HipLocal wants to improve the resilience of their MySQL deployment, while also meeting their business and technical requirements.
Which configuration should they choose?
HipLocal is configuring their access controls.
Which firewall configuration should they implement?
For this question refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal wants to reduce the latency of their services for users in global locations. They have created read replicas of their database in locations where their users reside and configured their service to read traffic using those replicas. How should they further reduce latency for all database interactions with the least amount of effort?
You are writing a single-page web application with a user-interface that communicates with a third-party API
for content using XMLHttpRequest. The data displayed on the UI by the API results is less critical than other
data displayed on the same web page, so it is acceptable for some requests to not have the API data
displayed in the UI. However, calls made to the API should not delay rendering of other parts of the user
interface. You want your application to perform well when the API response is an error or a timeout.
What should you do?
Your analytics system executes queries against a BigQuery dataset. The SQL query is executed in batch and passes the contents of a SQL file to the BigQuery CLI. Then it redirects the BigQuery CLI output to another process. However, you are getting a permission error from the BigQuery CLI when the queries are executed. You want to resolve the issue. What should you do?
You work for a web development team at a small startup. Your team is developing a Node.js application using Google Cloud services, including Cloud Storage and Cloud Build. The team uses a Git repository for version control. Your manager calls you over the weekend and instructs you to make an emergency update to one of the company’s websites, and you’re the only developer available. You need to access Google Cloud to make the update, but you don’t have your work laptop. You are not allowed to store source code locally on a non-corporate computer. How should you set up your developer environment?
You need to redesign the ingestion of audit events from your authentication service to allow it to handle a large increase in traffic. Currently, the audit service and the authentication system run in the same Compute Engine virtual machine. You plan to use the following Google Cloud tools in the new architecture:
Multiple Compute Engine machines, each running an instance of the authentication service
Multiple Compute Engine machines, each running an instance of the audit service
Pub/Sub to send the events from the authentication services.
How should you set up the topics and subscriptions to ensure that the system can handle a large volume of messages and can scale efficiently?
You are reviewing and updating your Cloud Build steps to adhere to Google-recommended practices. Currently, your build steps include:
1. Pull the source code from a source repository.
2. Build a container image
3. Upload the built image to Artifact Registry.
You need to add a step to perform a vulnerability scan of the built container image, and you want the results of the scan to be available to your deployment pipeline running in Google Cloud. You want to minimize changes that could disrupt other teams' processes What should you do?
You have an application deployed in Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). You need to update the application to make authorized requests to Google Cloud managed services. You want this to be a one-time setup, and you need to follow security best practices of auto-rotating your security keys and storing them in an encrypted store. You already created a service account with appropriate access to the Google Cloud service. What should you do next?
Before promoting your new application code to production, you want to conduct testing across a variety of different users. Although this plan is risky, you want to test the new version of the application with production users and you want to control which users are forwarded to the new version of the application based on their operating system. If bugs are discovered in the new version, you want to roll back the newly deployed version of the application as quickly as possible.
What should you do?
You need to configure a Deployment on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). You want to include a check that verifies that the containers can connect to the database. If the Pod is failing to connect, you want a script on the container to run to complete a graceful shutdown. How should you configure the Deployment?
You are deploying a microservices application to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). The application will receive daily updates. You expect to deploy a large number of distinct containers that will run on the Linux operating system (OS). You want to be alerted to any known OS vulnerabilities in the new containers. You want to follow Google-recommended best practices. What should you do?
You are deploying a Python application to Cloud Run using Cloud Build. The Cloud Build pipeline is shown below:

You want to optimize deployment times and avoid unnecessary steps What should you do?
You are tasked with using C++ to build and deploy a microservice for an application hosted on Google Cloud. The code needs to be containerized and use several custom software libraries that your team has built. You do not want to maintain the underlying infrastructure of the application How should you deploy the microservice?
You want to upload files from an on-premises virtual machine to Google Cloud Storage as part of a data
migration. These files will be consumed by Cloud DataProc Hadoop cluster in a GCP environment.
Which command should you use?
You are using Cloud Build to build a Docker image. You need to modify the build to execute unit and run
integration tests. When there is a failure, you want the build history to clearly display the stage at which the
build failed.
What should you do?
