risk assessment phase of the project the CISO discovered that a college within the University is collecting Protected Health Information (PHI) data via an application that was developed in-house. The college collecting this data is fully aware of the regulations for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and is fully compliant.
What is the best approach for the CISO?
During the risk assessment phase of the project the CISO discovered that a college within the University is collecting Protected Health Information (PHI) data via an application that was developed in-house. The college collecting this data is fully aware of the regulations for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and is fully compliant.
What is the best approach for the CISO?
Document the system as high risk
Perform a vulnerability assessment
Perform a quantitative threat assessment
Notate the information and move on
The best approach for the CISO is to notate the information and move on. A CISO is a Chief Information Security Officer, who is a senior executive responsible for overseeing and managing the information security strategy, policies, and programs of an organization. A risk assessment is a process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the risks that may affect the information and assets of an organization. In this scenario, the CISO discovered that a college within the University is collecting Protected Health Information (PHI) data via an application that was developed in-house. The college collecting this data is fully aware of the regulations for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and is fully compliant. HIPAA is a federal law that sets the standards and rules for the protection and privacy of PHI, which is any information that can be used to identify a person’s health condition, treatment, or payment. The best approach for the CISO is to notate the information and move on, as there is no need to take any further action or intervention, since the college is already compliant with the HIPAA regulations and has implemented the appropriate security measures for the PHI data. The other options are not the best approaches, but rather unnecessary or excessive actions. Documenting the system as high risk is not a best approach, as there is no evidence or indication that the system poses a high risk to the organization or the PHI data, as long as the college follows the HIPAA regulations and the security best practices. Performing a vulnerability assessment is not a best approach, as it is an intrusive and costly activity that may not be warranted or authorized, since the system is already compliant and secure. Performing a quantitative threat assessment is not a best approach, as it is a complex and time-consuming activity that may not be feasible or relevant, since the system is already compliant and secure. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, p. 22; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, p. 280.
Which of the following describes the BEST configuration management practice?
After installing a new system, the configuration files are copied to a separate back-up system and hashed to detect tampering.
After installing a new system, the configuration files are copied to an air-gapped system and hashed to detect tampering.
The firewall rules are backed up to an air-gapped system.
A baseline configuration is created and maintained for all relevant systems.
The best configuration management practice is to create and maintain a baseline configuration for all relevant systems. A baseline configuration is a documented and approved set of specifications and settings for a system or component that serves as a standard for comparison and evaluation. A baseline configuration can help ensure the consistency, security, and performance of the system or component, as well as facilitate the identification and resolution of any deviations or issues. A baseline configuration should be updated and reviewed regularly to reflect the changes and improvements made to the system or component12 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, p. 456; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 7: Security Operations, p. 869.
In which identity management process is the subject’s identity established?
Trust
Provisioning
Authorization
Enrollment
According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide1, the identity management process in which the subject’s identity is established is enrollment. Enrollment is the process of registering or enrolling a subject into an identity management system, such as a user into an authentication system, or a device into a network. Enrollment is the process in which the subject’s identity is established, as it involves verifying and validating the subject’s identity, as well as collecting and storing the subject’s identity attributes, such as the name, email, or biometrics of the subject. Enrollment also involves issuing and assigning the subject’s identity credentials, such as the username, password, or certificate of the subject. Enrollment helps to create and maintain the subject’s identity record or profile, as well as to enable and facilitate the subject’s access and use of the system or network. Trust is not the identity management process in which the subject’s identity is established, although it may be a factor that influences the enrollment process. Trust is the degree of confidence or assurance that a subject or an entity has in another subject or entity, such as a user in a system, or a system in a network. Trust may influence the enrollment process, as it may determine the level or extent of the identity verification and validation, as well as the identity attributes and credentials that are required or provided for the enrollment process. Provisioning is not the identity management process in which the subject’s identity is established, although it may be a process that follows or depends on the enrollment process. Provisioning is the process of creating, assigning, and configuring a subject’s account or resource with the necessary access rights and permissions to perform the tasks and functions that are required by the subject’s role and responsibilities, as well as the security policies and standards of the system or network. Provisioning is not the process in which the subject’s identity is established, as it does not involve verifying and validating the subject’s identity, or collecting and storing the subject’s identity attributes or credentials. Authorization is not the identity management process in which the subject’s identity is established, although it may be a process that follows or depends on the enrollment process. Authorization is the process of granting or denying a subject’s access or use of an object or a resource, based on the subject’s identity, role, or credentials, as well as the security policies and rules of the system or network. Authorization is not the process in which the subject’s identity is established, as it does not involve verifying and validating the subject’s identity, or collecting and storing the subject’s identity attributes or credentials. References: 1
Software Code signing is used as a method of verifying what security concept?
Integrity
Confidentiality
Availability
Access Control
Software code signing is used as a method of verifying the integrity of the software code. Integrity is the security concept that ensures that the data or code is not modified, corrupted, or tampered with by unauthorized parties. Software code signing is the process of attaching a digital signature to the software code, which is generated by applying a cryptographic hash function to the code and encrypting the hash value with the private key of the software developer or publisher. The digital signature can be verified by the software user or recipient by decrypting the signature with the public key of the developer or publisher and comparing the hash value with the hash value of the code.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, page 207; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, page 174
Knowing the language in which an encrypted message was originally produced might help a cryptanalyst to perform a
clear-text attack.
known cipher attack.
frequency analysis.
stochastic assessment.
Frequency analysis is a technique of cryptanalysis that exploits the statistical patterns of letters or symbols in an encrypted message. Frequency analysis assumes that the frequency distribution of the plaintext is preserved in the ciphertext, and that the frequency distribution of the plaintext is known or can be estimated. Knowing the language in which an encrypted message was originally produced might help a cryptanalyst to perform frequency analysis, as different languages have different letter frequencies, digraphs, and word lengths. For example, in English, the letter “e” is the most common, while in French, it is the letter “a”. By comparing the frequency distribution of the ciphertext with the expected frequency distribution of the plaintext language, a cryptanalyst can make educated guesses about the encryption key or algorithm23. References:
A security professional has been asked to evaluate the options for the location of a new data center within a multifloor building. Concerns for the data center include emanations and physical access controls.
Which of the following is the BEST location?
On the top floor
In the basement
In the core of the building
In an exterior room with windows
The best location for a new data center within a multifloor building is in the core of the building. This location can minimize the emanations and enhance the physical access controls. Emanations are the electromagnetic signals or radiation that are emitted by electronic devices, such as computers, servers, or network equipment. Emanations can be intercepted or captured by attackers to obtain sensitive or confidential information. Physical access controls are the measures that prevent or restrict unauthorized or malicious access to physical assets, such as data centers, servers, or network devices. Physical access controls can include locks, doors, gates, fences, guards, cameras, alarms, etc. The core of the building is the central part of the building that is usually surrounded by other rooms or walls. This location can reduce the emanations by creating a shielding effect and increasing the distance from the potential attackers. The core of the building can also improve the physical access controls by limiting the entry points and visibility of the data center12 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Engineering, p. 133; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 3: Security Engineering, p. 295.
A vulnerability in which of the following components would be MOST difficult to detect?
Kernel
Shared libraries
Hardware
System application
According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide, a vulnerability in hardware would be the most difficult to detect. A vulnerability is a weakness or exposure in a system, network, or application, which may be exploited by threats and cause harm to the organization or its assets. A vulnerability can exist in various components of a system, network, or application, such as the kernel, the shared libraries, the hardware, or the system application. A vulnerability in hardware would be the most difficult to detect, as it may require physical access, specialized tools, or advanced skills to identify and measure the vulnerability. Hardware is the physical or tangible component of a system, network, or application that provides the basic functionality, performance, and support for the system, network, or application, such as the processor, memory, disk, or network card. Hardware may have vulnerabilities due to design flaws, manufacturing defects, configuration errors, or physical damage. A vulnerability in hardware may affect the security, reliability, or availability of the system, network, or application, such as causing data leakage, performance degradation, or system failure. A vulnerability in the kernel would not be the most difficult to detect, although it may be a difficult to detect. The kernel is the core or central component of a system, network, or application that provides the basic functionality, performance, and control for the system, network, or application, such as the operating system, the hypervisor, or the firmware. The kernel may have vulnerabilities due to design flaws, coding errors, configuration errors, or malicious modifications. A vulnerability in the kernel may affect the security, reliability, or availability of the system, network, or application, such as causing privilege escalation, system compromise, or system crash. A vulnerability in the kernel may be detected by using various tools, techniques, or methods, such as code analysis, vulnerability scanning, or penetration testing. A vulnerability in the shared libraries would not be the most difficult to detect, although it may be a difficult to detect. The shared libraries are the reusable or common components of a system, network, or application, that provide the functionality, performance, and compatibility for the system, network, or application, such as the dynamic link libraries, the application programming interfaces, or the frameworks.
Order the below steps to create an effective vulnerability management process.
Who is ultimately responsible to ensure that information assets are categorized and adequate measures are taken to protect them?
Data Custodian
Executive Management
Chief Information Security Officer
Data/Information/Business Owners
The individuals who are ultimately responsible to ensure that information assets are categorized and adequate measures are taken to protect them are the data/information/business owners. Data/information/business owners are the individuals who have the authority or accountability for the information assets of an organization, such as data, systems, or processes. Data/information/business owners are ultimately responsible to ensure that information assets are categorized and adequate measures are taken to protect them, which means that they have to define and implement the rules and guidelines for classifying and securing the information assets according to their sensitivity, value, or criticality. Data/information/business owners also have to assign and oversee the roles and responsibilities of the data custodians and users, who are the individuals who have the duty or privilege to maintain or access the information assets of the organization. The other options are not the individuals who are ultimately responsible to ensure that information assets are categorized and adequate measures are taken to protect them, but rather different or subordinate roles. A data custodian is an individual who has the duty to maintain or safeguard the information assets of an organization, such as backup, restore, or encryption. A data custodian is responsible to follow the instructions or directions of the data/information/business owner, but not to make the decisions or policies for the information assets. Executive management is the group of individuals who have the highest level of authority or leadership in an organization, such as board of directors, chief executive officer, or chief financial officer. Executive management is responsible to provide the support or approval for the information security strategy, policies, and programs of the organization, but not to directly manage or control the information assets. A chief information security officer is an individual who has the senior executive responsibility for overseeing and managing the information security strategy, policies, and programs of an organization. A chief information security officer is responsible to advise and assist the data/information/business owners, executive management, and other stakeholders on the information security matters, but not to own or operate the information assets. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, p. 28; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, p. 286.
An application developer is deciding on the amount of idle session time that the application allows before a timeout. The BEST reason for determining the session timeout requirement is
organization policy.
industry best practices.
industry laws and regulations.
management feedback.
The session timeout requirement is the maximum amount of time that a user can be inactive on an application before the session is terminated and the user is required to re-authenticate. The best reason for determining the session timeout requirement is the organization policy, as it reflects the organization’s risk appetite, security objectives, and compliance obligations. The organization policy should specify the appropriate session timeout value for different types of applications and data, based on their sensitivity and criticality12. References:

TESTED 02 Jul 2025