You recently migrated an on-premises monolithic application to a microservices application on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). The application has dependencies on backend services on-premises, including a CRM system and a MySQL database that contains personally identifiable information (PII). The backend services must remain on-premises to meet regulatory requirements.
You established a Cloud VPN connection between your on-premises data center and Google Cloud. You notice that some requests from your microservices application on GKE to the backend services are failing due to latency issues caused by fluctuating bandwidth, which is causing the application to crash. How should you address the latency issues?
You have an application deployed in production. When a new version is deployed, you want to ensure that all production traffic is routed to the new version of your application. You also want to keep the previous version deployed so that you can revert to it if there is an issue with the new version.
Which deployment strategy should you use?
You have an application in production. It is deployed on Compute Engine virtual machine instances controlled
by a managed instance group. Traffic is routed to the instances via a HTTP(s) load balancer. Your users are
unable to access your application. You want to implement a monitoring technique to alert you when the
application is unavailable.
Which technique should you choose?
You have a web application that publishes messages to Pub/Sub. You plan to build new versions of the application locally and need to quickly test Pub/Sub integration tor each new build. How should you configure local testing?
You have an application running on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). The application is currently using a logging library and is outputting to standard output You need to export the logs to Cloud Logging, and you need the logs to include metadata about each request. You want to use the simplest method to accomplish this. What should you do?
You are developing an application hosted on Google Cloud that uses a MySQL relational database schema. The application will have a large volume of reads and writes to the database and will require backups and ongoing capacity planning. Your team does not have time to fully manage the database but can take on small administrative tasks. How should you host the database?
You recently developed an application. You need to call the Cloud Storage API from a Compute Engine instance that doesn’t have a public IP address. What should you do?
You are deploying your application to a Compute Engine virtual machine instance. Your application is
configured to write its log files to disk. You want to view the logs in Stackdriver Logging without changing the
application code.
What should you do?
You work on an application that relies on Cloud Spanner as its main datastore. New application features have occasionally caused performance regressions. You want to prevent performance issues by running an automated performance test with Cloud Build for each commit made. If multiple commits are made at the same time, the tests might run concurrently. What should you do?
Your company has deployed a new API to App Engine Standard environment. During testing, the API is not behaving as expected. You want to monitor the application over time to diagnose the problem within the application code without redeploying the application.
Which tool should you use?
You are a lead developer working on a new retail system that runs on Cloud Run and Firestore. A web UI requirement is for the user to be able to browse through alt products. A few months after go-live, you notice that Cloud Run instances are terminated with HTTP 500: Container instances are exceeding memory limits errors during busy times
This error coincides with spikes in the number of Firestore queries
You need to prevent Cloud Run from crashing and decrease the number of Firestore queries. You want to use a solution that optimizes system performance What should you do?
You are using Cloud Build to create a new Docker image on each source code commit to a Cloud Source Repositoties repository. Your application is built on every commit to the master branch. You want to release specific commits made to the master branch in an automated method. What should you do?
You migrated your applications to Google Cloud Platform and kept your existing monitoring platform. You now
find that your notification system is too slow for time critical problems.
What should you do?
You are developing an internal application that will allow employees to organize community events within your company. You deployed your application on a single Compute Engine instance. Your company uses Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), and you need to ensure that the company employees can authenticate to the application from anywhere. What should you do?
You are developing an application that will handle requests from end users. You need to secure a Cloud Function called by the application to allow authorized end users to authenticate to the function via the application while restricting access to unauthorized users. You will integrate Google Sign-In as part of the solution and want to follow Google-recommended best practices. What should you do?
You recently migrated a monolithic application to Google Cloud by breaking it down into microservices. One of the microservices is deployed using Cloud Functions. As you modernize the application, you make a change to the API of the service that is backward-incompatible. You need to support both existing callers who use the original API and new callers who use the new API. What should you do?
Your application is running on Compute Engine and is showing sustained failures for a small number of requests. You have narrowed the cause down to a single Compute Engine instance, but the instance is unresponsive to SSH. What should you do next?
You are designing a chat room application that will host multiple rooms and retain the message history for each room. You have selected Firestore as your database. How should you represent the data in Firestore?
Your operations team has asked you to create a script that lists the Cloud Bigtable, Memorystore, and Cloud SQL databases running within a project. The script should allow users to submit a filter expression to limit the results presented. How should you retrieve the data?
You are developing an ecommerce web application that uses App Engine standard environment and Memorystore for Redis. When a user logs into the app, the application caches the user’s information (e.g., session, name, address, preferences), which is stored for quick retrieval during checkout.
While testing your application in a browser, you get a 502 Bad Gateway error. You have determined that the application is not connecting to Memorystore. What is the reason for this error?
You have an application deployed in Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) that reads and processes Pub/Sub messages. Each Pod handles a fixed number of messages per minute. The rate at which messages are published to the Pub/Sub topic varies considerably throughout the day and week, including occasional large batches of messages published at a single moment.
You want to scale your GKE Deployment to be able to process messages in a timely manner. What GKE feature should you use to automatically adapt your workload?
Your team has created an application that is hosted on a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster You need to connect the application to a legacy REST service that is deployed in two GKE clusters in two different regions. You want to connect your application to the legacy service in a way that is resilient and requires the fewest number of steps You also want to be able to run probe-based health checks on the legacy service on a separate port How should you set up the connection?
You are developing an application that needs to store files belonging to users in Cloud Storage. You want each user to have their own subdirectory in Cloud Storage. When a new user is created, the corresponding empty subdirectory should also be created. What should you do?
You have decided to migrate your Compute Engine application to Google Kubernetes Engine. You need to build a container image and push it to Artifact Registry using Cloud Build. What should you do? (Choose two.)
A)
Run gcloud builds submit in the directory that contains the application source code.
B)
Run gcloud run deploy app-name --image gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app-name in the directory that contains the application source code.
C)
Run gcloud container images add-tag gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app-name gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app-name:latest in the directory that contains the application source code.
D)
In the application source directory, create a file named cloudbuild.yaml that contains the following contents:
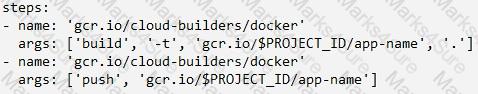
E)
In the application source directory, create a file named cloudbuild.yaml that contains the following contents:
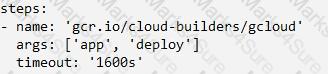
Your team develops services that run on Google Cloud. You need to build a data processing service and will use Cloud Functions. The data to be processed by the function is sensitive. You need to ensure that invocations can only happen from authorized services and follow Google-recommended best practices for securing functions. What should you do?
You are planning to deploy your application in a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster The application
exposes an HTTP-based health check at /healthz. You want to use this health check endpoint to determine whether traffic should be routed to the pod by the load balancer.
Which code snippet should you include in your Pod configuration?

You are developing an application using different microservices that should remain internal to the cluster. You want to be able to configure each microservice with a specific number of replicas. You also want to be able to address a specific microservice from any other microservice in a uniform way, regardless of the number of replicas the microservice scales to. You need to implement this solution on Google Kubernetes Engine. What should you do?
HipLocal's APIs are showing occasional failures, but they cannot find a pattern. They want to collect some
metrics to help them troubleshoot.
What should they do?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal's application uses Cloud Client Libraries to interact with Google Cloud. HipLocal needs to configure authentication and authorization in the Cloud Client Libraries to implement least privileged access for the application. What should they do?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
A recent security audit discovers that HipLocal’s database credentials for their Compute Engine-hosted MySQL databases are stored in plain text on persistent disks. HipLocal needs to reduce the risk of these credentials being stolen. What should they do?
In order for HipLocal to store application state and meet their stated business requirements, which database service should they migrate to?
In order to meet their business requirements, how should HipLocal store their application state?
HipLocal wants to reduce the number of on-call engineers and eliminate manual scaling.
Which two services should they choose? (Choose two.)
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal is expanding into new locations. They must capture additional data each time the application is launched in a new European country. This is causing delays in the development process due to constant schema changes and a lack of environments for conducting testing on the application changes. How should they resolve the issue while meeting the business requirements?
HipLocal has connected their Hadoop infrastructure to GCP using Cloud Interconnect in order to query data stored on persistent disks.
Which IP strategy should they use?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
How should HipLocal redesign their architecture to ensure that the application scales to support a large increase in users?
HipLocal's.net-based auth service fails under intermittent load.
What should they do?